| [1] 黄杰文,李颖,黄宏兴,等.补肾方对去卵巢大鼠血清TRACP5b和BGP 影响的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(6): 474-476,522. [2] 李颖,黄宏兴,庄洪,等.中药骨康对去势大鼠骨质疏松作用机制的实验研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2009,24(2):160-163.[3] 万雷,黄宏兴,刘庆思,等.骨康对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨密度血清E2、SOD、MDA 的影响[J].医药前沿,2012,2(14):93-94. [4] Loser K,Mehling A,Loeser S,et al.Epidermal RANKL control sregulatory T-cell numbers via activation of dendritic cells. Nat Med. 2006;12(12):1372-1379. [5] Boyce BF, Xing L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008; 473(2):139-146.[6] Abdallah BM,Jensen CH,Gutierrez G,et al. Regulation of hu-man skeletal stem cells differentiation by Dlk1/Pref-1.J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(5):841-852. [7] 魏合伟,林一峰,曲崇正,等. 中药骨康含药血清对骨质疏松性骨折愈合过程中血小板衍生生长因子表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(37):7290-7293.[8] 王洪复,金慰芳,高建军,等.骨细胞图谱与骨细胞体外培养技术[M]. 上海:上海科技出版社, 2001. [9] Rossou JE,Anderson GL,Prentice RL,et al. Risks and benefit of estrogen plus progestin in healthy post menopausal women:principal results from the womens healthy initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002;288(3):321-333.[10] 郭帮富,罗江,邵敏, 等.骨康对体外培养人成骨细胞OPG及RANKL基因表达的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2012,29(4): 392-396. [11] 乔荣勤,刘海全,魏合伟, 等.中药骨康对羟化酶活性影响的研究[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2011,9(24):114-116. [12] Qian G, Zhang X, Lu L, et al. Regulation of cbfal expression by total falvonoids of Herbal Epimedii. Endocr J. 2006;53(1): 87.[13] 翟远坤, 李志忠, 陈克明, 等.淫羊藿苷对体外培养乳鼠颅骨成骨细胞增殖、分化及成熟的影响[J].中药材, 2011, 34(6):917.[14] 徐苓.骨质疏松症[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2011:17. [15] 王建钧, 张晓荣, 李晓东, 等.淫羊藿苷对SD大鼠成骨-破骨细胞共育体系的影响[J].江西中医学院学报, 2010, 22(2):75. [16] 马慧萍, 贾正平, 陈克明, 等.含淫羊藿总黄酮大鼠血清对成骨细胞发育的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2008, 33(8):928. [17] 宋敏, 罗晓, 李宁, 等.淫羊藿总黄酮含药血清对成骨细胞0PG/OPGL基因表达的影响[J].时珍国医国药, 2012, 23(4): 884.[18] 翟远坤, 王鸣刚, 李志忠, 等.淫羊藿苷含药血清对体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨性分化的影响[J].中国中医药杂志, 2012, 27(2):480.[19] 刘洪江,刘海全,秦佳佳, 等. 不同浓度淫羊藿含药血清干预骨髓基质干细胞的成脂分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(14):2583-2586. [20] Tsuji K,Ito Y,Noda M,et al. Expression of the PEBP2alphaA/ AML3/ CB2FA1 gene is regulated by BMP4/7 heterodimer and its overexpression sup2presses type Ⅰcollagen and osteocalcin gene expression in osteoblastic andnonosteoblastic mesenchymal cells. Bone. 1998;22 : 87-92. [21] Thirunavukkarasu K, Halladay DL, Miles RR, et al. Theosteoblast-specific transcription factor Cbfa1 contributes to theexpression of osteoprotegerin , a potent inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation and function. J Biol Chem. 2000;275 (33) :25163-25172. [22] Kim IS, Song YM, Cho TH, et al. In vitro response of primary human bone marrow stromal cells to recombinant human bone morphogenie protein-2 in the early and late stages of osteoblast differentiation. Dev Growth Differ. 2008;50: 553-564.[23] Leeka-Czemik B, Gub L, Moerman EJ, et al.Inhibition of Osf2/Cbfal expression and terminal osteoblast differentiation by PPAR gamma2.J Cell Biechem. 1999;74:357-371.[24] Taranta A, Brama M, Teti A, et al. The selective estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene regulates osteoclast and esteoblast activity invitro. Bone. 2002;30:368-376. |

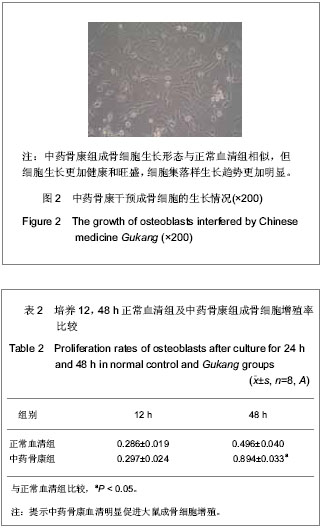
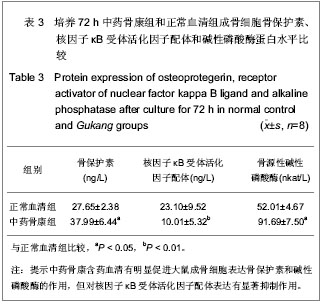
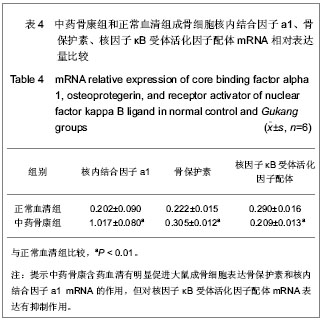
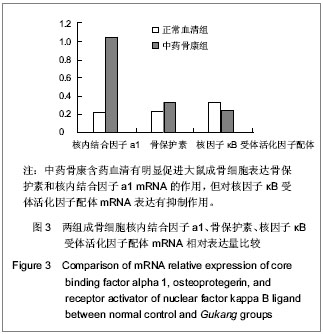
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)