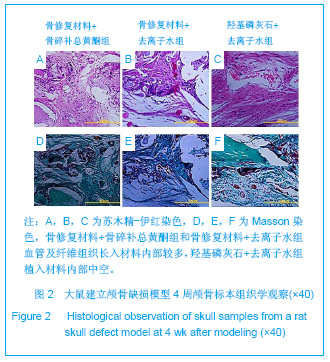
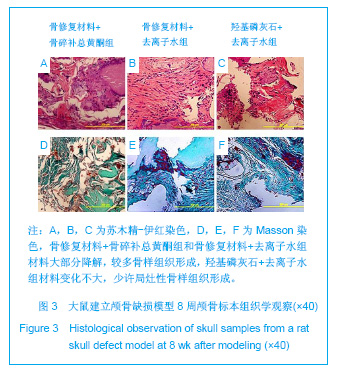
| [1] Yu X, Xu L, Bi LY, et al.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2005;13(8): 586-588. 俞兴,徐林,毕连涌,等.腰椎后外侧融合应用纳米晶胶原基骨材料初步效果分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(8):586-588.[2] Rose FR,Oreffo RO.Bone tissue engineering:hope vs hype.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2002;292(1):1-7.[3] LeGeros RZ.Properties of osteoconductive biomaterials: calcium phosphates.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2002;(395):81-98.[4] Nishida J,Shimamura T. Methods of reconstruction for bone defect after tumor excision: a review of alternatives.Med Sci Monit.2008;14(8):107-113.[5] Nandi SK,Kundu B,Ghosh SK,et al.Efficacy of nano-hydroxyapatite prepared by anaqueous solution combustion technique in healing bone defects of goat.J Vet Sci.2008;9(2):183-191.[6] PetiteH,Viateau V,Bensaïd W,et al.Tissue-engineered bone Regeneration.Nat Biotechnol.2000;18(9):959-963.[7] Yu X, Xu L,Cui FZ.Shengwu Guke Cailiao yu Linchuang Yanjiu. 2003;1(1):14-16. 俞兴,徐林,崔福斋.纳米晶胶原基骨材料在颈椎前路中的临床应用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2003,1(1):14-16.[8] Cynthia MK,Ross MW.Treatment of benign bone lesions with an injectable calcium sulfate-based bone graft substitute. Orthopedics.2004;27(1):131-135.[9] Wei G,Ma PX.Structure and properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/polymer composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2004;25 (19):4749-4757.[10] Feng QL,Cui FZ,Zhang W.Zhongguo Yixue Kexueyuan Xuebao.2002;24(2):124-128. 冯庆玲,崔福斋,张伟.纳米羟基磷灰石胶原骨修复材料[J].中国医学科学院学报,2002,24(2):124-128.[11] Li DP,Shen TC,Huang YH.In vitro co-culture of nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen and mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(25):4973-4976.[12] Shen TC,Xia Q,Huang YH,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Zazhishe. 2007;11(1):48-51. 沈铁城,夏青,黄永辉,等.纳米晶胶原基骨材料在骨科疾病中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(1):48-51.[13] LIU Jiangang,XIE Yanming,et al.Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi.2006;12(1):46-49. 刘剑刚,刘剑刚,谢雁鸣,等.骨碎补总黄酮的活血化瘀作用及对实验性微循环障碍和骨质疏松症的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2006,12(1):46-49.[14] Xu ZW,Zhang JX,Tan GQ,et al.Zhongyi Zhenggu.2006;18(16): 15-16. 徐展望,张建新,谭国庆,等.中药骨碎补总黄酮血清对兔骨髓基质细胞体外成骨分化的影响[J].中医正骨,2006,18(16):15-16.[15] Jeonq JC,Lee JW,Yoon CH,et al.Stimulative effects of Drynariae Rhizoma extracts on the proliferation an differentiation of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;96(3):489-495.[16] Liu HC,Chen RM,Jian WC,et al.Cytotoxic and antioxidant effects of the water extract of the traditional Chinese herb gusuibu(Drynaria fortunei)on rat osteoblasts.J Formos Med Assoc.2001;100(6):383-388.[17] Wong RW,Rabie AB.Systemic effect of crude extract from rhizome of Drynaria fortunei on bone formation in mice. Phytother Res.2006;20(4):313-315.[18] Wong RW,Rabie B,Bendeus M,et al.The effects of Rhizoma Curculiginis and Rhizoma Drynariae extracts on bones.Chin Med.Chin Med.2007;19(2):13.[19] Jeonq JC,Lee JW,Yoon CH,et al.Drynariae Rhizoma promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in MC3T3-E1 cells through regulation of bone morphogenetic protein-2,alkaline phosphatase,typeⅠcollagen and collagenase-1.ToxicolIn Vitio.2004;18(6):829-834.[20] Wang SH.Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi.2001;9(4): 10-11. 王华松.骨碎补对骨折愈合中TGF-1表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2001,9(4):10-11.[21] Jeonq JC,Lee JW,Yoon CH,et al.Stimulative effects of Drynariae Rhizoma extracts on the proliferation and differetiation of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells.J Ethnophar-macol. 2005;96(3):489-495.[22] Jin H, Li JY, Yu X, Xu L, et al.Zhongguo Gushang.2012;25(9): 757-760. 金合,李晋玉,俞兴,等.骨碎补总黄酮对颅骨缺损修复大鼠血清碱性磷酸酶、钙、磷的影响[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(9):757-760.[23] Suh SJ,Yun WS,Kim KS,et al.Stimulative effects of Ulmus davidiana Planch (Ulmaceae) on osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells.J Ethnopharmacol.2007;109(3):480-485.[24] Jin He,Li JY,Yu Xing,Xu Lin.Shengwu Guke Cailiao yu Linchuang Yanjiu.2012;9(1):26-29. 金合,李晋玉,俞兴,徐林.可注射骨修复材料结合骨碎补总黄酮修复极量颅骨缺损的实验研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012, 9(1):26-29. |