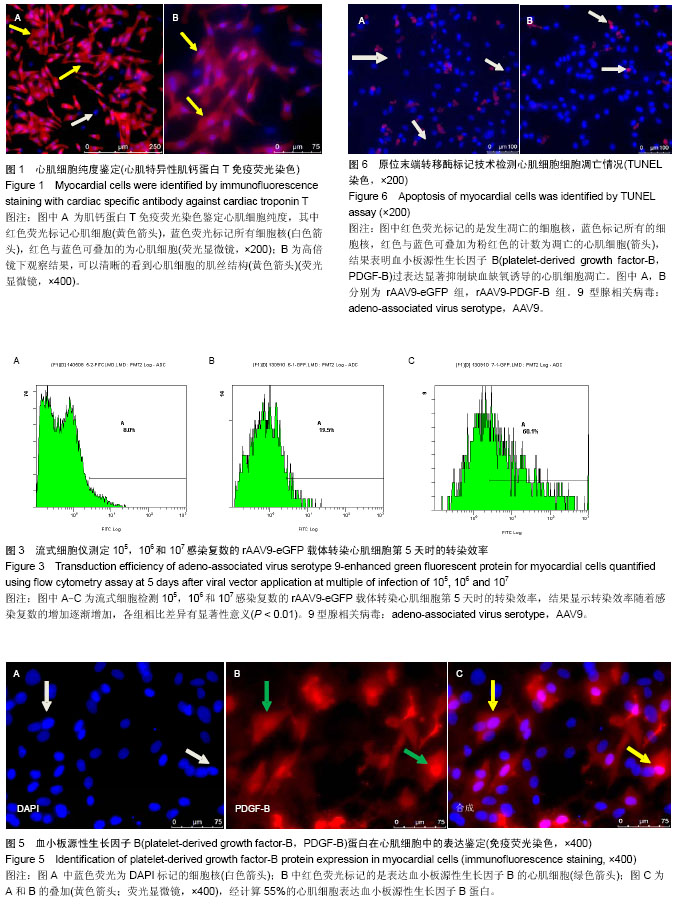
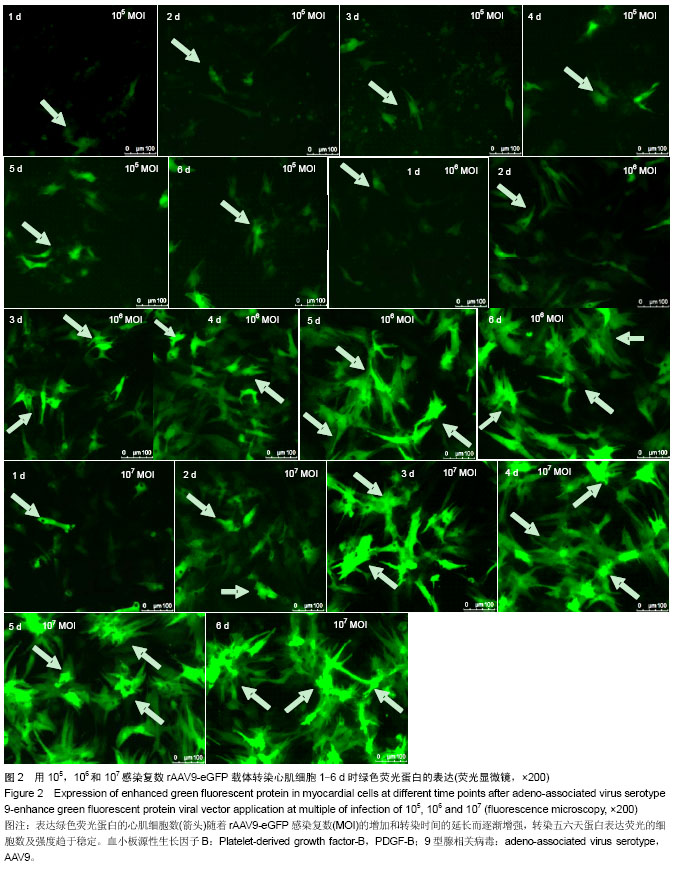
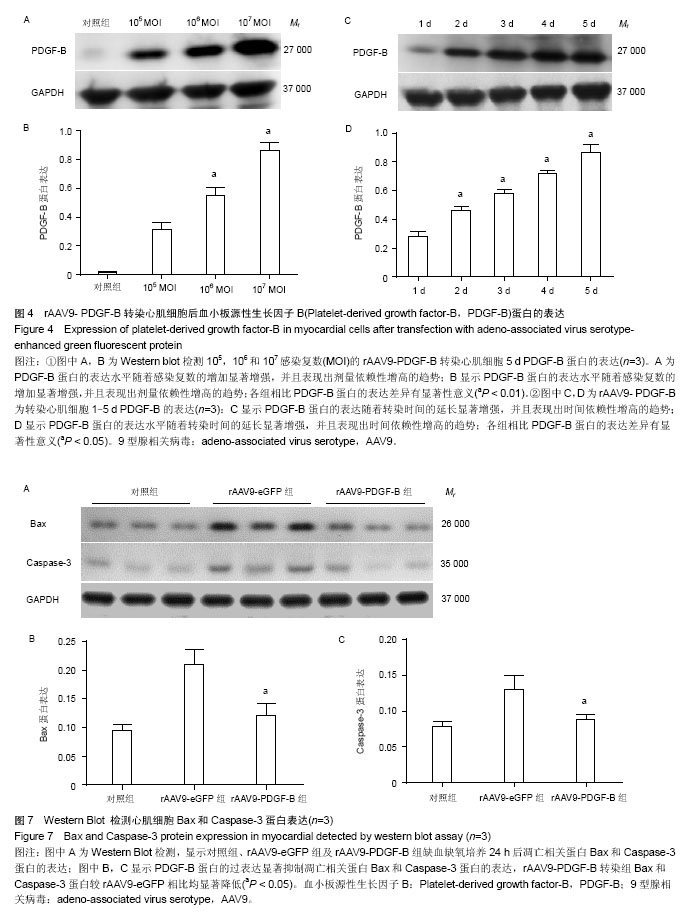
| [1] Yi GY, Zhang X, Zhang J, et al. Factors related to the use of reperfusion strategies in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;9(1):111.
[2] Nascimento BR, de Sousa MR, Demarqui FN, et al. Risks and benefits of thrombolytic, antiplatelet, and anticoagulant therapies for ST segment elevation myocardial infarction: systematic review. ISRN Cardiol. 2014:1-11.
[3] Tao Z, Chen B, Tan X, et al. Coexpression of VEGF and angiopoietin-1 promotes angiogenesis and cardiomyocyte proliferation reduces apoptosis in porcine myocardial infarction (MI) heart. PNAS. 2011;108(5):2064-2069.
[4] Wang G, Hamid T, Keith RJ, et al. Cardioprotective and antiapoptotic effects of heme oxygenase-1 in the failing heart. Circulation. 2010;121(17):1912-1925.
[5] Vantler M, Karikkineth BC, Naito H, et al. PDGF-BB protects cardiomyocytes from apoptosis and improves contractile function of engineered heart tissue. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010; 48(6):1316-1323.
[6] Lange S, Heger J, Euler G, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor BB stimulates vasculogenesis of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells by calcium- mediated generation of reactive oxygen species. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;81(1): 159-168.
[7] Scimia MC, Gumpert AM, Koch WJ. Cardiovascular gene therapy for myocardial infarction. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014; 14(2):183-115.
[8] Korpisalo P, Ylä-Herttuala S. Stimulation of functional vessel growth by gene therapy. Integr Biol (Camb). 2010;2(2-3): 102-112.
[9] Prasad KM, Xu Y, Yang Z, et al. Robust cardiomyocyte- specific gene expression following systemic injection of AAV: in vivo gene delivery follows a Poisson distribution. Gene Ther. 2011;18(1):43-52.
[10] Pacak CA, Mah CS, Thattaliyath BD, et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 9 leads to preferential cardiac transduction in vivo. Circ Res. 2006;99(4):e3-e9.
[11] Inagaki K, Fuess S, Storm TA, et al. Robust systemic transduction with AAV9 vectors in mice: efficient global cardiac gene transfer superior to that of AAV8. Mol Ther. 2006;14(1):45-53.
[12] 向阳,马依彤,杨毅宁,等.重组9型腺相关病毒载体转染小鼠心脏及对心功能的影响[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2009,29(10): 899-902.
[13] Pulicherla N, Shen S, Yadav S, et al. Engineering liver-detargeted AAV9 vectors for cardiac and musculoskeletal gene transfer. Mol Ther. 2011;19(6): 1070-1078.
[14] Bostick B, Ghosh A, Yue Y, et al. Systemic AAV9 transduction in mice is influenced by animal age but not by the route of administration. Gene Therapy. 2007;14(22): 1605-1609.
[15] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.
[16] Sreejit P, Kumar S, Verma RS. An improved protocol for primary culture of cardiomyocyte from neonatal mice. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(3-4):45-50.
[17] Lu DF, Yao Y, Su ZZ, et al. Downregulation of HDAC1 is involved in the cardiomyocyte differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells in a myocardial microenvironment. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e93222.
[18] Excoffon KJ, Gerber JT, Dickey DD. et al. Directed evolution of adeno-associated virus to an infectious respiratory virus. PNAS. 2009;106(10):3865-3870.
[19] 杜雷,马依彤,杨毅宁,等.9型重组腺相关病毒转染大鼠心脏成纤维细胞的体外研究[J].心血管康复医学杂志,2010,19(2): 121-125.
[20] Martherus RS, Zeijlemaker VA, Ayoubi TA. Electrical stimulation of primary neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes using pacemakers. Biotechniques. 2010;48(1):65-67.
[21] 刘霞,王常勇.新生大鼠心肌细胞的分离和培养[J].西北农林科技大学学报,2005,33(6):36-39.
[22] 邸美仙,李应东.乳鼠心肌细胞的培养[J].中华中医药学刊, 2005, 25(4):691-692.
[23] Nickson P, Toth A, Erhardt P, et al. PUMA is critical for neonatal cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;73(1):48-56.
[24] Hajjar RJ. Potential of gene therapy as a treatment for heart failure. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):53-61.
[25] Yang L, Xiao X. Creation of a cardiotropic adeno-associated virus: the story of viral directed evolution. Virol J. 2013;10:50.
[26] Hadad I, Veithen A, Springael JY, et al. Stroma cell-derived factor-1alpha signaling enhances calcium transients and beating frequency in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56007.
[27] Nguyen PD, Hsiao ST, Sivakumaran P, et al. Enrichment of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in primary culture facilitates long-term maintenance of contractility in vitro. Am J Physiol cell Physiol. 2012;303(12):C1220-C1228.
[28] Louch WE, Sheehan KA, Wolska BM. Methods in cardiomyocyte isolation, culture, and gene transfer. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51(3):288-298.
[29] 高霞,马依彤,杨毅宁,等.9型重组腺相关病毒转染体外培养大鼠心肌细胞的影响[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2010,26(01): 18-20.
[30] 姚永钊,马依彤,赵爱超,等.腺相关病毒介导血小板源性生长因 子-B基因转染心肌细胞的研究[J].中华生物医学工程杂志, 2013, 19(5):377-381.
[31] Bakar E, Ulucam E, Cerkezkayabekir A. Protective effects of proanthocyanidin and vitamin E against toxic effects of formaldehyde in kidney tissue. Biotech Histochem. 2014; 1-10.
[32] Yang L, Yang Q, Zhang K, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Daphnetin against NMDA Receptor-Mediated Excitotoxicity. Molecules. 2014;19(9):14542-14555.
[33] Yang SD, Bai ZL, Zhang F, et al. Levofloxacin increases the effect of serum deprivation on anoikis of rat nucleus pulposus cells via Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 pathway. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2014:1-21.
[34] Zhang J, Shen MH, Ruan SM. Beta-HIVS combined cisplatin inhibited activities of human ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3 in vitro. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014;34(8): 987-990.
[35] Zhao JY, Liu LY, Shen AL, et al. Effect of bear bile powder on STAT3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;34(8):976-81. Chinese.
[36] Song E, Fu J, Xia X, et al. Bazhen Decoction Protects against Acetaminophen Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mice. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e107405.
[37] Kukreja RC, Xi L. eNOS phosphorylation: a pivotal molecular switch in vasodilatation and cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42(2):280-282.
[38] Bajt ML, Farhood A, Lemasters JJ. et al. Mitochondrial bax translocation accelerates DNA fragmentation and cell necrosis in a murine model of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324(1):8-14. |