中国组织工程研究 ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9221-9225.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.018
• 干细胞与中医药 stem cells and traditional Chinese medicine • 上一篇 下一篇
虫草多糖体外诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为类肝细胞样细胞
刘江凯1,宋雅芳2,刘友章2,杨谕晨2,张久梅2
- 1河南中医学院第一附属医院,河南省郑州市450008;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510405
Cordyceps polysaccharide induces differentiation of adult rat mesenchymal stem cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro
Liu Jiang-kai1, Song Ya-fang2, Liu You-zhang2, Yang Yu-chen2, Zhang Jiu-mei2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450008, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
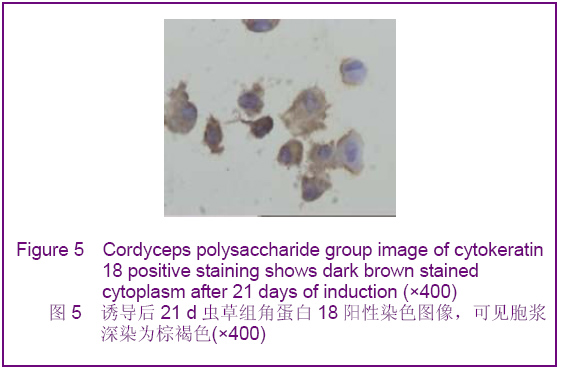
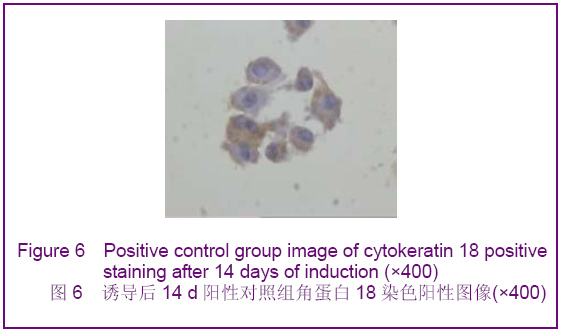
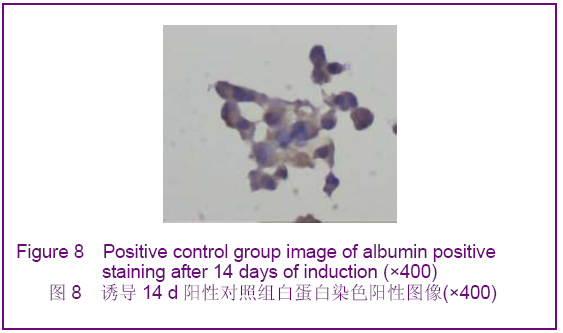
背景:如何促进骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞完全意义上的转化,以便更有效改善病变肝组织的结构和功能将成为未来相关研究的重中之重。 目的:探讨虫草多糖在体外诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为类肝细胞样细胞的可行性。 方法:采用贴壁法培养Wistar大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,实验分3组对骨髓间充质干细胞进行诱导分化,虫草组培养液中加虫草多糖进行诱导,终末质量浓度为0.15 g/L;阳性对照组培养液中加肝细胞生长因子和表皮生长因子联合诱导,质量浓度分别为20 μg/L和10 μg/L;空白对照组仅用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养液。 结果与结论:分离纯化的骨髓间充质干细胞经流式细胞仪检测显示CD34阴性表达,CD44阳性表达。诱导分化7 d时虫草组及阳性对照组细胞出现甲胎蛋白表达,14 d时表达增强,28 d时表达减弱,阳性对照组甲胎蛋白阳性率高于虫草组;诱导分化7 d时阳性对照组细胞角蛋白18出现表达,14 d时表达增强,虫草组则在14 d时出现表达,而后持续。诱导分化7 d时虫草组及阳性对照组白蛋白表达阴性,14 d时出现阳性。诱导分化14 d时虫草组及阳性对照组细胞糖原染色阳性,28 d时表达减弱。空白对照组结果皆为阴性。结果可见虫草多糖可以在体外诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为类肝细胞样细胞。
中图分类号:
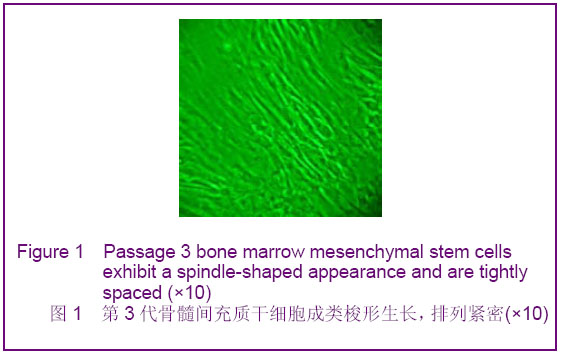
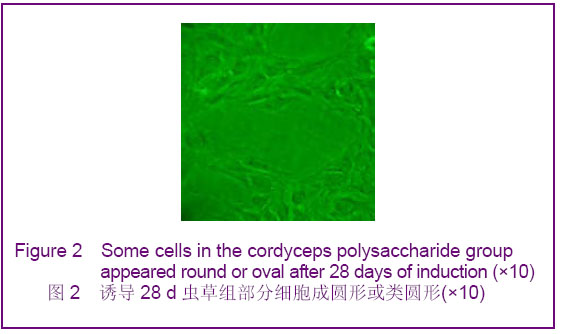
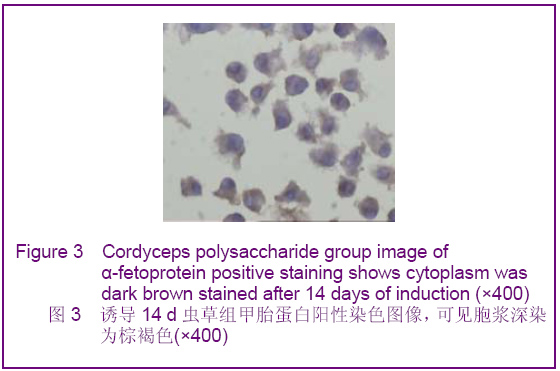
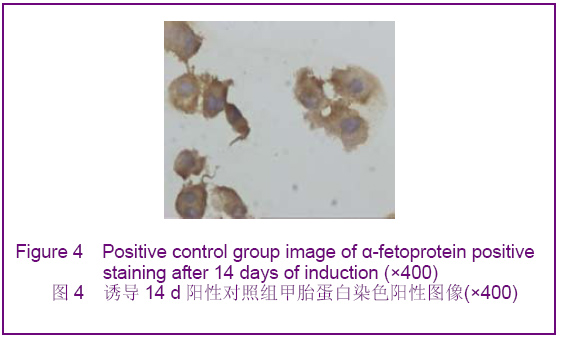

.jpg)