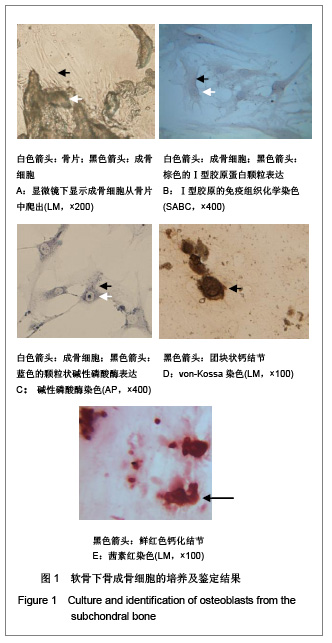
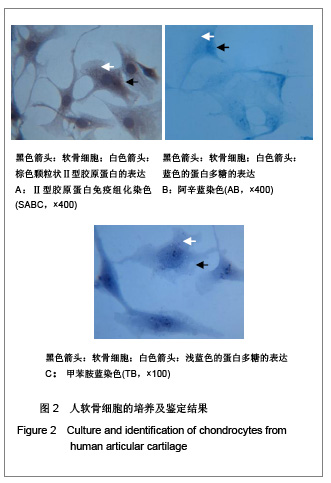
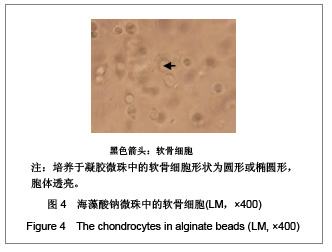
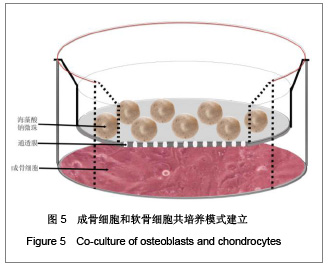
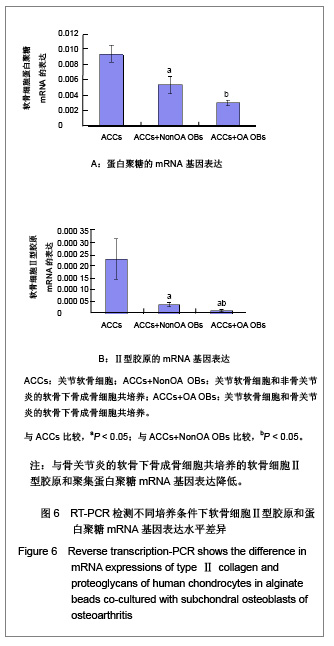
| [1] Madry H, Grün UW, Knutsen G. Cartilage repair and joint preservation: medical and surgical treatment options. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011;108(40):669-677.[2] Jiang YZ, Zhang SF, Qi YY, et al. Cell transplantation for articular cartilage defects: principles of past, present, and future practice. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(5):593-607.[3] Trewenack AJ, Please CP, Landman KA. A continuum model for the development of tissue-engineered cartilage around a chondrocyte. Math Med Biol. 2009;26(3):241-262.[4] Neogi T.Clinical significance of bone changes in osteoarthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4): 259-267.[5] Mansfield JC, Winlove CP. A multi-modal multiphoton investigation of microstructure in the deep zone and calcified cartilage. J Anat. 2012;220(4):405-416.[6] Henrotin Y, Pesesse L, Sanchez C.Subchondral bone and osteoarthritis: biological and cellular aspects. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23 Suppl 8:847-851.[7] Zhang LZ, Zheng HA, Jiang Y,et al. Mechanical and biologic link between cartilage and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(7):960-967.[8] Quasnichka HL, Anderson-MacKenzie JM, Bailey AJ. Subchondral bone and ligament changes precede cartilage degradation in guinea pig osteoarthritis. Biorheology. 2006; 43(3-4):389-397.[9] Anderson-MacKenzie JM, Quasnichka HL, Starr RL,et al. Fundamental subchondral bone changes in spontaneous knee osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(1): 224-236.[10] Mahjoub M, Berenbaum F, Houard X.Why subchondral bone in osteoarthritis? The importance of the cartilage bone interface in osteoarthritis.Osteoporos Int. 2012;23 Suppl 8: 841-846.[11] Kwan Tat S, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JP,et al.Targeting subchondral bone for treating osteoarthritis: what is the evidence. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24(1):51-70.[12] Castañeda S, Roman-Blas JA, Largo R,et al. Subchondral bone as a key target for osteoarthritis treatment.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83(3):315-323.[13] Zhang LZ, Mei J, Qian ZK,et al.The role of VE-cadherin in osteosarcoma cells. Pathol Oncol Res. 2010;16(1):111-117.[14] Lin J, Fransen M, Kang X,et al. Marked disability and high use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs associated with knee osteoarthritis in rural China: a cross-sectional population-based survey. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6): R225.[15] Goldring MB. Chondrogenesis, chondrocyte differentiation, and articular cartilage metabolism in health and osteoarthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4): 269-285.[16] Henrotin Y, Pesesse L, Sanchez C.Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis physiopathology: state-of-the art and perspectives. Biomed Mater Eng. 2009;19(4-5):311-316. [17] Goldring SR. Alterations in periarticular bone and cross talk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4): 249-258.[18] Cox LG, van Donkelaar CC, van Rietbergen B,et al. Decreased bone tissue mineralization can partly explain subchondral sclerosis observed in osteoarthritis. Bone. 2012; 50(5):1152-1161.[19] Lories RJ, Luyten FP.The bone-cartilage unit in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):43-49.[20] Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:230-237.[21] Cox LG, van Rietbergen B, van Donkelaar CC,et al. Bone structural changes in osteoarthritis as a result of mechanoregulated bone adaptation: a modeling approach.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(6):676-682.[22] Mastbergen SC, Lafeber FP. Changes in subchondral bone early in the development of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(9):2561-2563.[23] Funck-Brentano T, Lin H, Hay E,et al. Targeting bone alleviates osteoarthritis in osteopenic mice and modulates cartilage catabolism. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33543.[24] Sanchez C, Deberg MA, Bellahcène A,et al. Phenotypic characterization of osteoblasts from the sclerotic zones of osteoarthritic subchondral bone. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58(2): 442-455.[25] Heiligenstein S, Cucchiarini M, Laschke MW,et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of non-biomedical and biomedical grade alginates for articular chondrocyte transplantation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011. [Epub ahead of print]. [26] Cohen J, Zaleski KL, Nourissat G,et al. Survival of porcine mesenchymal stem cells over the alginate recovered cellular method. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;96(1):93-99.[27] Heiligenstein S, Cucchiarini M, Laschke MW,et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of nonbiomedical- and biomedical-grade alginates for articular chondrocyte transplantation.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(8): 829-842.[28] Domm C, Schünke M, Steinhagen J,et al. Influence of various alginate brands on the redifferentiation of dedifferentiated bovine articular chondrocytes in alginate bead culture under high and low oxygen tension.Tissue Eng. 2004;10(11-12): 1796-1805.[29] Baghaban Eslaminejad M, Taghiyar L, Falahi F.Q uantitative analysis of the proliferation and differentiation of rat articular chondrocytes in alginate 3D culture. Iran Biomed J. 2009; 13(3):153-160.[30] Hoemann CD, Lafantaisie-Favreau CH, Lascau-Coman V,et al. The cartilage-bone interface.J Knee Surg. 2012;25(2): 85-97.[31] Suri S, Walsh DA. Osteochondral alterations in osteoarthritis. Bone. 2012;51(2):204-211.[32] Burr DB, Radin EL. Microfractures and microcracks in subchondral bone: are they relevant to osteoarthrosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2003;29(4):675-685.[33] Pesesse L, Sanchez C, Henrotin Y. Osteochondral plate angiogenesis: a new treatment target in osteoarthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2011;78(2):144-149.[34] Massicotte F, Fernandes JC, Martel-Pelletier J,et al. Modulation of insulin-like growth factor 1 levels in human osteoarthritic subchondral bone osteoblasts. Bone. 2006; 38(3):333-341.[35] Hulejová H, Baresová V, Klézl Z,et al. Increased level of cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritic subchondral bone. Cytokine. 2007;38(3):151-156.[36] Sakao K, Takahashi KA, Mazda O,et al. Enhanced expression of interleukin-6, matrix metalloproteinase-13, and receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand in cells derived from osteoarthritic subchondral bone. J Orthop Sci. 2008;13(3): 202-210.[37] Prasadam I, van Gennip S, Friis T,et al. ERK-1/2 and p38 in the regulation of hypertrophic changes of normal articular cartilage chondrocytes induced by osteoarthritic subchondral osteoblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(5):1349-1360.[38] Lin YY, Tanaka N, Ohkuma S,et al. Applying an excessive mechanical stress alters the effect of subchondral osteoblasts on chondrocytes in a co-culture system. Eur J Oral Sci. 2010; 118(2):151-158.[39] Madry H, van Dijk CN, Mueller-Gerbl M.The basic science of the subchondral bone.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(4):419-433.[40] Bugbee W, Cavallo M, Giannini S.Osteochondral allograft transplantation in the knee.J Knee Surg. 2012;25(2):109-116.[41] Goldring SR, Goldring MB.Bone and cartilage in osteoarthritis: is what's best for one good or bad for the other. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):143. |