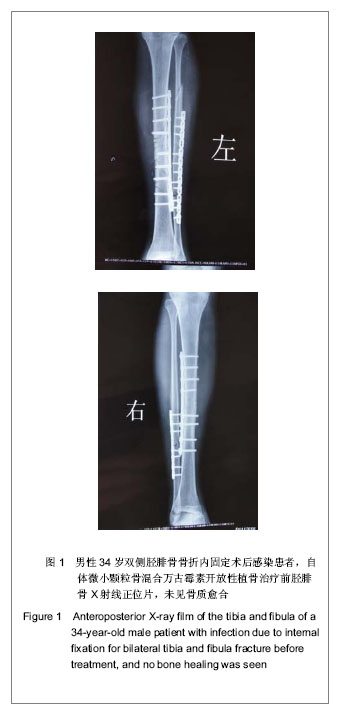
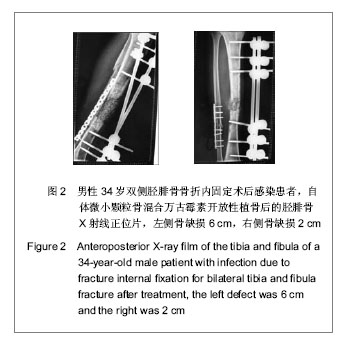
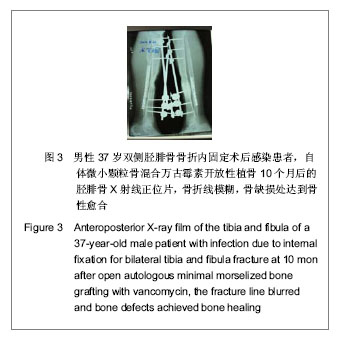
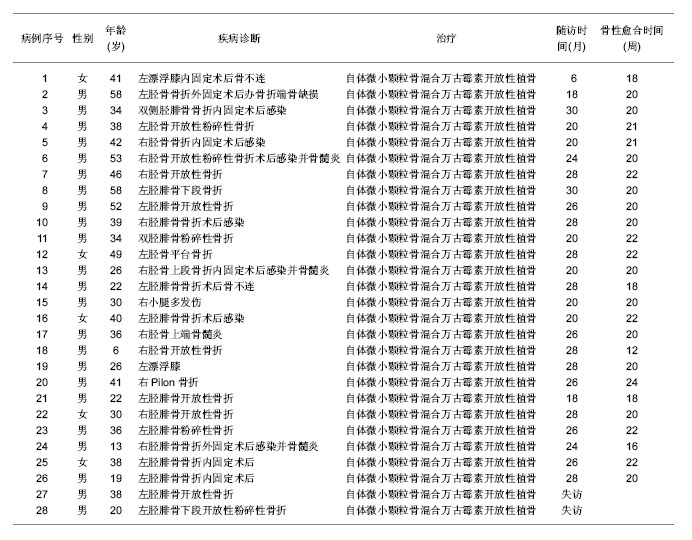
| [1] Li WL,Shang XK,Li G,et al.Jiankang Bidu:zhongunkan. 2012;11(5):23-24.李文龙,尚小可,李刚,等.自体微小颗粒骨复合脂肪充质干细胞治疗兔骨缺损的实验研究[J].健康必读:中旬刊,2012,11(5):23-24.[2] Wu JQ,Liu J,Wang LL,et al.Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi. 2011;5(10):3011-3013.吴景泉,刘俊,王琳琳,等. 自体微小颗粒骨移植修复兔下颌骨部分缺损的骨密度检测[J].中华临床医师杂志,2011,5(10): 3011-3013.[3] Wang XT,Yan JL,Yang XS,et al.Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2008;10(3):260-265.王新涛,闫景龙,杨显声,等. 微小颗粒骨移植骨细胞活性的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(3):260-265.[4] Liu DQ,Zhang BS,Liu HB,et al. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2004;6(12):1370-1373.刘德全,张伯松,刘洪波,等. 一期开放松质骨植骨治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(12):1370-1373.[5] Zhu YZ,Pan MP,Wang Q.Dangdai Yixue. 2009,15(10):81.朱耀宗,潘梅圃,王强. 开放性胫骨骨折伴骨缺损一期植骨36例临床探讨[J].当代医学,2009,15(10):81.[6] Liu HY,Tong XJ.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 1999;6(6): 440.刘好源,童兴杰.自身骨泥成骨活性的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,1999,6(6):440.[7] Zhang M,Yang ZX,Shi ZY,et al.Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;9(30):76-77.张明,杨智贤,石展英,等.自体骨泥混入骨膜碎片植骨与单纯自体骨泥植骨修复骨缺损的效果对比实验[J].中国临床康复,2008, 9(30):76-77.[8] Xia JJ,Yan JL,Zhang ZP,et al.Haerbin Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2002;36(2):141-143.夏景君,闫景龙,张志鹏,等.颗粒骨和块状骨对骨髓基质细胞作用的实验研究[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2002,36(2):141-143.[9] Xia JJ, Zhang ZP,Yan JL,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2007;15(10):762-764.夏景君,张志鹏,闫景龙,等.微小颗粒骨复合自体骨空心螺纹内固定器用于颈椎椎间融合[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(10): 762-764.[10] Yu GP,Chen DH,Hu NM,et al.Ningxia Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2011;33(4):322-325.喻赣鹏,陈丹袆,胡宁敏.自体微小颗粒骨移植治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2011,33(4):322-325.[11] Stevenson S.Biology of bone grafts.Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30(4):543-552.[12] Li ZY,Li G,Jing H,et al. Ningxia Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2012; 34(4): 385-387.李志远,李刚,荆浩,等.自体微小颗粒骨一期治疗感染性骨缺损及骨不连的临床研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2012,34(4):385-387.[13] Tang SY,Xu HR,Qi LJ,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005; 9(46):91-93.汤苏阳,徐获荣,齐连军,等.封闭式负压引流技术对失神经支配创面愈合过程中血管生成的影响[J].中国临床康复, 2005,9(46): 91-93.[14] McLaren AC, Miniaci A. In vivo study to determine the efficacy of cancellous bone graft as a delivery vehicle for antibiotics. Trans Soc Biomat.1986;12(1): 32-35.[15] Wang YN,Hao LB.Shandong Yiyao. 2010;50(20):29-30.王羽凝,郝立波.抗生素混合自体骨治疗胫骨感染骨缺损临床疗效分析[J].山东医药,2010,50(20):29-30.[16] Tang H,Xu YQ,Zheng TE,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(10):1907-1910.唐辉,徐永清,郑天娥,等.复合抗生素的人工骨及异体骨材料[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(10):1907-1910.[17] Li G,Hu NM,Jing H,et al. Ningxia Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2012; 34(5):462-465.李刚,胡宁敏,荆浩,等.自体微小颗粒骨复合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗兔感染性骨缺损的实验研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2012, 34(5): 462-465. |