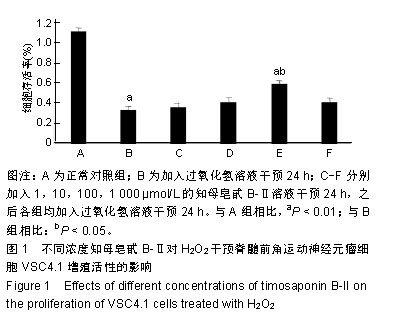
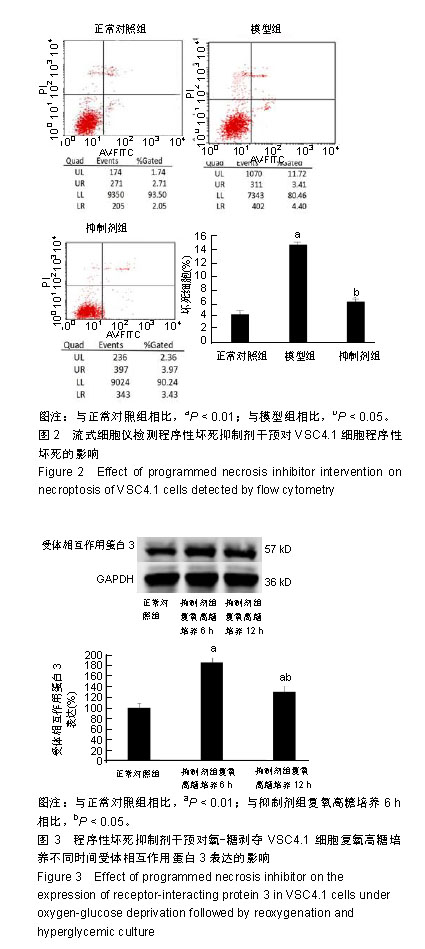
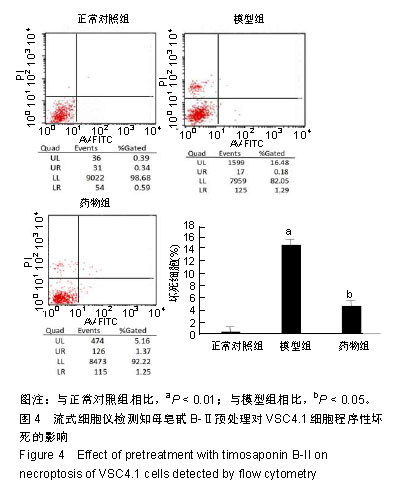
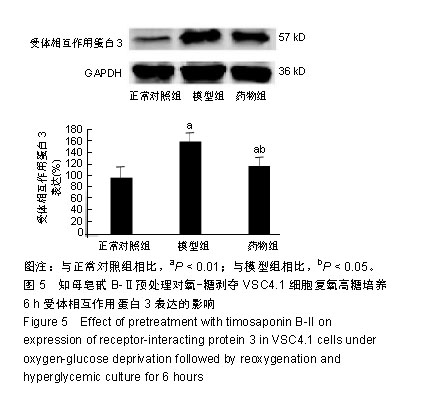
| [1]Kim SJ,Li J. Caspase blockade induces RIP3-mediated programmed necrosis in Toll-like receptor-activated microglia. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e716.[2]Wu YT,Tan HL,Huang Q,et aI.zVAD-induced necroptosis in L929 cells depends on autocrine production of TNFa mediated by the PKC-MAPKs-AP-1 pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2011;18(1):26-37.[3]Hu Y,Xia Z,Sun Q,et al.A new approach to the pharmacological regulation of memory:Sarsasapogenin improves memory by elevating the low muscarinic acetylcholine receptor density in brains of memory-deficit rat models.Brain Res.2005;1060(12):26-31.[4]Moujalled DM,Cook WD,Okamoto T,et al.TNF can activate RIPK3 and cause programmed necrosis in the absence of RIPK1.Cell Death Dis.2013;4:e465.[5]Zhang M, Li J, Geng R,et al.The inhibition of ERK activation mediates the protection of necrostatin-1 on glutamate toxicity in HT-22 cells.Neurotox Res.2013;24(1):64-70.[6]Chen WW,Yu HL,Hong F,et al.RIP1 mediates the protection of geldanamycin on neuronal injury induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation combined with zVAD in primary cortical neurons.J Neurochem.2012;120(1): 70-77.[7]Laird MD,Wakade C,Alleyne CH Jr,et al.Hemin-induced necroptosis involves glutathione depletion in mouse astrocytes.Free Radic Biol Med.2008;45(8):1103-1114.[8]冯毅凡,吉星,等.知母中皂甙类研究进展[J].中草药,2010, 41(4): 12-15.[9]邓云,徐秋萍,刘振权.知母皂甙化合物对脑缺血再灌注大鼠的保护作用[J].北京中医药大学学报,2005,28(2):33-37.[10]Huang JF,Shang L,Liu P,et al.Timosaponin-BII inhibits the up-regulation of BACE1 induced by Ferric Chloride in rat retina. BMC Complement Altern Med.2012;12:189.[11]Huang JF,Shang L,Xiong K,et al.Differential neuronal expression of receptor interacting protein 3 in rat retina: involvement in ischemic stress response.BMC Neurosci. 2013;14:16.[12]Ding W,Shang L,Huang JF,et al. Receptor interacting protein 3-induced RGC-5 cell necroptosis following oxygen glucose deprivation.BMC Neurosci.2015;16:49.[13]Wang SC,Liao LS,Wang M,et al.Pin1 Promotes Regulated Necrosis Induced by Glutamate in Rat Retinal Neurons via CAST/Calpain2 Pathway. Front Cell Neurosci.2018;11:425.[14]Nikseresht S,Khodagholi F,Ahmadiani A. Protective effects of ex-527 on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through necroptosis signaling pathway attenuation.J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1816-1826.[15]Macchi B, Mastino A.Programmed cell death and natural killer cells in multiple sclerosis: new potential therapeutic targets?Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(5):733-734.[16]Li W,Liu J,Chen JR,et al.Neuroprotective Effects of DTIO, A Novel Analog of Nec-1, in Acute and Chronic Stages After Ischemic Stroke.Neuroscience.2018;390:12-29.[17]Fang T,Cao R,Wang W,et al.Alterations in necroptosis during ALDH2 mediated protection against high glucose induced H9c2 cardiac cell injury.Mol Med Rep.2018;18(3):2807-2815.[18]Yan JK,Yan WH,Cai W.Fish oil-derived lipid emulsion induces RIP1-dependent and caspase 8-licensed necroptosis in IEC-6 cells through overproduction of reactive oxygen species. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):148.[19]Chen R,Xu J,She Y,et al.Necrostatin-1 protects C2C12 myotubes from CoCl2-induced hypoxia.Mol Med.2018;41(5): 2565-2572.[20]Ni Y,Gu WW,Liu ZH,et al.RIP1K Contributes to Neuronal and Astrocytic Cell Death in Ischemic Stroke via Activating Autophagic-lysosomal Pathway.Neuroscience. 2018;371: 60-74.[21]Wang Z,Guo LM,Wang Y,et al.Inhibition of HSP90αprotects cultured neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation induced necroptosis by decreasing RIP3 expression.J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(6):4864-4884.[22]Hao J,Li S,Shi X,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against n-hexane-induced neuropathy through beclin 1-independent inhibition of autophagy.Sci Rep.2018;8(1): 4516.[23]Lu WQ,Qiu Y,Li TJ,et al.Timosaponin B-II inhibits proin-flammatory cytokine induction by lipopolysaccharide in BV2 cell.Ach Pharm Res.2009;32(9):1301-1305.[24]Xiao S,Xu M,Ge Y,et al.Inhibitory Effects of Saponins From Anemarrhene asphodeloides Bunge on the Growth of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Biomed Environ. 2006;19(3): 185-189.[25]邓云,马百平.知母皂苷B2对AB25-35诱导的原代大鼠神经细胞损伤的保护作用[J].中国药理学通报,2009,25(2):244-247.[26]Xie Q,Zhao H,Li N,et al.Protective effects of Timosaponin B-II on oxidative stress damage in PC12 cells based on metabolomics.Biomed Chromatogr.2018,10;32(10):e4321.[27]Li N,Liu B,Zhang J,et al.Acute toxicity, 28-day repeated-dose toxicity and toxicokinetic study of Timosaponin B-II in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.2017;90:244-257.[28]Yuan YL,Guo CR,Cui LL,et al.Timosaponin B-II ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via TXNIP, mTOR, and NF-κB signaling pathways in alloxan-induced mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015; 9:6247-6258.[29]Jiang SH,Shang L,Xue LX,et al. The effect and underlying mechanism of Timosaponin B-II on RGC-5 necroptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:459.[30]Zhao X,Liu C,Qi Y,et al.Timosaponin B-II ameliorates scopolamine-induced cognition deficits by attenuating acetylcholinesterase activity and brain oxidative damage in mice.Metab Brain Dis.2016;31(6):1455-1461.[31]Shulga N,Pastorino JG.Mitoneet mediates TNFalpha-induced necroptosis promoted by exposure to fructose and ethanol.J Cell Sci.2014;127(Pt 4):896-907.[32]Cabon L,Galán-Malo P,Bouharrour A,et al.BID regulates AIF-mediated caspase-independent necroptosis by promoting BAX activation.Cell Death Differ.2012;19(2):245-256.[33]Hou H,Wang Y,Li Q,et al.The role of RIP3 in cardiomyocyte necrosis induced by mitochondrial damage of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin.2018;50(11): 1131-1140.[34]Cruz SA, Qin Z, Stewart AFR, et al.Dabrafenib, an inhibitor of RIP3 kinase-dependent necroptosis, reduces ischemic brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(2):252-256.[35]Yang Z,Li C,Wang Y,et al.Melatonin attenuates chronic pain related myocardial ischemic susceptibility through inhibiting RIP3-MLKL/CaMKII dependent necroptosis.Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018;125: 185-194.[36]Wang S,Wu J,Zeng YZ,et al.Necrostatin-1 Mitigates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress After Spinal Cord Injury. Neurochem Res.2017;42(12):3548-3558.[37]Su X,Wang H,Lin Y,et al.RIP1 and RIP3 mediate hemin-induced cell death in HT22 hippocampal neuronal cells. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.2018;14:3111-3119.[38]Zhang L,Feng Q,Wang T.Necrostatin-1 Protects Against Paraquat-Induced Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction via RIP1-RIP3-MLKL-Dependent Necroptosis Pathway. Cardiovasc Toxicol.2018;18(4):346-355.[39]Zhu C,Liu Y,Guan Z,et al.Hypoxia-reoxygenation induced necroptosis in cultured rat renal tubular epithelial cell line. Basic Med Sci.2018;21(8):863-868.[40]Lu B,Wang Z,Ding Y,et al.RIP1 and RIP3 contribute to shikonin- induced glycolysis suppression in glioma cells via increase of intracellular hydrogen peroxide.Cancer Lett. 2018; 425:31-42.[41]Qiu X,Zhang Y,Han J.RIP3 is an upregulator of aerobic metabolism and the enhanced respiration by necrosomal RIP3 feeds back on necrosome to promote necroptosis.Cell Death Differ.2018;25(5):821-824.[42]Chen Y,Zhang L,Yu H,et al.Necrostatin-1 Improves Long-term Functional Recovery Through Protecting Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice.Neuroscience. 2018;371:229-241.[43]Yan B,Zhang H,Dai T,et al.Necrostatin-1 promotes ectopic periodontal tissue like structure regeneration in LPS-treated PDLSCs.PloS One.2018;13(11):e0207760. |
.jpg)
.jpg)