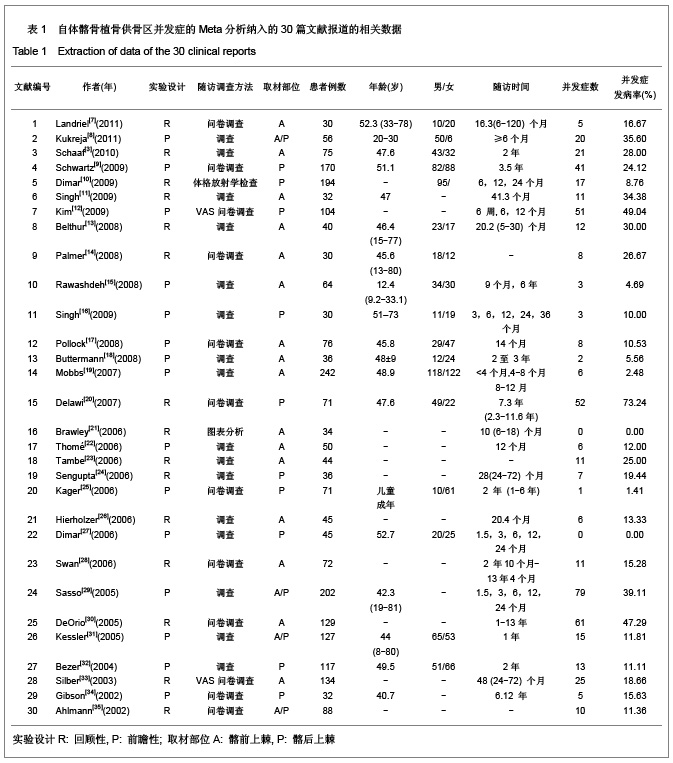
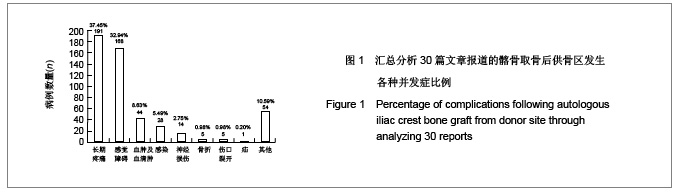
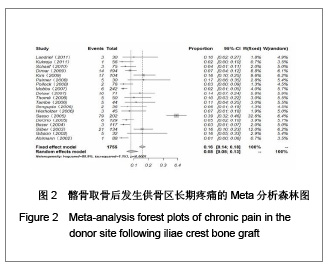
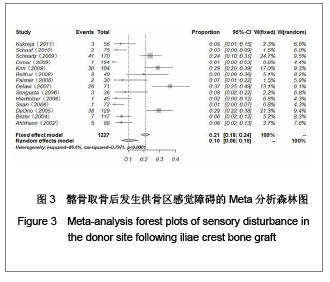
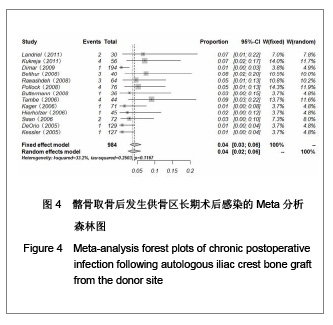
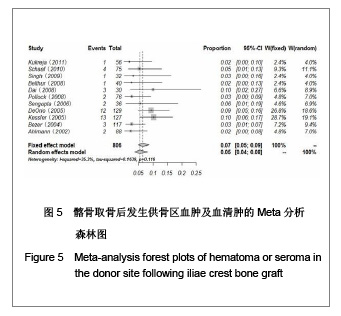
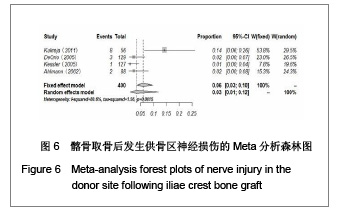
| [1] Miyazaki M, Tsumura H, Wang JC, et al. An update on bone substitutes for spinal fusion.Eur Spine J. 2009;18(6):783-799.[2] Giannoudis PV, Dinopoulos H, Tsiridis E. Bone substitutes: an update. Injury. 2005;36 Suppl 3:S20-27.[3] Schaaf H, Lendeckel S, Howaldt HP,et al. Donor site morbidity after bone harvesting from the anterior iliac crest.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(1):52-58.[4] Younger EM, Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites. J Orthop Trauma. 1989;3(3):192-195. [5] Summers BN, Eisenstein SM. Donor site pain from the ilium. A complication of lumbar spine fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71(4):677-680. [6] Missiuna PC, Gandhi HS, Farrokhyar F,et al. Anatomically safe and minimally invasive transcrestal technique for procurement of autogenous cancellous bone graft from the mid-iliac crest.Can J Surg. 2011;54(5):327-332.[7] Landriel FA, Hem S, Goldschmidt E,et al. Polyetheretherketone Interbody Cages Versus Autogenous Iliac Crest Bone Grafts With Anterior Fixation for Cervical Disc Disease. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011. [Epub ahead of print] [8] Kukreja S, Raza HKT, Agrawal AC. Iliac Crest Bone Graft Harvesting: Prospective Study Of Various Techniques And Donor Site Morbidity. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2011. [Epub ahead of print][9] Schwartz CE, Martha JF, Kowalski P,et al. Prospective evaluation of chronic pain associated with posterior autologous iliac crest bone graft harvest and its effect on postoperative outcome. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009;7: 49.[10] Dimar JR 2nd, Glassman SD, Burkus JK,et al. Two-year fusion and clinical outcomes in 224 patients treated with a single-level instrumented posterolateral fusion with iliac crest bone graft. Spine J. 2009;9(11):880-885.[11] Singh JR, Nwosu U, Egol KA. Long-term functional outcome and donor-site morbidity associated with autogenous iliac crest bone grafts utilizing a modified anterior approach. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67(4):347-351.[12] Kim DH, Rhim R, Li L,et al. Prospective study of iliac crest bone graft harvest site pain and morbidity.Spine J. 2009; 9(11):886-892.[13] Belthur MV, Conway JD, Jindal G,et al. Bone graft harvest using a new intramedullary system.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(12):2973-2980.[14] Palmer W, Crawford-Sykes A, Rose RE. Donor site morbidity following iliac crest bone graft.West Indian Med J. 2008;57(5): 490-492. [15] Rawashdeh MA. Morbidity of iliac crest donor site following open bone harvesting in cleft lip and palate patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;37(3):223-227.[16] Ohtori S, Koshi T, Yamashita M,et al. Single-level instrumented posterolateral fusion versus non-instrumented anterior interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis: a prospective study with a 2-year follow-up.J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(4):352-358.[17] Pollock R, Alcelik I, Bhatia C,et al. Donor site morbidity following iliac crest bone harvesting for cervical fusion: a comparison between minimally invasive and open techniques. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(6):845-852.[18] Buttermann GR. Prospective nonrandomized comparison of an allograft with bone morphogenic protein versus an iliac-crest autograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J. 2008;8(3):426-435.[19] Mobbs RJ, Rao P, Chandran NK. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: analysis of surgical outcome with and without plating. J Clin Neurosci. 2007;14(7):639-642.[20] Delawi D, Dhert WJ, Castelein RM,et al. The incidence of donor site pain after bone graft harvesting from the posterior iliac crest may be overestimated: a study on spine fracture patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(17):1865-1868.[21] Brawley SC, Simpson RB. Results of an alternative autogenous iliac crest bone graft harvest method. Orthopedics. 2006;29(4):342-346.[22] Thomé C, Leheta O, Krauss JK,et al. A prospective randomized comparison of rectangular titanium cage fusion and iliac crest autograft fusion in patients undergoing anterior cervical discectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4(1):1-9.[23] Tambe AD, Cutler L, Murali SR,et al. In scaphoid non-union, does the source of graft affect outcome? Iliac crest versus distal end of radius bone graft. J Hand Surg Br. 2006;31(1): 47-51.[24] Sengupta DK, Truumees E, Patel CK,et al. Outcome of local bone versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the instrumented posterolateral fusion of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9):985-991.[25] Kager AN, Marks M, Bastrom T,et al. Morbidity of iliac crest bone graft harvesting in adolescent deformity surgery. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(1):132-134.[26] Hierholzer C, Sama D, Toro JB,et al. Plate fixation of ununited humeral shaft fractures: effect of type of bone graft on healing.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(7):1442-1447.[27] Dimar JR, Glassman SD, Burkus KJ,et al. Clinical outcomes and fusion success at 2 years of single-level instrumented posterolateral fusions with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/compression resistant matrix versus iliac crest bone graft. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(22): 2534-2539.[28] Swan MC, Goodacre TE. Morbidity at the iliac crest donor site following bone grafting of the cleft alveolus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;44(2):129-133.[29] Sasso RC, LeHuec JC, Shaffrey C,et al. Iliac crest bone graft donor site pain after anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective patient satisfaction outcome assessment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18 Suppl:S77-S81.[30] DeOrio JK, Farber DC. Morbidity associated with anterior iliac crest bone grafting in foot and ankle surgery. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(2):147-151.[31] Kessler P, Thorwarth M, Bloch-Birkholz A,et al. Harvesting of bone from the iliac crest--comparison of the anterior and posterior sites. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;43(1):51-56.[32] Bezer M, Kocao?lu B, Aydin N,et al. Comparison of traditional and intrafascial iliac crest bone-graft harvesting in lumbar spinal surgery. Int Orthop. 2004;28(6):325-328. [33] Silber JS, Anderson DG, Daffner SD,et al. Donor site morbidity after anterior iliac crest bone harvest for single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(2):134-139.[34] Gibson S, McLeod I, Wardlaw D,et al. Allograft versus autograft in instrumented posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a randomized control trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(15): 1599-1603.[35] Ahlmann E, Patzakis M, Roidis N,et al. Comparison of anterior and posterior iliac crest bone grafts in terms of harvest-site morbidity and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(5):716-720.[36] Zou SS,Hu HL. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(37):6991-6994. 邹沙沙,胡洪亮. Hedgehog信号通路与骨发育[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(37):6991-6994.[37] Hu H, Hilton MJ, Tu X,et al. Sequential roles of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling in osteoblast development. Development. 2005; 132(1):49-60. |