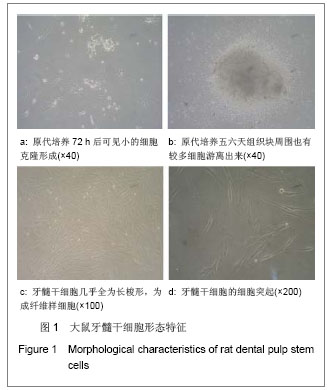
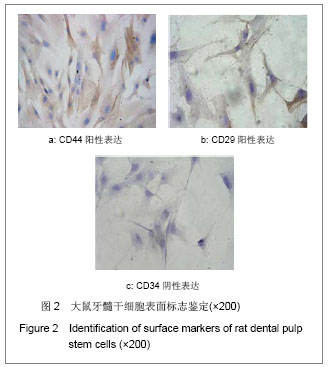
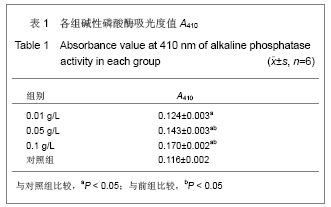
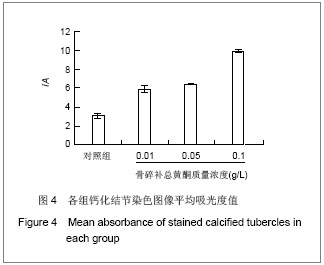
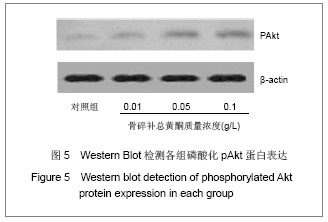
| [1] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25): 13625-13630.[2] Grottkau B E, Purudappa P P, Lin Y F. Multilineage differentiation of dental pulp stem cells from green fluorescent protein transgenic mice.Int J Oral Sci. 2010;2(1): 21-27.[3] Xu YZ,Gao YB,Guo JJ,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(2): 324-328.许彦枝,高永博,郭晶洁,等.不同浓度骨碎补提取液对体外培养人牙髓细胞增殖及超微结构的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(2): 324-328.[4] Hu QY,Chen LL,Wang RF.Zhejiang Daxue Xuebao:Yixueban. 2010;39(1): 79-83.胡其勇,陈莉丽,王仁飞.骨碎补柚皮苷对人牙周韧带细胞增殖和成骨分化潜能的影响[J].浙江大学学报:医学版,2010,39(1): 79-83.[5] Xiao W, Yang Y, Weng Q, et al. The role of the PI3K-Akt signal transduction pathway in Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells. Virology. 2009;391(1): 83-89.[6] Shi S, Gronthos S. Perivascular niche of postnatal mesenchymal stem cells in human bone marrow and dental pulp. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(4): 696-704.[7] Zhang XY,Li XT,Zeng XL.Zhonghua Kouqiang Zhengjixue Zazhi. 2009;16(3): 151-154.张晓艳,李小彤,曾祥龙.人牙髓干细胞体外分选分化的初步实验研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2009,16(3): 151-154.[8] Struys T, Moreels M, Martens W, et al. Ultrastructural and Immunocytochemical Analysis of Multilineage Differentiated Human Dental Pulp- and Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Cells Tissues Organs. 2010.[9] Yang X, Zhang W, van den Dolder J, et al. Multilineage potential of STRO-1+ rat dental pulp cells in vitro.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1(2): 128-135.[10] Sun JX,He WT,Liu K,et al.Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2008;14(10): 763-766.孙金谞,何伟涛,刘康,等.骨碎补总黄酮与骨质疏松症的研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2008, 14(10):763-766.[11] Jiang JQ,Ding Y,Li XY,et al.Huaxi Kouqiangxue Zazhi. 2009; 27(5): 538-541.蒋俊强,丁一,李小玉,等.骨碎补柚皮苷对人牙周膜细胞增殖、碱性磷酸酶活性影响的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009, 27(5): 538-541.[12] Guo JJ,Gao YB,Xu YZ.Tianjin Yiyao. 2008;36(9): 701-703.郭晶洁,高永博,许彦枝.骨碎补对人牙髓细胞体外诱导的作用[J].天津医药,2008, 36(9): 701-703.[13] Tsukamoto Y, Fukutani S, Shin-Ike T, et al. Mineralized nodule formation by cultures of human dental pulp-derived fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol. 1992;37(12): 1045-1055.[14] Roymans D, Slegers H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases in tumor progression. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268(3): 487-498.[15] Stephens L, Williams R, Hawkins P. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases as drug targets in cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5(4): 357-365.[16] Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism . Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(8): 606-619. |