| [1] Ingham E, Fisher J. The role of macrophages in osteolysis of total joint replacement. Biomaterials. 2005;26(11):1271-1286.[2] Wang CJ, Shi JF, Morgan C, et al. Design and simulation of a femoral component peg in total knee replacement. Key Eng Mater. 2011(450):111-114.[3] Harris WH. Wear and periprosthetic osteolysis: the problem. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(393):66-70.[4] Cobelli N, Scharf B, Crisi GM, et al. Mediators of the inflammatory response to joint replacement devices. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(10):600-608. [5] Bottner F, Wegner A, Winkelmann W, et al. Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and TNF-alpha: markers of peri-prosthetic infection following total joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(1):94-99.[6] Konttinen YT, Li TF, Xu JW, et al. Expression of laminins and their integrin receptors in different conditions of synovial membrane and synovial membrane-like interface tissue. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58(11):683-690.[7] Li TF, Xu JW, Santavirta S, et al. Expression of vitronectin and its integrin receptors in the synovial membrane-like interface tissue from aseptic loosening of total hip replacement. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(3):727-734.[8] Konttinen YT, Li TF, Michelsson O, et al. Expression of tenascin-C in aseptic loosening of total hip replacement. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(10):619-623.[9] Westacott CI, Sharif M. Cytokines in osteoarthritis: mediators or markers of joint destruction? Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 25(4):254-272.[10] Shao JJ, Jiang Y, Zhang XL, et al. Shanghai Yixue. 2002;25 (S1): 30-32.邵俊杰,蒋垚,张先龙,等.白介素-6和转化生长因子-β1在膝骨关节炎发病中的作用[J].上海医学,2002,25(S1):30-32.[11] Botha-Scheepers S, Watt I, Slagboom E, et al. Innate production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 10 is associated with radiological progression of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(8):1165-1169.[12] Hasegawa M, Sudo A, Nagakura T, et al. Tenascin-C levels in pseudosynovial fluid of loose hip prostheses. Scand J Rheumatol. 200534(6):464-468.[13] Venn G, Nietfeld JJ, Duits AJ, et al. Elevated synovial fluid levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor associated with early experimental canine osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36(6):819-826.[14] Li NH, Xue QY, Zhang Y, et al. ZHongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(33):6546-6549.李宁华,薛庆云,张毅,等.中国6个城市4577名中老年人手骨关节炎流行病学调查[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(33): 6546-6549.[15] Hasegawa M, Hirata H, Sudo A, et al. Tenascin-C concentration in synovial fluid correlates with radiographic progression of knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(10): 2021-6.[16] Schmalzried TP, Jasty M, Harris WH. Periprosthetic bone loss in total hip arthroplasty. Polyethylene wear debris and the concept of the effective joint space. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74(6):849-863.[17] Grassmé H, Kirschnek S, Riethmueller J, et al. CD95/CD95 ligand interactions on epithelial cells in host defense to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Science. 2000;290(5491): 527-530.[18] Zhao JN, Mei XL, Guo T, et al. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2011;13(1):21-24.赵建宁,梅晓亮,郭亭,等.全髋关节置换术后血清白细胞介素6、10与纤维蛋白原表达的特点分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2011, 13(1):21-24.[19] Rettig WJ, Erickson HP, Albino AP, et al. Induction of human tenascin (neuronectin) by growth factors and cytokines: cell type-specific signals and signalling pathways. J Cell Sci. 1994; 107 ( Pt 2):487-497.[20] Imanaka-Yoshida K, Hiroe M, Yoshida T. Interaction between cell and extracellular matrix in heart disease: multiple roles of tenascin-C in tissue remodeling. Histol Histopathol. 2004; 19(2):517-525.[21] Järvinen TA, Jozsa L, Kannus P, et al. Mechanical loading regulates tenascin-C expression in the osteotendinous junction. J Cell Sci. 1999;112 Pt 18:3157-3166.[22] Chiquet M, Sarasa-Renedo A, Tunç-Civelek V. Induction of tenascin-C by cyclic tensile strain versus growth factors: distinct contributions by Rho/ROCK and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1693(3):193-204.[23] Imai S, Konttinen YT, Jumppanen M, et al. High levels of expression of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in pathological conditions associated with a foreign-body reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(4):701-710.[24] Takei I, Takagi M, Santavirta S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in joint fluid of the patients with loose artificial hip joints. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;45(3):175-183.[25] Syggelos SA, Eleftheriou SC, Giannopoulou E, et al. Gelatinolytic and collagenolytic activity in periprosthetic tissues from loose hip endoprostheses. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28(6):1319-1329.[26] Siri A, Knäuper V, Veirana N, et al. Different susceptibility of small and large human tenascin-C isoforms to degradation by matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(15): 8650-8654.[27] Spring J, Beck K, Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Two contrary functions of tenascin: dissection of the active sites by recombinant tenascin fragments. Cell. 1989;59(2):325-334.[28] Weber P, Zimmermann DR, Winterhalter KH, et al. Tenascin-C binds heparin by its fibronectin type III domain five. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(9):4619-4623.[29] Day JM, Olin AI, Murdoch AD, et al. Alternative splicing in the aggrecan G3 domain influences binding interactions with tenascin-C and other extracellular matrix proteins. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):12511-12518. [30] Okamura N, Hasegawa M, Nakoshi Y, et al. Deficiency of tenascin-C delays articular cartilage repair in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(6):839-848. [31] Nakoshi Y, Hasegawa M, Akeda K, et al. Distribution and role of tenascin-C in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(5):666-673. [32] Sofat N, Robertson SD, Hermansson M, et al. Tenascin-C fragments are endogenous inducers of cartilage matrix degradation. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(9):2809-2817. |
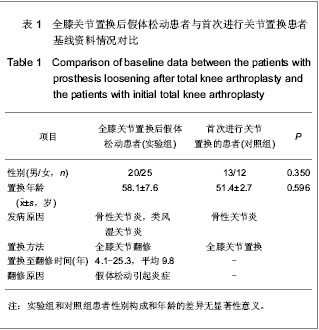
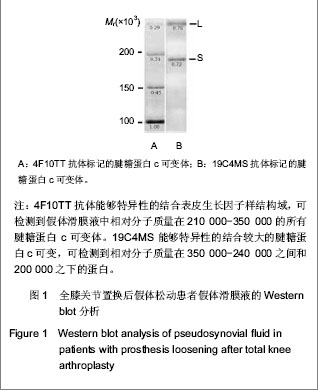
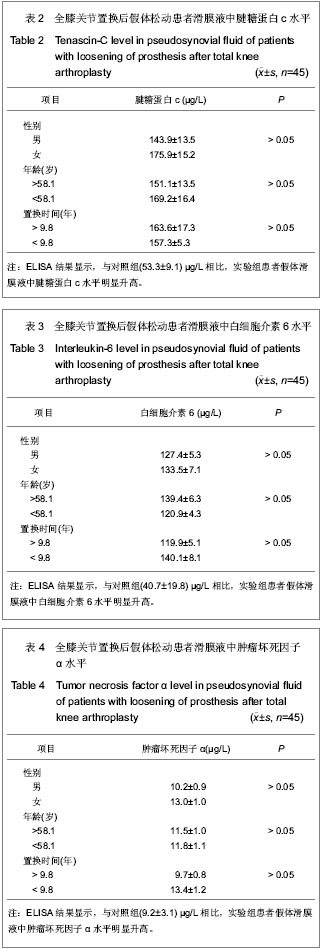
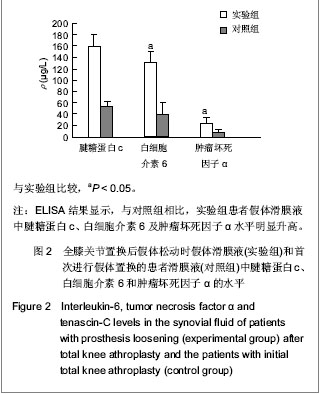
.jpg)