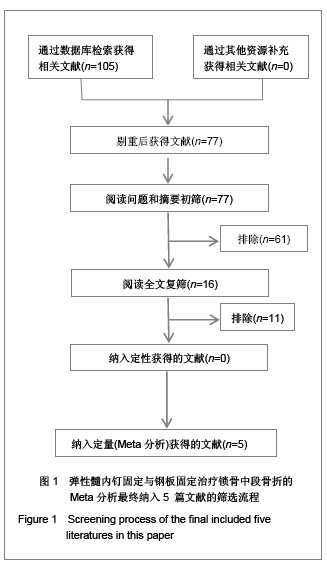
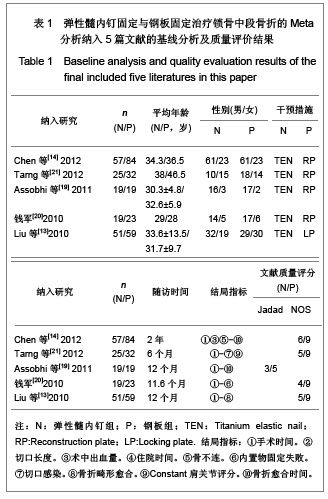
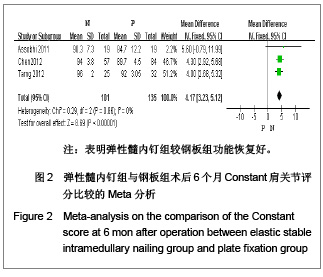
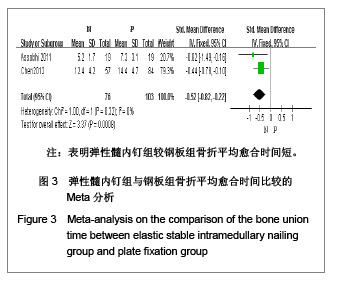
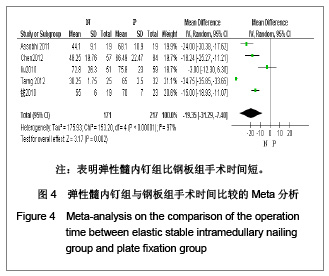
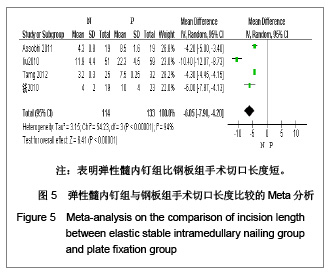
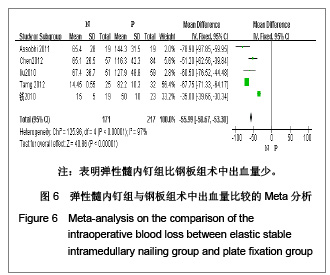
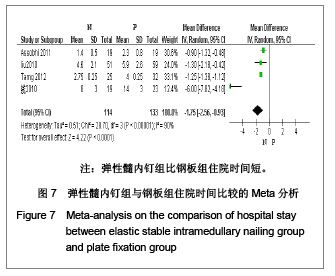
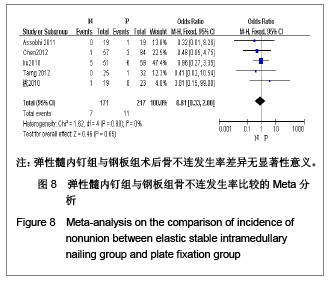
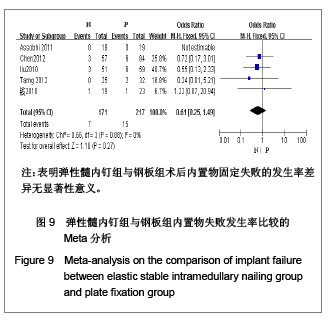
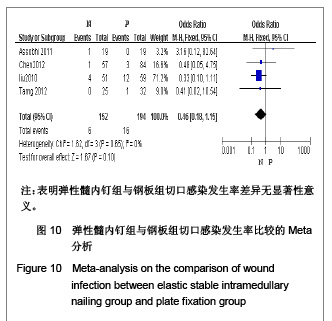
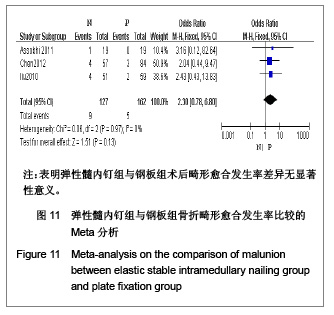
| [1] McKee MD. Clavicle fractures in 2010: sling/swathe or open reduction andinternal fixation? Orthop Clin North Am. 2010; 41(2):225-231.[2] Wijdicks FJ, Van der Meijden OA, Millett PJ, et al. Systematic review of thecomplications of plate fixation of clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(5):617-625.[3] Postacchini F, Gumina S, De Santis P, et al. Epidemiology of clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5): 452-456.[4] Nowak J, Mallmin H, Larsson S. The aetiology and epidemiology of clavicular fractures. A prospective study during a two-year period in Uppsala, Sweden. Injury. 2000; 31(5):353-358.[5] Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM, et al. Estimating the risk of nonunion following nonoperative treatment of a clavicular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(7):1359-1365.[6] Postacchini R, Gumina S, Farsetti P, et al. Long-term results of conservative management of midshaft clavicle fracture. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):731-736.[7] Smekal V, Oberladstaetter J, Struve P, et al. Shaft fractures of the clavicle: current concepts. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(6):807-815.[8] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Struve P, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures-a randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(2):106-112.[9] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Attal RE, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing is best for mid-shaft clavicular fractures without comminution: Results in 60 patients. Injury. 2011; 42(4): 324-329.[10] Bernstein J. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(8):1866-1867.[11] Bostman O, Manninen M,Pihlajamaki H. Complications of plate fixation in fresh displaced midclavicular fractures. J Trauma. 1997;43(5):778-783.[12] Duncan SF, Sperling JW,Steinmann S. Infection after clavicle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;439:74-78.[13] Liu HH, Chang CH, Chia WT, et al. Comparison of plates versus intramedullary nails for fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Trauma. 2010;69(6):E82-87.[14] Chen YF, Wei HF, Zhang C, et al. Retrospective comparison of titanium elastic nail (TEN) and reconstruction plate repair of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(4):495-501.[15] Fernandez FF, Egenolf M, Carsten C, et al. Unstable diaphyseal fractures of both bones of the forearm in children: plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2005;36(10):1210-1216.[16] Mueller M, Rangger C, Striepens N, et al. Minimally invasive intramedullary nailing of midshaft clavicular fractures using titanium elastic nails. J Trauma. 2008;64(6):1528-1534.[17] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12.[18] Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. URL: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp[19] Assobhi JEH. Reconstruction plate versus minimal invasive retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation for displaced midclavicular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4):185- 192.[20] Qian J. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(43):8024-8027. 钱军.钛制弹性髓内钉与重建钢板应用于锁骨中段骨折髓内外固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(43): 8024-8027.[21] Tarng YW, Yang SW, Fang YP, et al. Surgical management of uncomplicated midshaft clavicle fractures: a comparison between titanium elastic nails and small reconstruction plates. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(6):732-740.[22] Keller HW, Huber R,Rehm KE. Intramedullary nailing of fractures during the growth period with a new implant. Chirurg. 1993;64(3):180-184.[23] Niemeier U,Zimmermann HG. Kuntscher's open intramedullary nailing of the clavicle. An alternative in the treatment of an old clavicular fracture. Chirurg. 1990;61(6): 464-466.[24] Jubel A, Andermahr J, Schiffer G, et al.Technique of intramedullary osteosynthesis of the clavicle with elastic titanium nails. Unfallchirurg. 2002;105(6):511-516.[25] Kettler M, Schieker M, Braunstein V, et al. Flexible intramedullary nailing for stabilization of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: Technique and results in 87 patients. Acta Orthopaedica. 2007;78(3):424-429.[26] Jubel A, Andermahr J, Bergmann H, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of midclavicular fractures in athletes. Br J Sports Med. 2003;37(6):480-483.[27] Duan X, Zhong G, Cen S, et al. Plating versus intramedullary pin or conservative treatment for midshaft fracture of clavicle: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6):1008-1015.[28] Houwert RM, Wijdicks FJ, Steins Bisschop C, et al. Plate fixation versus intramedullary fixation for displaced mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2012;36(3): 579-585. |