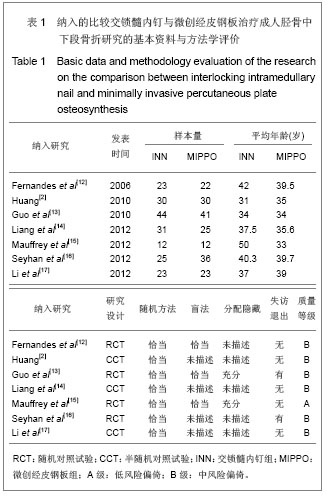
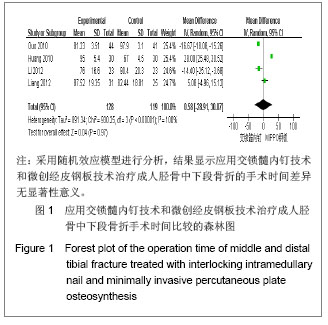
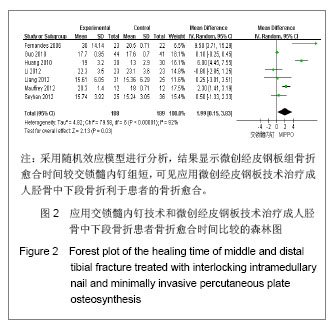
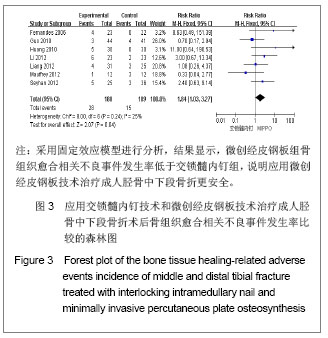
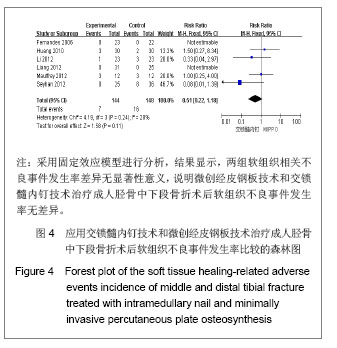
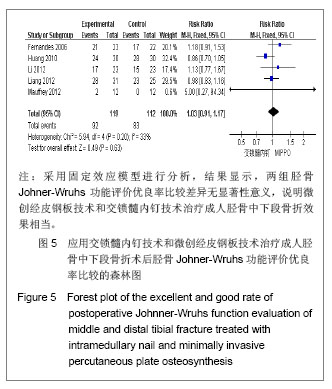
| [1]Tang X. Dalian: Dalian Yike Daxue. 2006.汤欣.胫骨血运的解剖研究及不同术式对胫骨血运的影响[D]. 大连:大连医科大学,2006.[2]Huang W. Changsha: Zhongnan Daxue. 2010.黄文.经皮微创钢板内固定与交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨干骨折的疗效比较[D].长沙:中南大学,2010.[3]Bedi A, Le TT, Karunakar MA. Surgical treatment of nonarticular distal tibia fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(7):406-416.[4]Wang ZK. Dalian: Dalian Yike Daxue. 2011.王自科.微创经皮钢板与交锁髓内钉固定治疗胫骨下端骨折的疗效比较[D].大连:大连医科大学,2011.[5]Xu ST, Ge BF, Xu YK. Beijing: Renmin Junyi Chubanshe. 2004.胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2004.[6]Fan CY, Chiang CC, Chuang TY, et al. Interlocking nails for displaced metaphyseal fractures of the distal tibia. Injury. 2005;36(5):669-674.[7]Xu HB, Zhang PS, Wang HB. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(32):6481-6483.徐海波,张普晟,王洪兵.微创经皮钢板置入内固定治疗胫腓骨骨折的技术操作特点[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(32): 6481-6483.[8]Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA Statement. Open Med. 2009;3(3):e123-130. [9]Li ZY, Feng HL, Zhang YY, et al. Hebei Yiyao. 2005;27(12): 888-889.李增炎,冯和林,张英泽,等.带锁髓内钉与微创经皮钢板治疗胫腓骨骨折的临床比较研究[J].河北医药,2005,27(12):888- 889.[10]Jüni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Systematic reviews in health care: Assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ. 2001;323(7303):42-46.[11]Johner R, Wruhs O. Classification of tibial shaft fractures and correlation with results after rigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;(178):7-25.[12]Fernandes HJ, Sakaki MH, Silva Jdos S, et al. Comparative multicenter study of treatment of multi-fragmented tibial diaphyseal fractures with nonreamed interlocking nails and with bridging plates. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2006;61(4):333-338.[13]Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, et al. A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):984-988.[14]Liang BW, Zhao JM, Yin GQ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(17):3116-3120.梁博伟,赵劲民,殷国前,等.经皮微创钢板固定治疗胫骨下段骨折:与交锁髓内钉固定和切开复位钢板内固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3116-3120.[15]Mauffrey C, McGuinness K, Parsons N, et al. A randomised pilot trial of "locking plate" fixation versus intramedullary nailing for extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):704-708.[16]Seyhan M, Unay K, Sener N. Intramedullary nailing versus percutaneous locked plating of distal extra-articular tibial fractures: a retrospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. In press.[17]Li Y, Liu L, Tang X, et al. Comparison of low, multidirectional locked nailing and plating in the treatment of distal tibial metadiaphyseal fractures. Int Orthop. 2012;36(7):1457-1462.[18]Dai P, Chen XL, Ma CZ. Dalian: 2006363. Beijing: Zhonghua Yixuehui Jizhen Yixue Fenhui. 2006.代平,陈新来,马灿泽.非扩髓髓内钉与钢板治疗胫骨干开放性骨折的疗效比较[C].大连:2006363.北京:中华医学会急诊医学分会, 2006.[19]Benirschke SK, Melder I, Henley MB, et al. Closed interlocking nailing of femoral shaft fractures: assessment of technical complications and functional outcomes by comparison of a prospective database with retrospective review. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7(2):118-122.[20]Klein MP, Rahn BA, Frigg R, et al. Reaming versus non-reaming in medullary nailing: interference with cortical circulation of the canine tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;109(6):314-316.[21]Lindvall E, Sanders R, Dipasquale T, et al. Intramedullary nailing versus percutaneous locked plating of extra-articular proximal tibial fractures: comparison of 56 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(7):485-492.[22]Giannoudis PV, Snowden S, Matthews SJ, et al. Temperature rise during reamed tibial nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (395):255-261.[23]Wu Y, Wang MY, Rong GW, et al. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 1998;36(8):461-463.武勇,王满宜,荣国威,等.非扩髓带锁髓内针治疗胫腓骨骨折[J].中华外科杂志,1998,36(8):461-463.[24]Robinson CM, O'Donnell J, Will E, et al. Dropped hallux after the intramedullary nailing of tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(3):481-484.[25]Court-Brown CM, Gustilo T, Shaw AD. Knee pain after intramedullary tibial nailing: its incidence, etiology, and outcome. J Orthop Trauma. 1997;11(2):103-105.[26]Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, et al. Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(1):76-79.[27]Im GI, Tae SK. Distal metaphyseal fractures of tibia: a prospective randomized trial of closed reduction and intramedullary nail versus open reduction and plate and screws fixation. J Trauma. 2005;59(5):1219-1223.[28]Beardi J, Hessmann M, Hansen M, et al. Operative treatment of tibial shaft fractures: a comparison of different methods of primary stabilisation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128 (7):709-715.[29]Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5):307-311.[30]Ozsoy MH, Tuccar E, Demiryurek D, et al. Minimally invasive plating of the distal tibia: do we really sacrifice saphenous vein and nerve? A cadaver study. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(2):132-138.[31]Tyllianakis M, Megas P, Giannikas D, et al. Interlocking intramedullary nailing in distal tibial fractures. Orthopedics. 2000;23(8):805-808.[32]Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury. 1997; 28 Suppl 1:A20-30.[33]Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, et al. Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures. Int Orthop. 2008;32(5):697-703.[34]Farouk O, Krettek C, Miclau T, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis: does percutaneous plating disrupt femoral blood supply less than the traditional technique? J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(6):401-406.[35]Stoffel K, Klaue K, Perren SM. Functional load of plates in fracture fixation in vivo and its correlate in bone healing. Injury. 2000 May;31 Suppl 2:S-B37-50.[36]El-Zayat BF, Zettl R, Efe T, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of geriatric and osteoporotic femur fractures with polyaxial locking implants (NCB-DF®). Unfallchirurg. 2012;115(2): 134-144.[37]Kao FC, Tu YK, Su JY, et al. Treatment of distal femoral fracture by minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis: comparison between the dynamic condylar screw and the less invasive stabilization system. J Trauma. 2009;67(4):719-726.[38]Kolb W, Guhlmann H, Windisch C, et al. Fixation of distal femoral fractures with the Less Invasive Stabilization System: a minimally invasive treatment with locked fixed-angle screws. J Trauma. 2008;65(6):1425-1434.[39]Walz M, Auerbach F, Kolbow B, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of monocondylar tibial plateau fractures. Percutaneous reduction and small fragment osteosynthesis. Unfallchirurg. 2006;109(5):367-376. |