| [1] Samartzis D, Cheung KM.Lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am.2011;42(4):xi-xii.[2] Bae WC, Masuda K.Emerging technologies for molecular therapy for intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):585-601, ix.[3] Risbud MV, Albert TJ, Shapiro IM: Stem cell regeneration of the nucleus pulposus. Spine J. 2004;4(6 Suppl):348S-353S.[4] Oh SK, Chen AK, Mok Y, et al,Long-term microcarrier suspension cultures of human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res.2009;2(3):219-230.[5] Botchwey EA, Pollack SR, Levine EM, Laurencin CT,et al.Bone tissue engineering in a rotating bioreactor using a microcarrier matrix system. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;55 (2):242-253.[6] Temenoff JS, Mikos AG. Review: Tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000;21(5): 431-440.[7] Thompson JP, Pearce RH, Schechter MT, et al. Preliminary evaluation of a scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine.1990;15:411-415.[8] Kandel R, Roberts S, Urban JP. Tissue engineering and the intervertebral disc: the challenges. Eur Spine J. 2008;17 Suppl 4:480-491.[9] Nomura T, Mochida J, Okuma M, et al. Nucleus pulposus allograft retards intervertebral disc degeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(389):94-101. [10] Thissen H, Chang KY, Tebb TA, et al. Synthetic biodegradable microparticles for articular cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A.2006;77(3):590-598.[11] Yella Martin, Mohamed Eldardiri, Diana J. et al. Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews. February 2011, 17(1): 71-80[12] Malda J, Blitterswijk CA, Grojec M,et al. Expansion of bovinechondrocytes on microcarriers enhances redifferentiation.Tissue Eng. 2003; 9(5):939-948[13] Liu Y,Hu YG,Ning B. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi.2007;17(5):376-379. 刘勇,胡有谷,宁斌. 退变腰椎间盘髓核细胞立体培养与单层培养的生物活性比较[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(5):376-379.[14] Liu TQ,Li XQ,Sun XY,et al. Analysis on forces and movement of cultivated particles in a rotatingwall vessel bioreactor.Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2004,2:97-104.[15] Ni M ,Xie HQ, Chen JW, et al. Rapid Expansion of Bone Mesenchymal Cells in Stirring Bioreactor. Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2009;(1):28-33. 倪明,谢慧琪,陈俊伟,等.利用旋转式生物反应器快速扩增骨髓间充质干细胞[J].医用生物力学,2009,24(1):28-33.[16] Verfallie CM. Adhesion receptors as regulators of the hematopoietic process. Blood,1998,92(8):2609-2612.[17] Wang CY. Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng yu Linchuang.2002;6:51-54. 王常勇. 采用微载体技术大规模培养组织工程种子细胞[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2002,6(1):51-54. [18] Salin N, Ishak AK, Abdul Rahman S, et al. In-vitro expression of adhesion molecules and bone specific markers are depending on the cell culture material. Med J Malaysia. 2008; 63 Suppl A: 67-68.[19] Schrobback K, Klein TJ, Schuetz M, et al.Adult human articular chondrocytes in a microcarrier-based culture system: expansion and redifferentiation. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(4): 539-546.[20] Surrao DC, Khan AA, McGregor AJ, et al. Can Microcarrier-Expanded Chondrocytes Synthesize Cartilaginous Tissue In Vitro? Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17 (15-16): 1959-1967.[21] Zhang L, Ning B, Jia T, et al. Microcarrier bioreactor culture system promotes propagation of human intervertebral disc cells. Ir J Med Sci.2010;179(4):529-534.[22] Gruber HE, Hoelscher GL, Hanley EN,et al. cells from more degenerated human discs show modified gene expression in 3D culture compared with expression in cells from healthier discs.Spine J. 2010;10(8):721-727.[23] Johansson A, Nielsen V.Biosilon: a new microcarrier. Dev Biol Stand. 1980;46:125-129.[24] Maxson S, Orr D, Burg KJL et al.Bioreactors for tissue engineering.Tissue engineering.2011;Part 1:179–197[25] Moreira-Teixeira LS, Georgi N, Leijten J, et al.Cartilage tissue engineering. Endocr Dev. 2011;21:102-115.[26] Schrobback K, Klein TJ, Schuetz M, et al. Adult human articular chondrocytes in a microcarrier-based culture system: expansion and redifferentiation. J Orthop Res.2011;29(4): 539-546. |
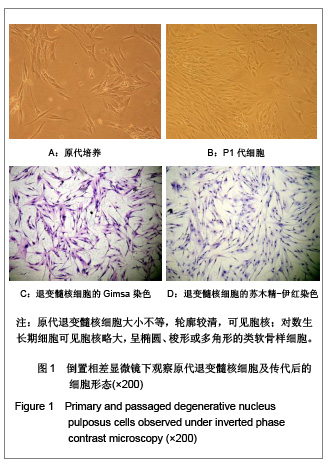
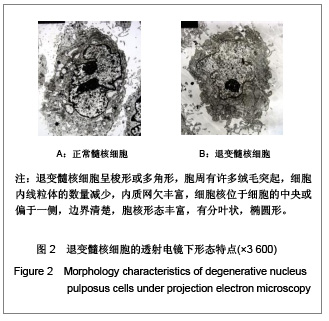
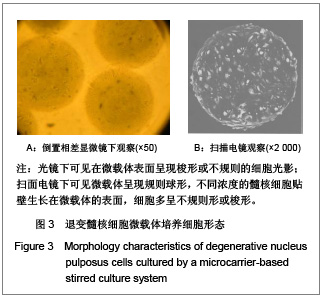
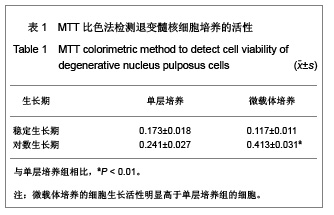
.jpg)