• 神经组织构建 nerve tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
双向脉冲可实现的神经纤维选择性兴奋
朱晓瑾1,王 辉2,张 旭1,任朝晖1,刘庆凯1,李春婵1,阎立丽1
- 1首都医科大学生物医学工程学院,北京市 100069;2首都医科大学附属北京朝阳医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,首都医科大学耳鼻喉科学院,首都医科大学耳鼻咽喉头颈科学教育部重点实验室,北京市 100020
Selective nerve excitability induced by symmetric biphasic pulses
Zhu Xiao-jin1, Wang Hui2, Zhang Xu1, Ren Zhao-hui1, Liu Qing-kai1, Li Chun-chan1, Yan Li-li1
- 1School of Biomedical Engineering, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China; 2Department of Otolaryngology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital of Capital Medical University, Capital University of Medical Sciences School of Otolaryngology, Key Laboratory of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (Capital Medical University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100020, China
摘要:
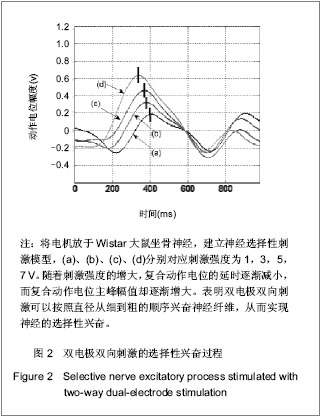
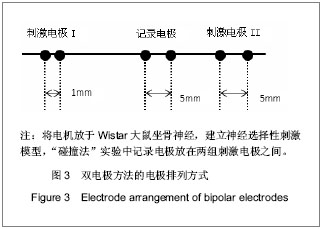
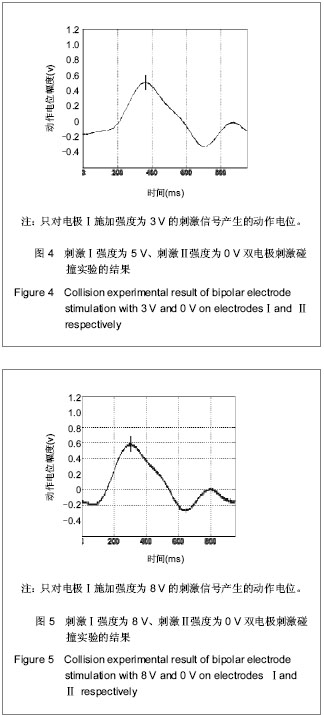
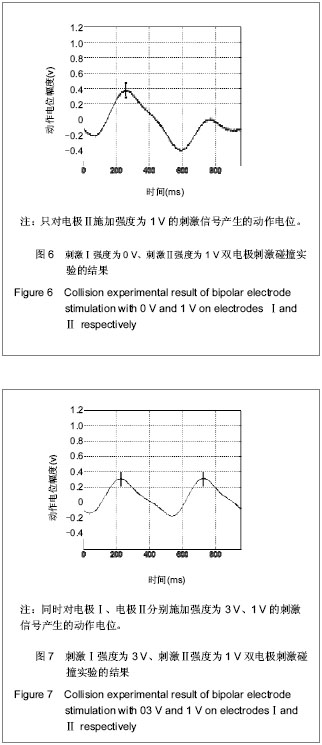
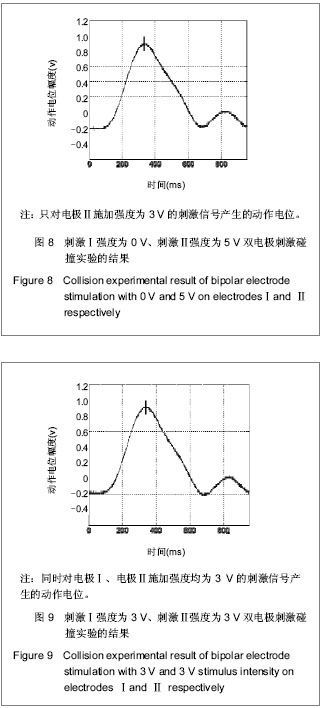
背景:研究证明利用电刺激外周神经纤维可恢复一些因失去中枢神经控制的肌肉的功能。 目的:验证双电极1 mm较近距离下双向方波脉冲实现神经选择性兴奋的正确性,并基于此实现神经的选择性兴奋。 方法:成年Wistar大鼠8只,麻醉后暴露大鼠坐骨神经,将电极小心放于坐骨神经干,建立神经选择性刺激模型。实验用电极为自制Cuff双极性电极,刺激器采用的是Grass S88刺激器和AWG2005任意波形信号发生器。采取双电极双向刺激方式,两个电极之间距离为1 mm,刺激波形选用脉宽为0.2 ms的对称双向脉冲,其输出脉冲的幅度、脉宽和延时均可调。调节刺激强度,研究双电极双向刺激下神经兴奋性的规律,以此实现神经的选择性兴奋,并利用“碰撞法”原理验证利用双电极双向刺激方法实现神经选择性兴奋的可行性。 结果与结论:实验过程中神经动作电位的变化将经P511放大器放大后接入示波器显示,双电极刺激波形为脉宽为0.2 ms的对称双向脉冲。随着刺激幅度的增大,实现神经的选择性兴奋。说明用距离很近(1 mm)的双电极双向对称脉冲的方法实现了神经的选择性兴奋,并利用“碰撞法”原理证实了此种方法的有效性和可行性。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)