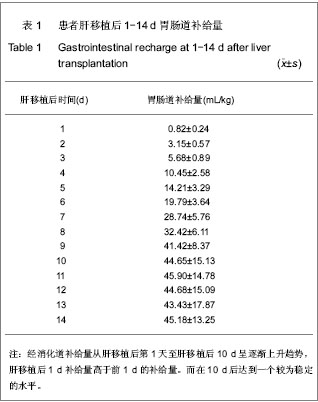
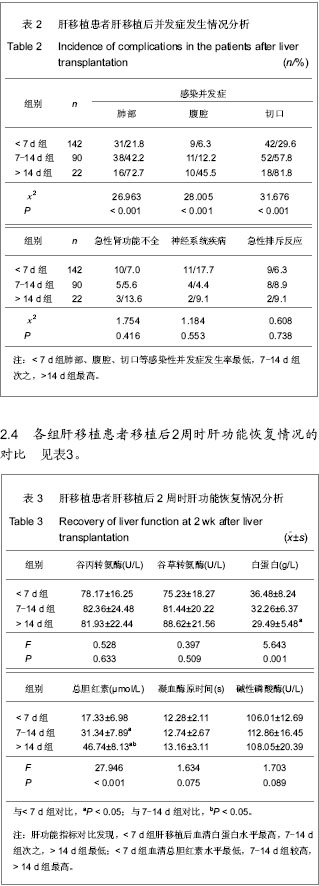
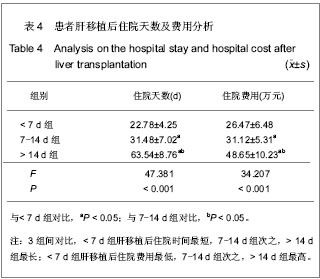
| [1] Johnson TM, Overgard EB, Cohen AE,et al.Nutrition assessment and management in advanced liver disease.Nutr Clin Pract.2013;28(1):15-29.[2] Chandok N.Polycystic liver disease:a clinical review.Ann Hepatol. 2012;11(6):819-26. [3] Anastácio LR, Ferreira LG, Ribeiro Hde S,et al.Weight loss during cirrhosis is related to the etiology of liver disease.Arq Gastroenterol. 2012;49(3):195-198.[4] 江艺,蔡秋程.肠内营养在肝移植中的作用[J].腹部外科,2007, 20(2):76-77.[5] McCullough AJ ,Bugianesi E. Protein - caloric malnutrition and the etiology of cirrhosis.Am J Gastroenterol.1997;92(5): 734-738.[6] Kachaamy T, Bajaj JS.Diet and cognition in chronic liver disease.Curr Opin Gastroenterol.2011;27(2):174-179.[7] Bavdekar A,Bhave S,Pandit A.Nutrition management in chronic liver disease.Indian J Pediatr. 2002;69(5):427-431.[8] Rao R.Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease.Hepatology. 2009;50(2):638-644.[9] Norman K, Pirlich M. Gastrointestinal tract in liver disease: which organ is sick?Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008; 11(5):613-619. [10] Kim JW, Jeon WK, Yun JW,et al.Intestinal permeability in patients with viral and alcoholic liver disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004 Feb;43(2):104-11. [11] 张英才,杨扬,张琪,等.成人良性终末期肝病肝移植术后中远期死亡的危险因素分析[J].中华外科杂志,2010,14(5):1083-1087.[12] 罗文峰,时军,周凯,等.肝移植后早期营养支持的评估[J].中国组织工程研究和临床康复,2001,15(5):800-805.[13] Esmat Gamil M, Pirenne J, Van Malenstein H,et al.Risk factors for bleeding and clinical implications in patients undergoing liver transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2012;44(9):2857-2860. [14] Wang Y, Yang JM, Hu MH,et al.Effect of the amount of portal blood stasis removal on endotoxemia and liver function after liver transplantation.Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.2008;46(15): 1136-1138. [15] Stadlbauer V,Davies NA,Wright GA,et al.Endotoxemia during liver transplantation.Liver Transpl. 2007;13(11):1616-1617.[16] Xie YR, Liu SL, Liu X,et al.Intestinal microbiota and innate immunity-related gene alteration in cirrhotic rats with liver transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(10): 3973-3979.[17] 江艺,蔡秋程.肠内营养在肝移植中的作用[J].腹部外科, 2007, 20(2):76-77.[18] Wallia A, Parikh ND, O'Shea-Mahler E,et al.Glycemic control by a glucose management service and infection rates after liver transplantation.Endocr Pract. 2011;17(4):546-551. [19] Pageaux GP,Faure S,Bouyabrine H,et al.Long-term outcomes of liver transplantation: diabetes mellitus.Liver Transpl.2009; 15 Suppl 2:S79-82.[20] Perseghin G, Caumo A, Mazzaferro V,et al.Assessment of insulin sensitivity based on a fasting blood sample in men with liver cirrhosis before and after liver transplantation. Transplantation.2003;76(4):697-702.[21] 中华人民共和国卫生部.医院感染诊断标准(试行)[J].中华医学杂志,2001,81(5):314-320.[22] Rimola A,Gavaler JS, Schade RR.Effects of renal impairment on liver transplantation.Gastroenterology.1987.[23] Lucky A, Livingston E, Tach Y. Mechanisms and treatment of post operat ive ileus. A rch Surg.2003;138(2):206-214.[24] Reintam Blaser A, Malbrain ML, Starkopf J,et al. Gastrointestinal function in intensive care patients: terminology, definitions and management. Recommendations of the ESICM Working Group on Abdominal Problems. Intensive Care Med.2012;38(3):384-394.[25] Ehlert FJ, Pak KJ, Griffin MT.Muscarinic agonists and antagonists: effects on gastrointestinal function.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2012;(208):343-374.[26] Chowdhury AH, Lobo DN.luids and gastrointestinal function Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.2011;14(5):469-476.[27] Viteri FE.INCAP studies of hematologic and gastrointestinal function in healthy individuals and those with protein-energy malnutrition and infection.Food Nutr Bull. 2010;31(1):130-140.[28] Grady P, Clark N, Lenahan J,et al.Effect of intraoperative intravenous lidocaine on postoperative pain and return of bowel function after laparoscopic abdominal gynecologic procedures. AANA J. 2012;80(4):282-288.[29] 余国芝,林平,刘维. 肠内营养对肝胆外科大手术患者术后胃肠功能恢复效果研究[J]. 当代医学,2012,18(33):87-87.[30] 张斌,王轩,李增才,等.肝移植术后早期肠内营养支持治疗效果评估:同期对照比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12 (18):3557-3560.[31] 陈小凤.早期进食对腹腔镜胆囊切除术后病人肠功能恢复的探讨[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2005,26(6):716.[32] Xu WX,Fang LC,Liu LJ.Zhongguo Jijiu Yixue. 2010;6:502-504.徐文秀,方理超,刘励军.影响危重症患者早期肠内营养达标的因素[J].中国急救医学,2010,6:502-504.[33] Wang Y.Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi.2011;32(10):607-610.王营.急诊肝移植治疗急性肝功能衰竭22例的临床分析[J].中华器官移植杂志.2011,32(10):607-610. [34] 古维立,翁杰锋,肖海,等.不同灌注方式对供肝质量的影响[J].广东医学2008,29(10):1623-1625. [35] 施晓敏,傅志仁,丁国善,等.供肝获取术中供肝质量和灌注情况的快速判断[J].肝胆外科杂志,2005,13(3):184-186. [36] Vitale A, Bertacco A, Gambato M,et al. Model for end-stage liver disease-sodium and survival benefit in liver transplantation.Transpl Int.2013;26(2):138-44.13.[37] Esmat Gamil M, Pirenne J, Van Malenstein H,et al.Risk factors for bleeding and clinical implications in patients undergoing liver transplantation.Transplant Proc.2012;44(9): 2857-2860. [38] Cabeza de Vaca VG, Bellido CB, Martínez JN,et al.Impact of the model for end-stage liver disease score on mortality after liver transplantation.Transplant Proc.2012;44(7): 2069-2070. [39] Alves RC, Fonseca EA, Mattos CA,et al.Predictive factors of early graft loss in living donor liver transplantation.Arq Gastroenterol.2012;49(2):157-161.[40] 宇汝胜,钱海鑫,汪泳,等.肝移植大鼠胃肠动力改变及机制[J].江苏医药,2008,34(5):472-474.[41] 刘秀红,李宁,李伟华,等.肝移植患者术后早期肠黏膜屏障功能损伤的研究[J]. 肝胆外科杂志,2008,16(2):103-105.[42] Cisneros JM,Varo E.Prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus infection in liver transplantation.Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2011;29 Suppl 6:42-45.[43] Soong RS, Chan KM, Chou HS,et al.The risk factors for early infection in adult living donor liver transplantation recipients.Transplant Proc.2012;44(3):784-786. [44] van Hoek B, de Rooij BJ, Verspaget HW.Risk factors for infection after liver transplantation.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26(1):61-72. [45] Villet S, Chiolero RL, Bollmann MD, et al.Negative impact of hypocaloric Feeding and energy balance on clinical outcome in ICU patients. Clin Nutr.2005;24:502–509.[46] Stickel F, Inderbitzin D, Candinas D. Role of nutrition in liver transplantation for end-stage chronic liver disease. Nutr Rev. 2008;66(1):47-54.[47] Hasse JM.Examining the role of tube feeding after liver transplantation. Nutr Clin Pract.2006;21(3):299-311.[48] Figueiredo FA,Dickson ER,Pasha TM,et al. Impact of nutritional status on outcomes after liver transplantation. Transplantation.2000;(70):1347-1352.[49] 黎介寿.肠内营养-外科临床营养支持的首选途径[J].中国实用外科杂志,2003 ,23(2):67.[50] 张霁,任辉.早期肠内营养对肝移植术后肠黏膜屏障的影响[J].护士进修杂志,2007,22(1):10-11. |