| [1] Jiang S, Di Y, Chen XL. Yanke Xinjinzhan. 2011;31(7): 609-611. 姜双,底煜,陈晓隆.MMP-2和VEGF在视网膜新生血管的表达[J].眼科新进展,2011,31(7):609-611.[2] Hua CH, Shen SF. Zhongguo Fuyou Baojian. 2011;26(22): 3468-3470. 华彩红,申素芳.羊膜对大鼠皮肤切创愈合中TGF-β表达的影响[J].中国妇幼保健,2011,26(22):3468-3470.[3] White P, David WT, Steven F, et al. Deletion of the homeobox gene prx-2 af-fects fetal but not adult fibroblast wound healing responses. Invest Dermatol. 2003;120(1):135-144.[4] Huang CX, Shen ZY. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2002;16(1):64-69. 黄晨显,沈祖尧.血管内皮细胞生长因子的研究及在组织修复中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(1):64-69.[5] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [6] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.[7] Guo EQ. Beijing: People's Military Medical Press. 2000. 郭恩覃.现代整形外科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2000.[8] Zhao WH, Huang TY, Li XJ, et al. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi. 2002;10(5):46. 赵文海,黄铁银,李新建,等.新鲜羊膜移植治疗创伤性足部严重皮肤缺损[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2002,10(5):46.[9] Zhu HB, Zhang L, Wnag ZH, et al. Therapeutic effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats and its primary mechanisms. Asian Nat Prod Res. 2005; 7(4):603-613.[10] Ren Y, Wang J. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2008; 26(suppl 44):150-151. 任媛,王军.羊膜在组织工程皮肤的研究进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2008,26(Suppl 4):150-151.[11] Xiong H, Zuo YJ, Luo ZY, et al. Zhongyi Zhenggu. 2004;16(4): 8-10. 熊辉,左亚杰,罗志勇,等.桃红四物汤对实验性骨折愈合过程中VGEFmNRA表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2004,16(4):8-10.[12] Shen FJ, Liu RG, Yang SH, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2004; 17(5):260-262. 沈冯君,刘日光,杨述华,等.活血补肾中药对培养成骨细胞VEGF活性的影响[J].中国骨伤,2004,17(5):260-262.[13] Yang L, Zhang ZY, Li YP, et al. Heibei Zhongyiyao Xuebao. 2004;19(3):26-29. 杨蕾,张志云,李云鹏,等.红花提取物对自发性高血压大鼠血压影响的实验研究[J].河北中医药学报,2004,19(3):26-29.[14] Pei YN. Shizhen Guoyiguoyao. 2005;16(2):144-146. 裴永娜.红花的药理作用和临床应用[J].时珍国医国药,2005, 16(2):144-146.[15] Sun JB, Jiang XD, Zhang PX, et al. 2004;24(7):650-651. 孙佳彬,江旭东,张鹏霞,等.红花总黄素对衰老模型小鼠肝线粒体的保护作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2004,24(7):650-651.[16] Zhao Q, Du JS, Han XM, et al. Zhongguo Shiyan Zhenduanxue. 2004;8(1):21-23. 赵晴,杜建时,韩雪梅,等.大鼠急性全脑缺血再灌注损伤后细胞凋亡及红花保护作用的研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2004,8(1):21-23.[17] Xia P, Dong WX, Yu YM, et al. Chongqing Yikedaxue Xuebao. 2010;35(8):1167-1170. 夏鹏,童文祥,喻永敏,等.大鼠皮肤切创愈合过程中VEGF, TGF-β1蛋白的表达[J].重庆医科大学报,2010,35(8):1167-1170.[18] Tang R, Du SH. Zhongguo Linchuang Yaolixue yu Zhiliaoxue. 2006;11(3):282-285. 唐蓉,杜胜华.红花对大鼠肾间质纤维化和肾功能的影响[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2006,11(3):282-285.[19] He YL, Dai W, Sun M, et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Baojian Zazhi. 2004;7(3):169-172. 何来英,戴伟,孙明,等.红花水提取物的安全性研究[J].中国临床保健杂志,2004,7(3):169-172.[20] Liu YL, Song XR. Zhongguo Zhongliu Shengwu Zhiliao Zazhi. 2004;11(3):229-232. 柳永蕾,宋现让.乏氧诱导因子-1与肿瘤乏氧的研究进展[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2004,11(3):229-232.[21] Liu PY, Liu K, Wang XT, et al. Efficacy of combination gene therapy with multicple growth factor cDNAs to enhance skin flap survival in a rat model. DNA Cell Biol. 2005;24(11):751.[22] Yu GY, Gao SZ, Zhang TT, et al. Renmin Junyi. 2008;51(2): 79-80. 于广远,高素珍,赵婷婷,等.人胎羊膜对糖尿病难愈性创面愈合影响的应用研究[J].人民军医, 2008,51(2):79-80.[23] Zhang P, Ji L, Li JP, et al. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2010;20(11):1665-1668. 张鹏,纪亮,李静平,等.MMP-1和TIMP-1在人增生性瘢痕中的动态变化[J].中国现代医学杂志,2010,20(11):1665-1668. |
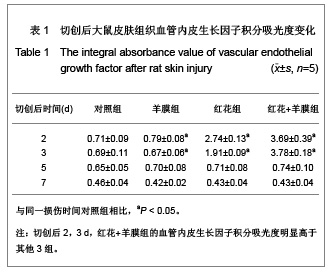

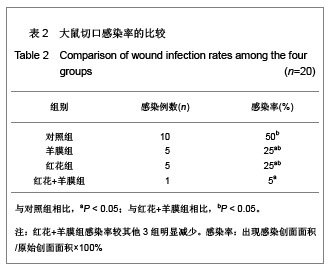

.jpg)


