中国组织工程研究 ›› 0, Vol. ›› Issue (0): 72-76.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1870
• 胚胎干细胞 embryonic stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
两种传代方法影响人胚胎干细胞转染效率的比较
孙 莉1,2,纵艳艳1,魏建峰1,3
- 1江苏省脑病生物信息重点实验室,江苏省徐州市 221004;徐州医科大学,2护理学院, 3基础医学院组织胚胎学教研室,江苏省徐州市 221004
Comparison of two passage methods affecting the transfection efficiency of human embryonic stem cells#br#
Sun Li1, 2, Zong Yanyan1, Wei Jianfeng1, 3
- 1Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Brain Disease Bioinformation, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China; 2School of Nursing, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
胚胎干细胞:是一类起源于胚胎发育早期囊胚内细胞群中未分化的细胞,具有自我更新、无限增殖和多向分化的潜能。
转染:是真核细胞主动或被动导入外源DNA片段而获得新的表型的过程。
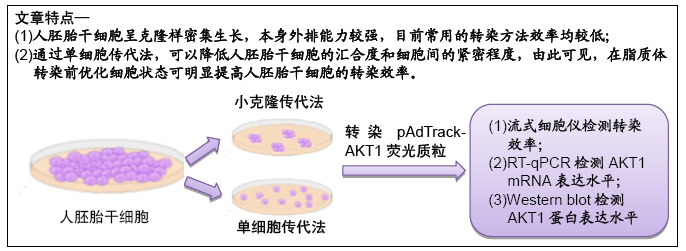
背景:现有方法将外源分子如DNA导入到人胚胎干细胞用于科学研究的效率普遍较低,如何优化现有条件,提高转染效率显得尤为重要。目的:比较两种不同的传代方法对人胚胎干细胞系H9转染效率的影响,优化胚胎干细胞转染条件。
方法:人胚胎干细胞系H9分别采用小克隆传代法和单细胞传代法进行传代,传代后继续培养细胞48 h,用Lipofectamine 3000转染pAdTrack-AKT1荧光质粒2 d后,荧光显微镜下观察荧光质粒的表达,流式细胞仪检测人胚胎干细胞的转染效率;RT-qPCR和Western blot分别检测转染后AKT1在mRNA和蛋白质水平的表达。
结果与结论:①荧光显微镜下观察发现单细胞传代组表达荧光质粒的细胞数量更多,流式细胞仪检测单细胞传代法的转染效率[(47.18±2.00)%]高于小克隆传代法的转染效率[(19.52±0.86)%],差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.01);②单细胞传代组转染后AKT1 mRNA和蛋白的表达均高于小克隆传代组,差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.01);③结果表明,采用单细胞传代法,增加细胞与转染试剂脂质体的接触面积可提高人胚胎干细胞的转染效率。ORCID: 0000-0002-1800-8057(孙莉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: