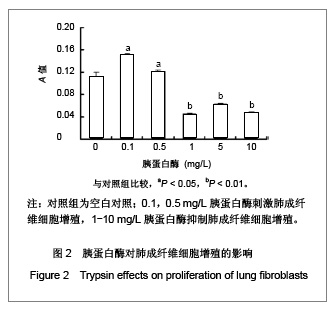
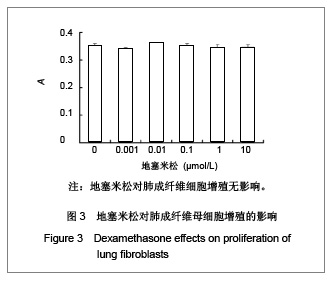
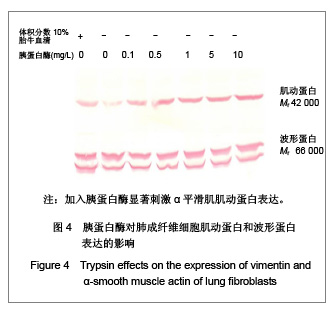
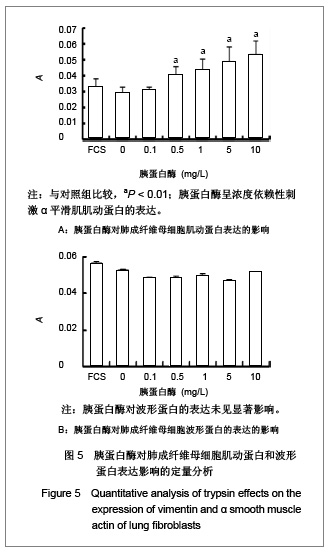
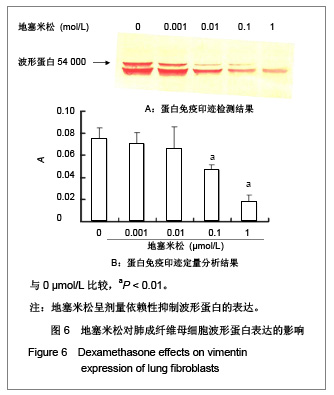
| [1] Fang Q, Liu X, Abe S, et al.Thrombin induces collagen gel contraction partially through PAR1 activation and PKC-epsilon. Eur Respir J. 2004; 24(6): 918-924. [2] Fang QH,Ma YM,Liu XD,et al.Zhongguo Shiyong Neike Zazhi. 2008;28(4):264-266. 方秋红,马迎民,刘相德,等.蛋白激酶C-ε对人胚肺成纤维细胞趋化运动调节的研究[J].中国实用内科杂志,2008,28(4):264-266.[3] Fehervari Z. Lung fibroblasts call the shots. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:816.[4] Weibel ER, Crystal RG. Structural organization of the pulmonary interstitium//Crystal RG, West JB, eds. The Lung: Scientific Foundations. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven.1997: 685–695.[5] Saetta M, Turato G, Maestrelli P, et al. Cellular and structural bases of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1304-1309.[6] Mackie EJ, Pagel CN, Smith R. et al. Protease-activated receptors: a means of converting extracellular proteolysis into intracellular signals. IUBMU Life. 2002;53(6): 277-281.[7] Strukova SM. Thrombin as a regulator of inflammation and reparative processes in tissues. Biochemistry (Mosc).2001; 66: 8-18.[8] Wang J,Li JH,Zhang J,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;28(14):5172-5176. 王晶,李继红,张捷,等.三维立体培养人胚肺成纤维母细胞前列腺素E2释放过程中蛋白酶激活受体的调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010;28(14):5172-5176.[9] Skold CM, Liu X, Zhu YK, et al. Glucocorticoids augment fibroblast mediated contraction of collagen gels by inhibition of endogenous PGE production. Proc Assn Am Phys 1999; 111: 249-258.[10] Miller M, Cho JY, McElwain K, McElwain S, et al. Corticosteroids prevent myofibroblast accumulation and airway remodeling in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2006;290:L162-169.[11] Tomic R, Lassiter CC, Ritzenthaler JD, et al. Anti-tissue remodeling effects of corticosteroids: fluticasone propionate inhibits fibronectin expression in fibroblasts. Chest.2005; 127: 257-265.[12] Fang Q , Liu X , Rennard SI. Protease-activated receptors modulating contraction of collagen gels mediated by fibroblast. Am J Respir and Crit Care Med.2002; April: 165(8): A360.[13] Fang Q, Liu X, Abe S, et al. Thrombin induces collagen gel contraction partially through PAR1 activation and PKC-epsilon. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:918-924. [14] Wang YY,Sui CX,Fang QH.Xibao Shengwuxue Zazhi. 2007;29(2):296-298. 王尧尧,税朝祥,方秋红.Western印迹中蛋白质定量分析的替代方法[J].细胞生物学杂志,2007,29(2):296-298.[15] Brewster CE, Howarth PH, Djukanovic R,et al. Myofibroblasts and subepithelial fibrosis in bronchial asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.1990; 3: 507-511.[16] Bogatkevich GS, Tourkina E, Silver RM, et al.Thrombin differentiates normal lung fibroblasts to a myofibroblast phenotype via the proteolytically activated receptor-1 and a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem.2001;276: 45184-45192. |