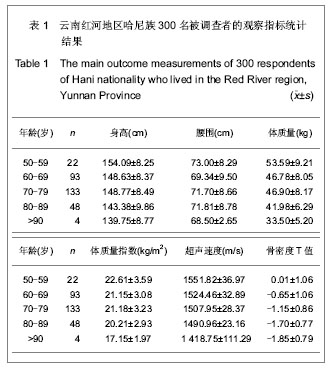
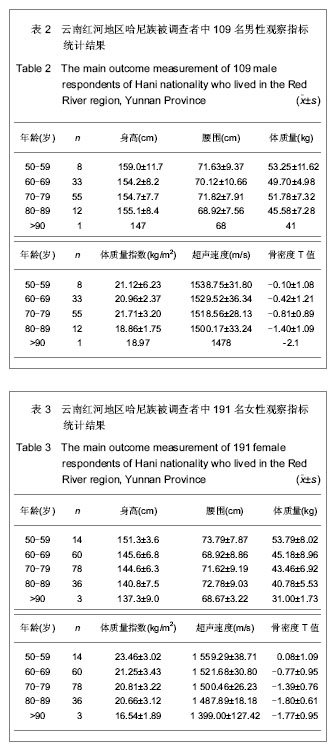
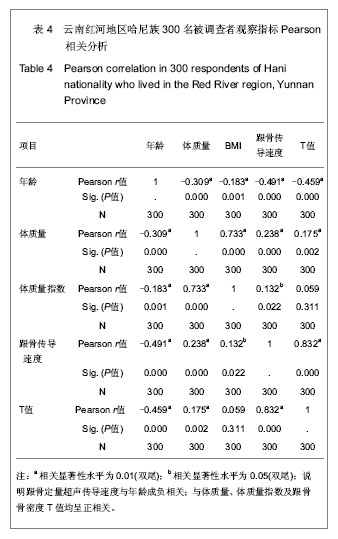
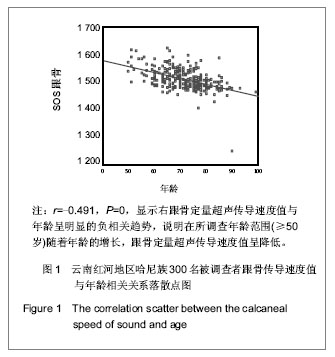
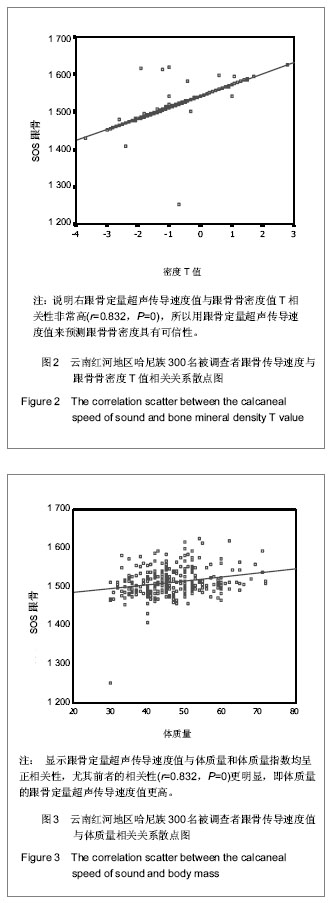
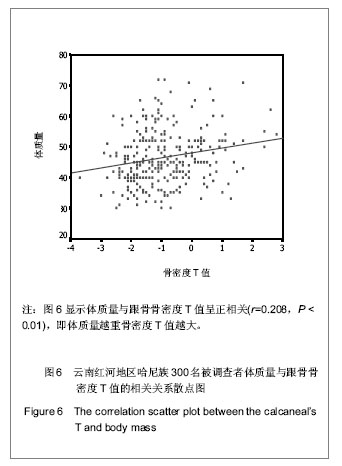
| [1] Rachner TD, Khosla S, Hofbauer LC. Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet.2011;377(9773):1276-1287.[2] Nordin BE,Redefining Osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int.2008; 83(6): 365–367.[3] Tuck SP, Francis RM.Osteoporosis.Postgrad Med J.2002; 78(923):526-532.[4] Megyesi MS, Hunt LM, Brody H. A critical review of racial/ethnic variables in osteoporosis and bone density research. Osteoporos Int.2011;22(6):1669-1679. [5] Guo L. Linchuang Huicui.2010;27(6):474-476.郭丽. 凉山彝族地区中老年人骨密度影响因素调查分析[J].临床荟萃,2010,27(6):474-476.[6] Holick MF,Vitamin D Deficiency. N Engl J Med.2007;357(3): 266-281.[7] Malhotra N,Mithal A.Osteoporosis in Indians. Indian J Med Res. 2008;127(3):263-268.[8] Zhao HB,Yu ZP,Wang JW,et al.Kunming Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2010,31(4):47-49.赵宏斌,俞志鹏,王建伟等.云南红河地区哈尼族髋部骨折流行病学调查[J].昆明医学院学报,2010,31(4):47-49.[9] Miller PD, Siris ES, Barrett-Connor E, et al. Prediction of fracture risk in postmenopausal white women with peripheral bone densitometry:evidence from the National Osteoporsis Risk Assessment. J Bone Miner Res.2002;17(12):2222-2230.[10] Sosa M,Saavedra P, Pino-Montes J,et al.Post- Menopausal women with Colles' fracture have lower values of bone mineral density than controls as measured by quantitative ultrasound and densitometry. J Clin Densitom.2005;8(4):430-435.[11] Su RK,Liu XM.Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi.2003;9(3): 220-221.苏汝堃,刘兴漠.中老年骨折妇女超声骨质测量中参数分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2003,9(3):220-221.[12] Holroyd C,Harvey N,Dennison E. Epigenetic influences in the developmental origins of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2012; 23(2):401-410. [13] Ferrari SL. Osteoporosis:a complex disorder of aging with multiple genetic and environmental determinants. World Rev Nutr Diet.2005;95:35-51.[14] Gao WK,Bai F,Wang W, et al. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi.2011;17(11):941-944.高文魁,白峰,王伟,等.高原低氧环境下骨质疏松大鼠模型的骨代谢生化指标观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2011,17(11):941-944.[15] Adler RA. Osteoporosis in Men:What has Changed ? . Curr Osteoporos Rep.2011;9(1):31-35[16] Patel R, Black GM, Fogelman I. Peripheral and central measurements of bone mineral density are equally strongly associated with clinical risk factors for osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int.2007;80(2):89-96.[17] Rhee EJ,Oh KW,Lee WY,et al. Age,body mass index,current smoking history ,and serum insulin-like growth factor-1 level associated with bone mineral density in middle-aged korean men.J Bone miner Metab.2004;22(4):392-398.[18] Jen KL,Buison A,Darga L,et al. The relationship between blood leptin level and bone density is specific to ethnicity and menopausal status. J Lab Clin Med. 2005;146(1):18-24.[19] Paniagua MA, Malphurs JE, Samos LF. BMI and low bone mass in an elderly male nursing home population. Clin Interv Aging.2006;1(3):283-287.[20] Travison TG, Araujo AB, Esche GR, et al. Lean mass and not fat mass is associated with male proximal femur strength. J Bone Miner Res.2008;23(2):189-198.[21] Zhou SJ,Huang XF,Pu HQ,et al. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2008,14(4):263-265.周善金,黄秀峰,浦洪琴,等.毛南族健康女性身高、体重、足长、体重指数与跟骨BUA的关系[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(4): 263-265.[22] Adami S,Giannini S,Giorgino R,et al.Effect of age,weight and lifestyle factors on calcaneal quantitative ultrasound in premenopausal women;the ESOPO study. Calcif Tissue Int.2004;74(4):317-321.[23] Huang CS,Huang HH,Pu HQ.Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2010;30(14):2045-2046.黄昌盛,黄何华,浦洪琴. 年龄、体重、体重指数对广西京族中老年人骨密度的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(14): 2045-2046.[24] Jorgensen NR;Schwarz P.Effects of Anti-osteoporosis Medications on Fracture Healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep.2011; 9(3):149-155.[25] Fu SF,Liu CX,Shen ZX,et al. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2011; 31(3):1068-1070.付松芳,刘翠鲜,沈志祥,等.运动与老年性骨质疏松[J].中国老年学杂志,2011,31(3):1068-1070.[26] Derman O,Cinemre A,Kanbur N,et al .Effect of swimming on bone metabolism in adolescents. Turk J Pediatr.2008; 50(2): 149-154.[27] Davey RA,Morris HA.Effects of dihydrotestrone on osteoblast gene expression in osteopenic ovariectomized rats.Endocr Res.2004;30(3):361-368.[28] Schuhfried O,Mittermaier C,Jovanovic T,et al. Effects of whole-body vibration in patients with multiple sclerosis:a pilot study.Clin Rehabil.2005;19(8):834-842.[29] Stewart JM,Karman C,Montgomery LD,et al. Plantar vibration improves leg fluid flow in perimenopausal women.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.2005;288(3):R623-R629.[30] Nordstrom A,Hogstrom M,Nordstrom P.Effects of different types of weight-bearing loading on bone mass and size in young males:a longitudinal study.Bone.2008;42(3):565-571.[31] Menkes A,Mazel S,Redmond RA,et al. Strength training increases regional bone mineral density and bone remodeling in middle-aged and older men.J Appl Physiol.1993;74(5): 2478-2484.[32] Simkin A,Ayalon J,Leighter I.Increased trabecular bone density due to bone-loading exercises in postmenopausal osteoporotic women.Calcif Tissue Int.1987;40(2):59-63.[33] Beverly MC,Rider TA,Evans MJ,et al. Local bone mineral response to brief exercise that stresses the skeleton.BMJ 1989;299(6693):233-235.[34] Dalsky GP,Stocke KS,Ehsoni AA,et al. Weight-bearing exercise training and lumbar bone mineral content in postmenopausal women.Ann Intern Med.1988;108(6): 824-828.[35] Witzke KA,Snow CM. Effects of plyometric jump training on bone mass in adolescent girls.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2000; 32(6): 1051-1057.[36] Flieger J,Karachalios T,Khaldi L,et al. Mechanical stimulation in the form of vibration prevents postmenopausal bone loss in ovariectomized rats.Calcif Tissue Int.1998;63(6):510-514.[37] Yang ZY,Di DH,Wang B. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi.2011; 31(1):109-110.杨震宇,狄东华,王波. 紫外线照射与运动对去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠骨密度的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(1):109-110.[38] Wang YJ,Yang FM,Li R,et al. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2012;32(2):727-728.汪元浚,杨发满,李蓉,等.综合营养干预措施对老年原发性骨质疏松患者骨密度的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2012,32(2):727-728. |