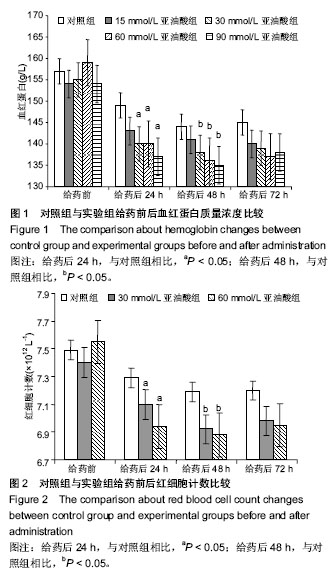
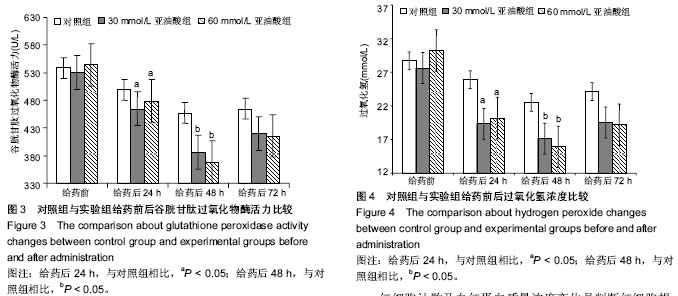
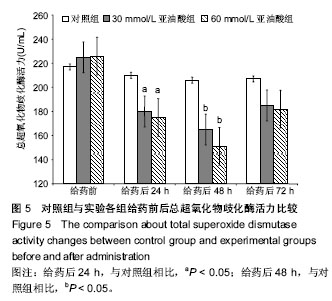
| [1] Qian M, Eaton JM. Free fatty acids enhance hypochlorous acid production by activated neutrophils. J Lab Clin Med. 1994;124(1): 86-95.
[2] Cortes-Rojo C, Fernández-Quintero M, Aguilar-Toral R, et al. Accelerated chronologic aging of S. cerevisiae induced by PUFA is associated to mitochondrial dysfunction, enhanced sensitivity to lipid peroxidation and ROS overproduction. FASEB J. 2013;27: 833.
[3] Bao N, Meng J, Zhou L, et al. Lesser trochanteric osteotomy in total hip arthroplasty for treating CROWE type IV developmental dysplasia of hip. Int Orthop. 2013;37(3): 385-390.
[4] Nie G. Quantization Determination Study of Micro-Raman Spectroscopy of Methemoglobin Induced by Sodium Nitrite. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2013;33(7): 1805-1809.
[5] Lu N, Chen P, Yang Q, et al. Anti-and pro-oxidant effects of (+)-catechin on hemoglobin-induced protein oxidative damage. Toxicol Vitro. 2011;25(4): 833-838.
[6] Potor L, Bányai E, Becs G, et al. Atherogenesis may involve the prooxidant and proinflammatory effects of ferryl hemoglobin. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013.
[7] Pandey KB, Rizvi SI. Anti-oxidative action of resveratrol: Implications for human health. Arab J Chem. 2011;4(3): 293-298.
[8] de M Bandeira S, da Fonseca LJS, da S Guedes G, et al. Oxidative stress as an underlying contributor in the development of chronic complications in diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(2): 3265-3284.
[9] Celedón G, González G, Gulppi F, et al. Effect of Human Serum Albumin Upon the Permeabilizing Activity of Sticholysin II, a Pore Forming Toxin from Stichodactyla heliantus. Protein J. 2013;32(8): 593-600.
[10] 李少斐,郭亭,赵建宁,等.围髋关节置换期隐性失血相关危险因素及预后[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(13): 2006-2011.
[11] 刘志刚,张上上,陈如见,等.全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2305-2312.
[12] Horstmann WG, Kuipers BM, Slappendel R, et al. Postoperative autologous blood transfusion drain or no drain in primary total hip arthroplasty? A randomised controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2012;36(10): 2033-2039.
[13] Koessler MJ,Fabiani R,Hamer H,et al. The clinical relevance of embolic events detected by transesophageal echocardiography during cemented total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Analg. 2001;92(1): 49-55.
[14] Pattison E,Protheroe K,Pringle RM, et al. Reduction in haemoglobin after knee joint surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973; 32(6): 582.
[15] Haien Z,Yong J, Baoan M, et al. Post-operative auto-transfusion in total hip or knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PloS One. 2013; 8(1): e55073.
[16] Monsef JB, Buckup J, Waldstein W, et al. Fibrin sealants or cell saver eliminate the need for autologous blood donation in anemic patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(1): 53-58.
[17] Barge S,Donadee C,Triulzi D,et al. Acute Effect Of Autologous Blood Transfusion On The Venous Level Of Hemolysis Markers Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187: A4681.
[18] Hatanaka E, Levada-Pires AC, Pithon-Curi TC, et al. Systematic study on ROS production induced by oleic, linoleic, and gamma-linolenic acids in human and rat neutrophils.Free. Radic Biol Med. 2006;41(7):1124-1132.
[19] Shen H, Li Z, Feng M, et al. Analysis on hidden blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in treating knee osteoarthritis. Chin Med J. 2011;124(11): 1653.
[20] Tetro AM, Rudan JF. The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2001; 44: 33-38.
[21] Du Z, Liu P, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of tourniquet on perioperative blood loss and short-term effectiveness in total knee arthroplasty.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(11):1318-1323.
[22] 马卫华,张树栋,王诗军,等.止血带的使用方式对膝关节置换术失血量和手术时间的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志,2012,5(6): 33-36.
[23] Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009; 33(5): 1263-1268.
[24] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg. 2004;86(4): 561-565.
[25] 刘志刚,张上上,陈如见,等.全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2305-2312.
[26] Kaikkonen JE, Kresanov P, Ahotupa M, et al. High serum n6 fatty acid proportion is associated with lowered LDL oxidation and inflammation: The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Free Rad Res. 2014;48(4): 420-426.
[27] Pratt DA, Tallman KA, Porter NA. Free radical oxidation of polyunsaturated lipids: new mechanistic insights and the development of peroxyl radical clocks. Acc Chem Res. 2011; 44(6): 458-467.
[28] Nowak JZ. Oxidative stress, polyunsaturated fatty acidsderived oxidation products and bisretinoids as potential inducers of CNS diseases: focus on age-related macular degeneration. Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65(2): 288-304.
[29] Jomova K, Baros S, Valko M. Redox active metal-induced oxidative stress in biological systems. Trans Met Chem. 2012; 37(2): 127-134.
[30] Beavers WN, Serwa R, Shimozu Y, et al. ω-Alkynyl Lipid Surrogates for Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Free Radical and Enzymatic Oxidations. J Ame Chem Soc. 2014.
[31] Nowak JZ. Oxidative stress, polyunsaturated fatty acidsderived oxidation products and bisretinoids as potential inducers of CNS diseases: focus on age-related macular degeneration. Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65(2): 288-304.
[32] Zhang M, Wang A, He W, et al. Effects of fluoride on the expression of NCAM, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Toxicology. 2007; 236(3): 208-216.
[33] Gao Y, Guo YK, Lin SH, et al. Hydrogen peroxide pretreatment alters the activity of antioxidant enzymes and protects chloroplast ultrastructure in heat-stressed cucumber leaves. Scientia Horticul. 2010;126(1): 20-26.
[34] Ahmida MHS. Protective role of curcumin in nephrotoxic oxidative damage induced by vancomycin in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2012;64(3): 149-153.
[35] Wang HF, Zhong XH, Shi W, et al. Study of malondialdehyde (MDA) content, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) activities in chickens infected with avian infectious bronchitis virus. Af J Biotechnol. 2013;10(45): 9213-9217.
[36] Liu J, Wen X, Lu J, et al. Free radical mediated grafting of chitosan with caffeic and ferulic acids: Structures and antioxidant activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;65: 97-106.
[37] Chen H, Liu L, Zhu J, et al. Effect of soybean oligosaccharides on blood lipid, glucose levels and antioxidant enzymes activity in high fat rats. Food Chem. 2010;119(4): 1633-1636.
[38] Rolo AP, Teodoro JS, Palmeira CM. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Rad Biol Med. 2012; 52(1): 59-69.
[39] de M Bandeira S, da Fonseca LJS, da S Guedes G, et al. Oxidative stress as an underlying contributor in the development of chronic complications in diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14(2): 3265-3284.
[40] 王雪艳,匡洪宇.糖尿病与糖尿病肾病患者氧化应激状态的分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2008, 29(6): 694-694.
[41] Kie?-Wilk B, Ma?ecki M, Gruca A, et al. Dietary Supplements and Herbs in Diabetes and Its Prevention. Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Diabetes: Bioactive Foods in Chronic Disease States, 2012: 121. |