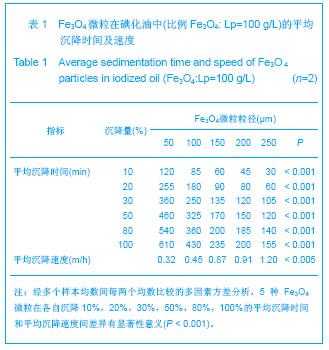
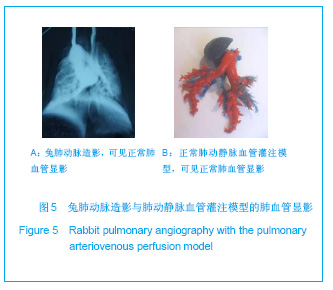
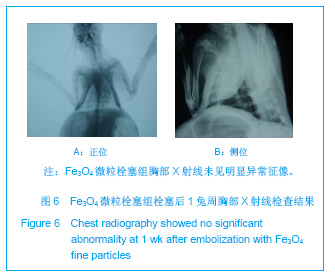
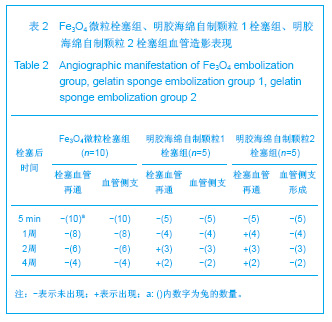
| [1] Bilbao JI, Martínez-Cuesta A, Urtasun F. Complications of embolization. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2006;23(2):126-142. [2] Walsh KP. Advanced embolization techniques. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005;26(3):275-288.[3] Al-Shahi R, Warlow C. Arteriovenous malformations of the brain: ready to randomisel. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(10):1327-1329[4] White RI Jr. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: how do I embolize? Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;10(4):283-290. [5] Kjeldsen AD, Andersen PE, Oxhøj H, et al. Percutaneous transluminal embolization of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Ugeskr Laeger. 1998;160(10):1465-1469.[6] Vaidya S, Kathleen R. An overview of embolic agents. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2008;25(3):204-215. [7] Becker TA, Preul MC, Bichard WD, et al. Calcium alginate gel as a biocompatible material for endovascular arteriovenous malformation embolization: six-month results in an animal model. Neurosurgery. 2005;56:793-801. [8] Becker TA, Preul MC, Bichard WD, et al. Preliminary investigation of calcium alginate gel as a biocompatible material for endovascular aneurysm embolization in vivo. Neurosurgery. 2007;60:1119-1128. [9] Vanninen R L, Manninen I. Onyx, a new liquid embolic material for peripheral interventions: preliminary experience in aneurysm, pseudoaneurysm, and pulmonary arteriovenous malformation embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007; 30(2):196-200. [10] Raffi L, Simonetti L, Cenni P, et al. Use of Glubran 2 acrylic glue in interventional neuroradiology. Neuroradiology. 2007; 49:829-836. [11] Pollak JS, White RI. The use of cyanoacrylate adhesives in peripheral embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12: 907-913. [12] Osuga K, Mikami K, Higashihara H, et al. Principles and techniques of transcatheter embolotherapy for peripheral vascular lesions. Radiat Med. 2006;24(4):309-314. [13] Spies J B, Cornell C, Worthington-Kirsch R, et al. Long-term outcome from uterine fibroid embolization with tris-acryl gelatin microspheres: results of a multicenter study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18(2):203-207. [14] Becker TA, Kipke DR, Brandon T. Calcium alginate gel: a biocompatible and mechanically stable polymer for endovascular embolization. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001; 54(1):76-86. [15] López-Benítez R, Richter GM, Kauczor HU, et al. Analysis of nontarget embolization mechanisms during embolization and chemoembolization procedures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32(4):615-622. [16] Hidaka K, Nakamura M, Osuga K, et al. Elastic characteristics of microspherical embolic agents used for vascular interventional radiology. 2010;3(7):497-503.[17] Hidaka K, Moine L, Collin G, et al. Elasticity and viscoelasticity of embolization microspheres. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(8):2161-2167.[18] Yoon W. Embolic agents used for bronchial artery embolisation in massive haemoptysis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004;5(2):361-367.[19] Loffroy R, Guiu B, Cercueil JP, et al. Endovascular therapeutic embolisation: an overview of occluding agents and their effects on embolised tissues. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009;7(2):250-263.[20] Lewis AL, Adams C, Busby W etal.Comparative in vitro evaluation of microspherical embolisation agents. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(12):1193-1204.[21] Stampfl S, Bellemann N, Stampfl U, et al. Arterial distribution characteristics of Embozene particles and comparison with other spherical embolic agents in the porcine acute embolization model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009;20(12): 1597-607. [22] Stampfl S, Bellemann N, Stampfl U, et al. Inflammation and recanalization of four different spherical embolization agents in the porcine kidney model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008;19(4): 577-586. [23] Bilbao JI, de Luis E, García de Jalón JA, et al. Comparative study of four different spherical embolic particles in an animal model: a morphologic and histologic evaluation. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008;19(11):1625-1638. [24] Abada HT, Golzarian J. Gelatine sponge particles: handling characteristics for endovascular use. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;10(4):257-260. [25] White RI Jr, Pollak JS, Wirth JA. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: diagnosis and transcatheter embolotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1996;7(6):787-804.[26] Gulati MS, Srinivasan A, Paul SB, et al. Uterine restoration following fibroid expulsion after uterine artery embolisation using gelfoam. J Postgrad Med. 2004;50(1):80.[27] Katsumori T, Kasahara T, Akazawa K. Long-term outcomes of uterine artery embolization using gelatin sponge particles alone for symptomatic fibroids. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 186(3):848-854.[28] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. |

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)