| [1] Salehi SA, Tawk R, Ganju A, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Surgical technique and results in 24 patients. Neurosurgery. 2004;54:368-374.[2] Glaser JA, Bernhardt M, Found E, et al. Lumbar arthrodesis for degenerative conditions. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53: 325-340. [3] Deyo RA, Nachemson A, Nirza SK. Spinal-fusion surgery: the case for restraint. N Engl J Med 2004;350:722-726. [4] Mummaneni PV, Haid RW, Rodts GE. Lumbar interbody fusion: state-of-the-art technical advances. J Neurosurg (Spine) 2004;1:24-30. [5] Coe JD. Instrumented transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bioabsorbable polymer implants and iliac crest autograft. Neurosurg Focus 2004;16:1-9. [6] Schwender JD, Holly LT, Rouben DP, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech 2005;18(suppl):1-6. [7] Butt MF, Dhar SA, Hakeem I, et al In situ instrumented posterolateral fusion without decompression in symptomatic low-grade isthmic spondylolis-thesis in adults. Int Orthop. (2007) May 11.[8] Inamdar DN, Alagappan M, Shyam L, et al.Devadoss APosterior lumbar interbody fusion versus intertransverse fusion in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Surg.2006;14(1):21-26.[9] Kho VK, Chen WC.Posterolateral fusion using laminec-tomy bone chips in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop. 2008;32(1):115-119.[10] Muschler GF,Nakamoto C,Griffith LG. Engineering principles of clinical cell-based tissue engineering. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86:1541-1558.[11] Sengupta DK. Dynamic stabilization devices in the treatment of low back pain. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004;35:43-56. [12] Wilke HJ,Rohlmann F,Neidlinger-Wilke C,et al.Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: part I. Lumbar spine. Eur Spine J.2006;15(6):720-730.[13] Tribus CB, Belanger TA, Zdeblick TA.The effect of operative position and short-segment fusion on maintenance of sagittal alignment of the lumbar spine. Spine(Phila Pa1976).1999; 24:58-61.[14] Djurasovic MO, Carreon LY, Glassman SD, et al. Sagittal alignment as a risk factor for adjacent level degeneration:a case-control study. Orthopedics.2008;31:546.[15] Lazennec JY, Ramare S, Arafati N,et al.Sagittal alignment in lumbosacral fusion: relations between radiological parameters and pain. Eur Spine J.2000;9:47-55.[16] Le Huec J, Basso Y, Mathews H,et al. The effect ofsingle- level,total disc arthroplasty on sagittal balance parameters: a prospectivestudy. Eur Spine J .2005; 14:480-486.[17] Glassman SD,Bridwell K, DimarJR,et al.The impact of positive sagittal balancein adultspinaldeformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2005;30:2024-2029.[18] Hioki A, Miyamoto K, Kodama H,et al. Two-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative disc disease: improved clinical outcome with restoration ofl umbar lordosis. Spine J.2005;5:600-607.[19] Jagannathan J,Sansur CA, Oskouian RJ Jr,et al. Radiographic restoration of lumbar alignment after transforaminal lumbar inter-body fusion. Neurosurgery. 2009;64:955-963.[20] Kawakami M,Tamaki T, Ando M,et al.Lumbar sagittal balance influences the clinical outcome after decompression and posterolateral spinal fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002;27:59-64.[21] Blumenthal S, McAfee PC, Guyer RD, et al. A prospective, randomized, multicenter Food and Drug Administrationi nvestigational device exemptions study of lumbar total disc replacement with the CHARITE artificial disc versus lumbar fusion:partI:evaluation of clinical outcomes.. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) .2005;30:1565-1575.[22] Guyer RD, McAfee PC,Banco RJ,et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption study of lumbar total disc replacement with the CHARITE artificial disc versus lumbar fusion:five-year follow-up. Spine J .2009;9: 374-386.[23] Kumar MN,Baklanov A, Chopin D. Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J .2001;10: 314-319.[24] Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC,et al. Adjacentsegmentdisease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion:review of the literature. Spine(Phila Pa 1976) .2004;29:1938-1944.[25] Schlegel JD, Smith JA, Schleusener RL. Lumbar motion segment pathology adjacent to thoracolumbar,lumbar, and lumbosacral fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1996;21: 970-981.[26] Cakir B, Richter M, Kafer W,et al.The impact of total lumbar disc replacementon segmental and total lumbar lordosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol,Avon).2005;20:357-364.[27] Chung SS,Lee CS, Kang CS,et al.The effect of lumbar total disc replacement on the spinopelvic alignment and range of motion of the lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord Tech .2006;19: 307-311.[28] Schmidt R, Obertacke U, Nothwang J, et al. The impact of implantation technique on frontal and sagittal alignment in total lumbar discreplacement:a comparison of anterior versus oblique implantation. Eur Spine J.2010;19:1534- 1539.[29] Tournier C, Aunoble S,Le HuecJC,et al.Total disc arthroplasty:consequences for sagittal balance and lumbar spine movement. Eur Spine J.2007;16:411-421.[30] Gilad R, Gandhi CD, Arginteanu MS,et al. Uncorrected sagittal plane imbalance predisposes to symptomatic instrumentation failure. Spine J.2008;8:911-917.[31] Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O’Shaughnessy BA,et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusionin comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion:implications for the restoration of foraminal height,local disc angle,lumbar lordosis,and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine.2007;7:379-386.[32] Kafchitsas K, Kokkinakis M, Habermann B,et al.Effect of lumbar discreplacement on the height of the discspace and the geometry of the facet joints:a cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010;92:595-601.[33] Bernhardt M,Bridwell KH.Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoraco-lumbar junction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14: 717-721.[34] Boulay C, Tardieu C, HecquetJ,et al.Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J.2006; 15: 415-422.[35] Kuntz Ct Levin LS, Ondra SL,et al. Neutral upright sagittal spinal alignment from the occiput to the pelvis in asymptomatic adults:a review and resynthesis of the literature. J Neurosurg Spine .2007;6:104-112. |
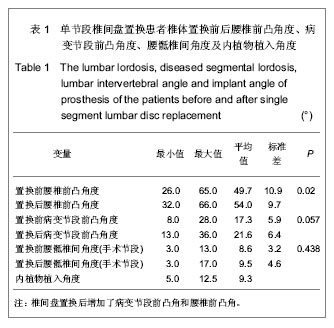
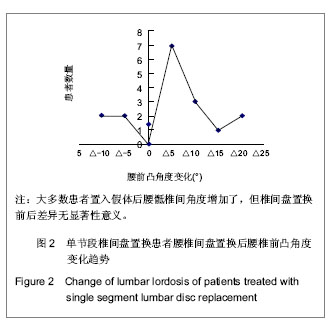
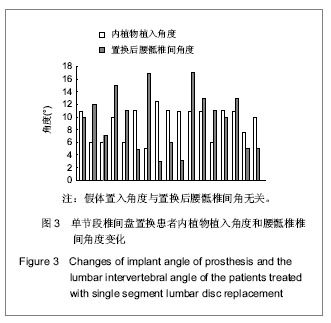
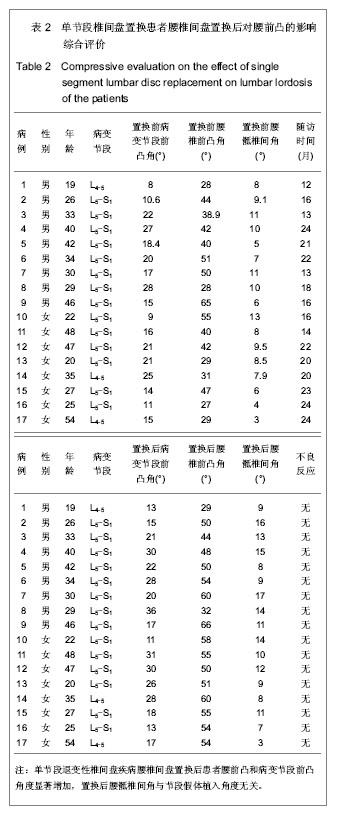
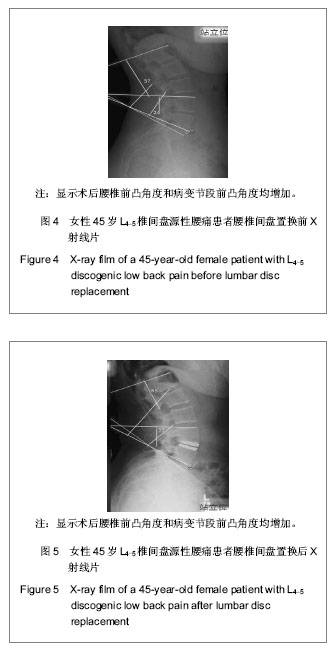
.jpg)