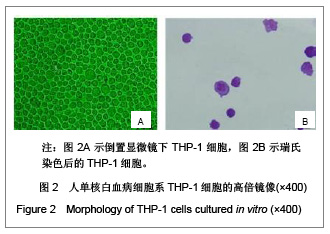
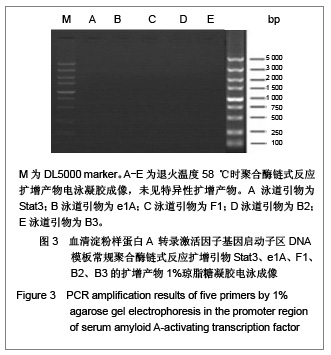
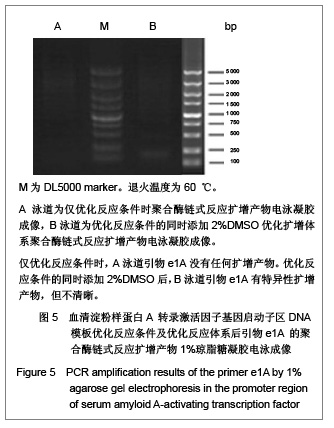
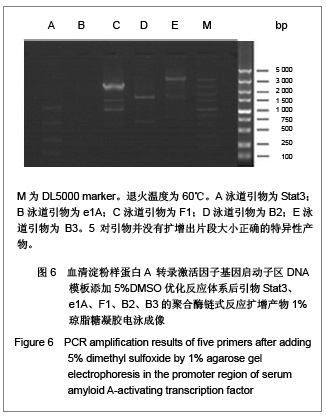
| [1] Ray BK, Murphy R, Ray P, et al. SAF-2, a splice variant of SAF-1,acts as a negative regulation of transcription. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(48):46822-46830.[2] Ray A, Dhar S, Shakya A, et al. SAF-3, a novel splice variant of the SAF-1/MAZ/Pur-1 family, is expressed during inflammation. FEBS J. 2009;276(15):4276-4286. [3] Ray A, Shakya A, Kumar D, et al. Inflammation-responsive transcription factor SAF-1 activity is linked to the development of amyloid A amyloidosis. J Immunol. 2006; 177(4):2601-2609.[4] Song J, Ugai H, Nakata-Tsutsui H, et al. Transcriptional regulation by zinc-finger proteins Sp1 and MAZ involves interactions with the same cis-elements. Int J Mol Med. 2003;11(5):547-553.[5] Auwerx J. The human leukemia cell line, THP-1: a multifacetted model for the study of monocyte-macrophage differentiation. Experientia. 1991;47(1):22-31. [6] Daigneault M, Preston JA, Marriott HM, et al. The identification of markers of macrophage differentiation in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells and monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS One. 2010;5(1): e8668. [7] Qin Z. The use of THP-1 cells as a model for mimicking the function and regulation of monocytes and macrophages in the vasculature. Atherosclerosis. 2012;221(1):2-11. [8] Zhou L, Shen LH, Hu LH, et al. Retinoid X receptor agonists inhibit phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)-induced differentiation of monocytic THP-1 cells into macrophages. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;335(1-2):283-289. [9] Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, et al. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988;239(4839):487-491. [10] Kramer MF, Coen DM. Enzymatic amplification of DNA by PCR: standard procedures and optimization. Curr Protoc Cytom. 2006; Appendix 3:Appendix 3K.[11] Whitney SE, Sudhir A, Nelson RM, et al. Principles of rapid polymerase chain reactions: mathematical modeling and experimental verification. Comput Biol Chem. 2004;28(3): 195-209. [12] Vosberg HP. The polymerase chain reaction: an improved method for the analysis of nucleic acids. Hum Genet. 1989;83(1):1-15.[13] Chang PL, Hsieh WS, Chiang CL, et al. Identification of individual DNA molecule of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by nested PCR-RFLP and capillary electrophoresis. Talanta. 2008;77(1):182-188. [14] Housley DJ, Zalewski ZA, Beckett SE, et al. Design factors that influence PCR amplification success of cross-species primers among 1147 mammalian primer pairs. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:253.[15] Harris S, Jones DB. Optimisation of the polymerase chain reaction. Br J Biomed Sci. 1997;54(3):166-173.[16] Orpana AK, Ho TH, Stenman J. Multiple heat pulses during PCR extension enabling amplification of GC-rich sequences and reducing amplification bias. Anal Chem. 2012;84(4): 2081-2087.[17] Chouljenko V, Jayachandra S, Rybachuk G, et al. Efficient long-PCR site-specific mutagenesis of a high GC template. Biotechniques. 1996;21(3):472-474,476-478,480.[18] Rychlik W, Spencer WJ, Rhoads RE. Optimization of the annealing temperature for DNA amplification in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18(21):6409-6412. [19] Wu DY, Ugozzoli L, Pal BK, et al. The effect of temperature and oligonucleotide primer length on the specificity and efficiency of amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. DNA Cell Biol. 1991;10(3):233-238. [20] Shaffer AL, Wojnar W, Nelson W. Amplification, detection, and automated sequencing of gibbon interleukin-2 mRNA by Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1990;190(2): 292-296.[21] Eggerding FA. A one-step coupled amplification and oligonucleotide ligation procedure for multiplex genetic typing. PCR Methods Appl. 1995;4(6):337-345.[22] Jensen MA, Fukushima M, Davis RW. DMSO and betaine greatly improve amplification of GC-rich constructs in de novo synthesis. PLoS One. 2010;5(6):e11024. [23] Hubé F, Reverdiau P, Iochmann S, et al. Improved PCR method for amplification of GC-rich DNA sequences. Mol Biotechnol. 2005;31(1):81-84. [24] Musso M, Bocciardi R, Parodi S, et al. Betaine, dimethyl sulfoxide, and 7-deaza-dGTP, a powerful mixture for amplification of GC-rich DNA sequences. J Mol Diagn. 2006;8(5):544-550.[25] Pratyush DD, Tiwari S, Kumar A, et al. A new approach to touch down method using betaine as co-solvent for increased specificity and intensity of GC rich gene amplification. Gene. 2012;497(2):269-272. [26] Bachmann HS, Siffert W, Frey Ulrich. Successful amplification of extremely GC-rich promoter regions using a novel ‘slowdown PCR’ technique. Pharmacogenetics. 2003;13(12): 759-766.[27] Frey UH, Bachmann HS, Peters J, et al. PCR-amplification of GC-rich regions: 'slowdown PCR'. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(8):1312-1317.[28] Hung T, Mak K, Fong K. A specificity enhancer for polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18(16):4953.[29] Kovárová M, Dráber P. New specificity and yield enhancer of polymerase chain reactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(13): E70.[30] Markoulatos P, Siafakas N, Moncany M. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction: a practical approach. J Clin Lab Anal. 2002;16(1): 47-51. |