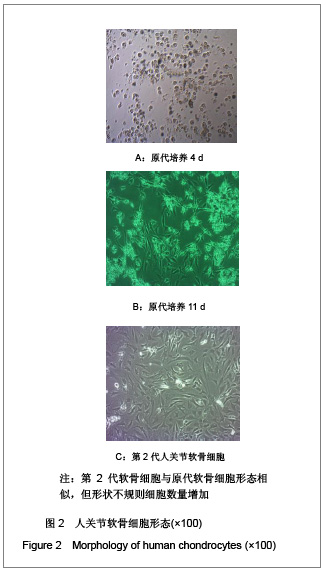
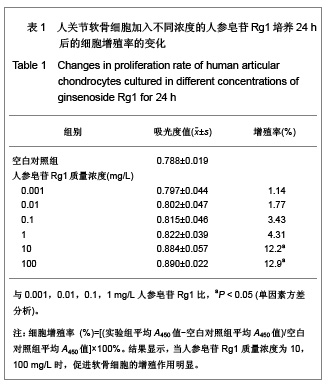
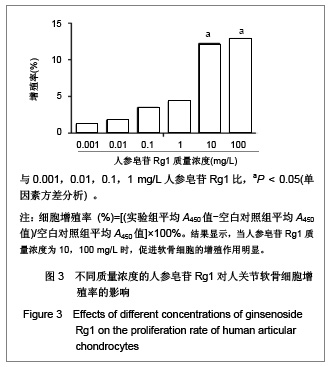
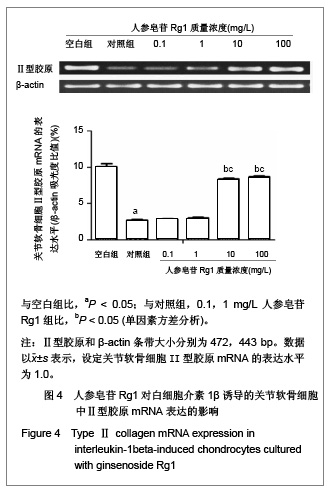
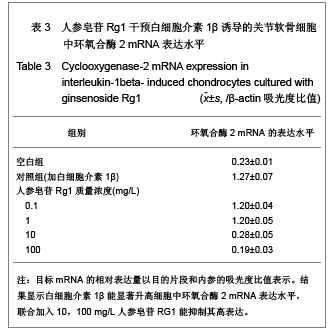
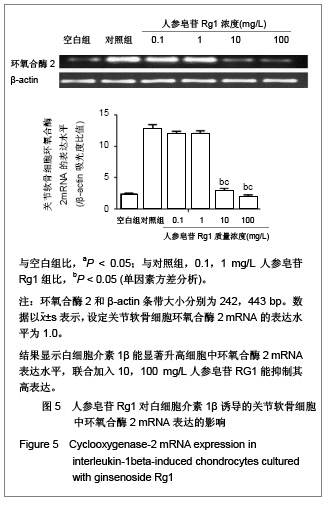
| [1] Malemud CJ, Islam N, Haqqi TM. Pathophysiological mechanisms in osteoarthritis lead to novel therapeutic strategies. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(1-2):34-48.[2] Blom AB, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB. Cytokine targeting in osteoarthritis. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8(2): 283-292.[3] Shakibaei M, John T, Schulze-Tanzil G, et al. Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by curcumin leads to inhibition of expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human articular chondrocytes: Implications for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;73(9):1434-1445. [4] Xia L, Chen Q, Cheng GL. Effects of ginseng total saponin on traumatic brain edema of rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012;32(12):1671-1674. [5] Ginseng helps cancer-related fatigue. Mayo Clin Health Lett. 2012;30(12):4. [6] Al-Hazmi MA, Rawi SM, Arafa NM, et al. The potent effects of ginseng root extract and memantine on cognitive dysfunction in male albino rats. Toxicol Ind Health. 2013, in press. [7] Avsar U, Karakus E, Halici Z, et al. Prevention of bone loss by panax ginseng in a rat model of inflammation-induced bone loss. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2013;59 Suppl:OL1835- 1841. [8] Mucalo I, Raheli? D, Jovanovski E, et al. Effect of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Coll Antropol. 2012;36(4):1435-1440. [9] Kim SD, Kim YJ, Huh JS, et al. Improvement of erectile function by Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) in a male rat model of metabolic syndrome. Asian J Androl. 2013, in press. [10] Hong SH, Suk KT, Choi SH, et al. Anti-oxidant and natural killer cell activity of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) and urushiol (Rhus vernicifera Stokes) on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease of rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013, in press. [11] Lee CS, Lee JH, Oh M, et al. Preventive effect of Korean red ginseng for acute respiratory illness: a randomized and double-blind clinical trial. J Korean Med Sci. 2012;27(12): 1472-1478. [12] Cheon SY, Cho KJ, Lee JE, et al. Cerebroprotective effects of red ginseng extract pretreatment against ischemia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Int J Neurosci. 2013, in press. [13] Lei Y, Tao LL, Wang GL. Effect of extracts from Panax ginseng, Panax notoginseng, and ligusticum chuanxiong on vascular smooth muscle cells of aging and hypertension rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012;32(10):1374-1379. [14] Ramesh T, Kim SW, Hwang SY, et al. Panax ginseng reduces oxidative stress and restores antioxidant capacity in aged rats. Nutr Res. 2012;32(9):718-726. [15] Jiao L, Wan D, Zhang X, et al. Characterization and immunostimulating effects on murine peritoneal macrophages of oligosaccharide isolated from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;144(3):490-496.[16] Shi AW, Wang XB, Lu FX, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes endothelial progenitor cell migration and proliferation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009;30(3):299-306. [17] Zhou Y, Yang B, Jiang R, et al. Mechanism of ginsenoside Rg1 in the delayed senescence of hematopoietic stem cell. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010;90(48):3421-3425.[18] Wang NY, Lu CJ, Chen XH. Study on effect of ginsenoside Rg1 in promoting myocardiac vascular endothelial cell regeneration through induction on bone marrow stem cell's migration and differentiation in rabbits of myocardial infarction. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2005;25(10):916-919.[19] Fang F, Chen X, Huang T, et al. Multi-faced neuroprotective effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 in an Alzheimer mouse model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(2):286-292.[20] Du J, Cheng B, Zhu X, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1, a novel glucocorticoid receptor agonist of plant origin, maintains glucocorticoid efficacy with reduced side effects. J Immunol. 2011;187(2):942-950.[21] Lv ZC, Guo YX, Cao XY, et al. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2010(1):32-34. 吕振超,郭艳幸,曹向阳,等.人参皂苷Rgl、Rbl对体外培养膝软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2010(1):32-34.[22] Kim HA, Kim S, Chang SH, et al. Anti-arthritic effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on collagen induced arthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007;7(10):1286-1291. [23] Cheng AW, Stabler TV, Bolognesi M, et al. Selenomethionine inhibits IL-1β inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) expression in primary human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(1):118-125. [24] Chen XY, Hao YR, Wang Z, et al. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on aggrecan and type Ⅱ collagen expression in rat articular chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32(11):3359-3364. [25] Goldring MB. Anticytokine therapy for osteoarthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2001;1(5):817-829.[26] Blom AB, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB. Cytokine targeting in osteoarthritis. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8(2): 283-292.[27] Lotz M. Cytokines in cartilage injury and repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(391 Suppl):S108-115.[28] Alvarez-Soria MA, Largo R, Santillana J, et al. Long term NSAID treatment inhibits COX-2 synthesis in the knee synovial membrane of patients with osteoarthritis: differential proinflammatory cytokine profile between celecoxib and aceclofenac. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(8):998-1005.[29] Giannoni P, Cancedda R. Articular chondrocyte culturing for cell-based cartilage repair: needs and perspectives. Cells Tissues Organs. 2006;184(1):1-15. |