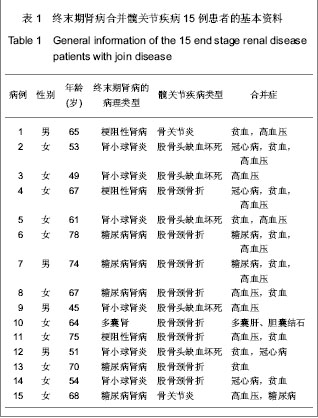
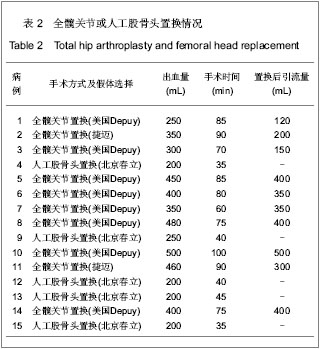
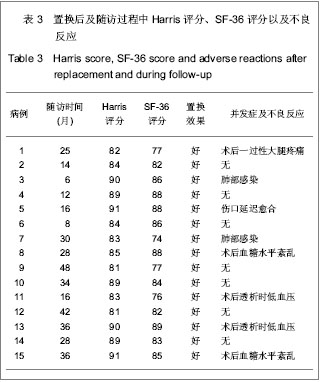
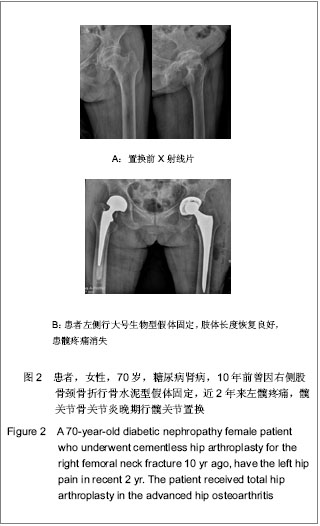
| [1] Dong HY. Yingguo Yixue Zazhi:Zhongwenban. 2006;9(3):136.董海燕.译后评沦:我囯慢性肾脏病的新数据及其警示[J].英囯医学杂志:中文版,2006,9(3):136.[2] Chinese Society of Blood Purification Administration. Zhongguo Xueye Jinghua. 2010;9(1):47-49.中国医院协会血液净化中心管理分会血液透析登记组.我国面临快速增长的终末期肾病治疗负担[J].中国血液净化,2010,9(1): 47-49.[3] Tang S,Gong ZF,Peng XM,et al. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2009;29(5): 613-614.唐盛,龚智峰,彭小梅,等.老年终末期肾病患者流行病学调查分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2009,29(5): 613-614.[4] Zhang LX,Wang M,Wang HY. Zhonghua Shenzhangbing Zazhi. 2005; 21(7):425-428.张路霞,王梅,王海燕.慢性肾脏病的流行病学研究[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2005, 21(7):425-428.[5] Goosen JH, Kums AJ, Kollen BJ,et al. Porous-coated femoral components with or without hydroxyapatite in primary uncemented total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129(9):1165-1169.[6] Epinette JA, Manley MT. Uncemented stems in hip replacement--hydroxyapatite or plain porous: does it matter? Based on a prospective study of HA Omnifit stems at 15-years minimum follow-up.Hip Int. 2008;18(2):69-74.[7] Rahmy AI, Gosens T, Blake GM,et al. Periprosthetic bone remodelling of two types of uncemented femoral implant with proximal hydroxyapatite coating: a 3-year follow-up study addressing the influence of prosthesis design and preoperative bone density on periprosthetic bone loss. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(4):281-289. [8] Nagoya S, Nagao M, Takada J,et al. Efficacy of cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients on long-term hemodialysis. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(1):66-71.[9] Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.[10] Ware JE Jr, Gandek B. Overview of the SF-36 Health Survey and the International Quality of Life Assessment (IQOLA) Project. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998;51(11):903-912.[11] Coco M, Rush H. Increased incidence of hip fractures in dialysis patients with low serum parathyroid hormone.Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;36(6):1115-1121.[12] Alem AM, Sherrard DJ, Gillen DL,et al. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease.Kidney Int. 2000;58(1):396-399.[13] Qiu MC. Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 2003: 1075-1098.邱明才.代谢性骨病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2003: 1075- 1098.[14] Qiu WQ. Linchuang Huicui. 2001;16(1):33-34.邱维强.肾性骨病诊断与治疗研究进展[J].临床荟萃,2001,16(1): 33-34.[15] Mataliotakis G, Lykissas MG, Mavrodontidis AN,et al. Femoral neck fractures secondary to renal osteodystrophy. Literature review and treatment algorithm. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2009;9(3):130-137.[16] Chen SY,Wu BD,Lian XJ,et al. Linchuang Shenzhangbing Zazhi. 2008;8(1):18-20.陈珊莹,吴彼得,连学坚,等.低分子肝素在连续血液净化中抗凝作用的探讨[J].临床肾脏病杂志,2008,8(1):18-20.[17] Chen JD,Hou SX,Li WF. Zhonghua Quanke Yishi Zazhi. 2007; 6(1):55-56.陈金栋,侯树勋,李文锋.慢性肾功能不全骨科患者的围手术期处理[J].中华全科医师杂志,2007,6(1):55-56.[18] Karaeminogullari O, Demirors H, Sahin O,et al. Analysis of outcomes for surgically treated hip fractures in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(2):324-331.[19] Kalra S, McBryde CW, Lawrence T. Intracapsular hip fractures in end-stage renal failure. Injury. 2006;37(2):175-184.[20] Lv HS. Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 2007.吕厚山.现代人工关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2007.[21] Li WC, Shih CH, Ueng SW,et al. Uncemented total hip arthroplasty in chronic hemodialysis patients.Acta Orthop. 2010;81(2):178-182. [22] Nagoya S, Nagao M, Takada J, et al. Efficacy of cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients on long-term hemodialysis. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(1):66-71.[23] Huang GY,Wei YB,Wu JG. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Shunshang Zazhi. 2010;25(1):60-61.黄钢勇,魏亦兵,吴建国.终末期肾病患者的全髋关节置换[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(1):60-61.[24] 中华医学会骨科学分会. 中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2009,3(3):380-383.[25] Zhang B,Shi W. Zhonghua Shenzhangbing Zazhi. 2004; 20(2):145-146.章斌,史伟.终末期肾病血管钙化机制[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2004, 20(2):145-146.[26] Zhou Y,Zhu N,Yuan WJ. Zhonghua Shenzhangbing Zazhi. 2012; 28(6):495-497.周益,朱楠,袁伟杰.慢性肾脏病患者骨-血管轴调节紊乱的研究现状[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2012, 28(6):495-497.[27] London GM, Marty C, Marchais SJ,et al. Arterial calcifications and bone histomorphometry in end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(7):1943-1951.[28] Raggi P, Boulay A, Chasan-Taber S,et al. Cardiac calcification in adult hemodialysis patients. A link between end-stage renal disease and cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002; 39(4):695-701.[29] Latos DL.Chronic dialysis in patients over age 65.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7(5):637-646.[30] Chen XM. Beijing:People’s Military Medical Press. 2006: 45-50, 238-258.陈香美.现代慢性肾衰治疗学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2006: 45-50,238-258.[31] Ryg J, Rejnmark L, Overgaard S,et al. Hip fracture patients at risk of second hip fracture: a nationwide population-based cohort study of 169,145 cases during 1977-2001.J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(7):1299-1307.[32] Kaukonen JP, Lüthje P, Nurmi-Lüthje I,et al.Second hip fracture and patients' medication after the first hip fracture: a follow-up of 221 hip fracture patients in Finland. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;52(2):185-189.[33] Lips P, van Schoor NM.Quality of life in patients with osteoporosis.Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(5):447-455.[34] Alvarez-Nebreda ML, Jiménez AB, Rodríguez P,et al. Epidemiology of hip fracture in the elderly in Spain.Bone. 2008; 42(2):278-285.[35] Abbott KC, Bucci JR, Agodoa LY.Total hip arthroplasty in chronic dialysis patients in the United States. J Nephrol. 2003; 16(1):34-39.[36] Sakai S, David D, Shoji H,et al. Bone injuries due to tetany or convulsions during hemodialysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (118):118-123.[37] Taylor LJ, Grant SC. Bilateral fracture of the femoral neck during a hypocalcaemic convulsion. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985;67(4):536-537.[38] Ye CY,Cao CH,Fu WC. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2004;10(1):87-89.叶朝阳,曹春华,付文成. 鲑鱼降钙素对血透患者肾性骨病的疗效观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2004,10(1):87-89.[39] Tang Y,Zhong YH,Gong SM. Zhonghua Shenzhangbing Zazhi. 2011;27(6):406-410.汤颖,钟一红,龚邵敏.终末期肾病血液透析患者感染死亡事件调查[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2011,27(6):406-410.[40] Sunday JM, Guille JT, Torg JS. Complications of joint arthroplasty in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(397):350-355.[41] Sakalkale DP, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH.Total hip arthroplasty in patients on long-term renal dialysis. J Arthroplasty. 1999; 14(5):571-575. |