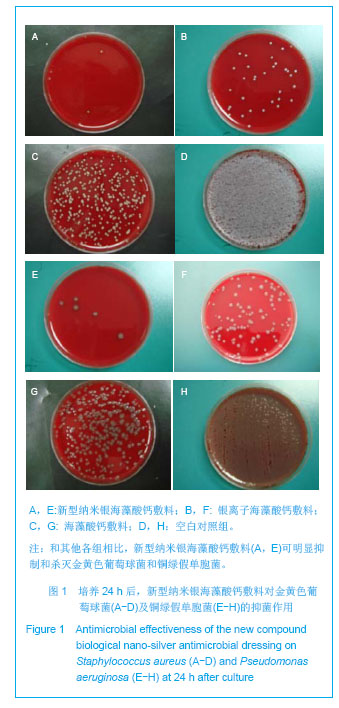
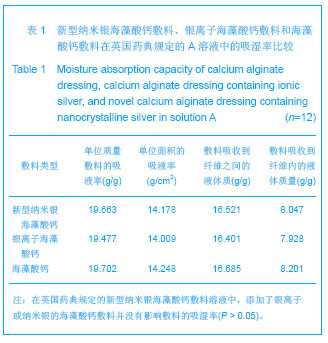
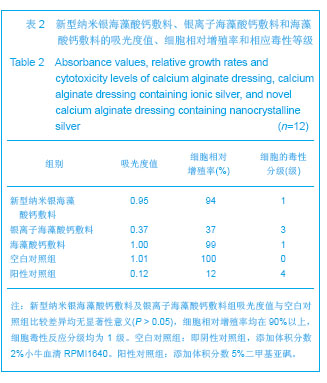
| [1]Kannon GA, Garrett AB. Moist wound healing with occlusive dressings. Dermatol Surg. 1995;21(7):583-590.[2]Chern PL, Baum CL, Arpey CJ. Biologic dressings: current applications and limitations in dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(6):891-906.[3]Lineen E, Namias N. Biologic dressing in burns. J Craniofac Surg. 2008;19(4):923-928.[4]Royal College of Nursing. The Management of Pressure Ulcers in Primary and Secondary Care: a Clinical Practice Guideline. London: Royal College of Nursing, UK. 2005. [5]Kasseroller RG, B enner E. A prospective randomised study of algina te-drenched low stretch bandages as an alternative to conventional lymphologic compression bandaging. Support Care Cancer. 2010;18(3):343-350.[6]Pielesz A, Katarzyna B, Klimczak M. Physico-chemical properties of commercial active alginate dressings. Polim Med. 2008;38(4):3-17.[7]Kumar R, Münstedt H. Silver ion release from antimicrobial polyamide/silver composites. Biomaterials. 2005;26(14): 2081-2088.[8]Balazs DJ, Triandafillu K, Wood P, et al. Inhibition of bacterial adhesion on PVC endotracheal tubes by RF-oxygen glow discharge, sodium hydroxide and silver nitrate treatments. Biomaterials. 2004;25(11):2139-151.[9]Melaiye A, Youngs WJ. Silver and its application as an antimicrobial agent. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2005;15:125-30.[10]Demling RH, DeSanti L. Effects of Silver: on Wound Management. Wounds. 2001;13(1 Suppl A):1-15.[11]Zhang G, Wang H, Wang FL, et al. Zhonghua Zhongxiyixue Zazhi. 2005;3(10):31- 32.张更,王禾,王福利,等.纳米银医用抗菌敷料对包皮环切术后疼痛缓解的疗效观察[J].中华中西医学杂志,2005,3(10):31-32.[12]Stoie N, Duffy B, McCormack DE, et al. Prevention of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation using a low- temperature processed silver-doped phenyltriethoxysilane sol–gel coating. Biomaterials 2008;29:963-969.[13]Hooper SJ, Percival SL, Hill KE. The visualisation and speed of kill of wound isolates on a silver alginate dressing. Int Wound J. 2012;9(6):633-642. [14]Ke LN, Feng XM, Wang CR. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(3):521-524.柯林楠,冯晓明,王春仁.医用敷料研究的现状与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(3):521-524.[15]Woo KY, Coutts PM, Sibbald RG. A randomized controlled trial to evaluate an antimicrobial dressing with silver alginate powder for the management of chronic wounds exhibiting signs of critical colonization. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2012; 25(11):503-508. [16]Qin YM. Fangzhi Xuebao. 2007;28(1):120-123.秦益民.银离子的释放及敷料的抗菌性能[J].纺织学报,2007, 28(1): 120-123.[17]Saarai A, Kasparkova V, Sedlacek T. On the development and characterisation of crosslinked sodium alginate/gelatine hydrogels. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;18:152-166. [18]Lansdown AB. A pharmacological and toxicological profile of silver as an antimicrobial agent in medical devices. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2010;2010:910686.[19]Lipp C, Kirker K, Agostinho A, et al. Testing wound dressings using an in vitro wound model. J Wound Care. 2010;19(6): 220-226.[20]Antimicrobial plastics-Test for antimicrobial activity and efficacy. QB/T 2591-2003. 2003.抗菌塑料抗菌性能试验方法和抗菌效果,QB/T 2591-2003.全国塑料制品标委会[S].2003.[21]Qin YM, Zhu ZJ, Feng DM, et al. Fangzhi Xuebao. 2007;28(3): 45-48.秦益民,朱长俊,冯德明,等.海藻酸钙医用敷料与普通棉纱布的性能比较[J].纺织学报,2007,28(3):45-48.[22]Falanga V. The chronic wound: impaired healing and solutions in the context of wound bed preparation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2004;32(1):88-94.[23]Bowler PG. The 10(5) bacterial growth guideline: reassessing its clinical relevance in wound healing. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2003;49(1):44-53. [24]Lansdown AB. Silver. I: Its antibacterial properties and mechanism of action. J Wound Care. 2002;11(4):125-130.[25]Barnea Y, Weiss J, Gur E. A review of the applications of the hydrofiber dressing with silver (Aquacel Ag®) in wound care. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2010;6:21-27.[26]James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R, et al. Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(1):37-44. [27]Liakos I, Rizzello L, Bayer IS. Controlled antiseptic release by alginate polymer films and beads. Carbohydr Polym. 2013; 92(1):176-183. [28]Nyanhongo GS, Sygmund C, Ludwig R. Synthesis of multifunctional bioresponsive polymers for the management of chronic wounds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013.[29]Kim JY. Understanding the evolution of methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;31(3):17-23.[30]Singh R, Singh D. Chitin membranes containing silver nanoparticles for wound dressing application. Int Wound J. 2012. |