中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3591-3598.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1741
• 生物材料循证医学 evidence-based medicine of biomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
软聚硅酮泡沫敷料对放射性皮肤损伤影响的Meta分析
史雪萍1,雷友金2,曾珠梅1,罗江荷1,黄锐娜1,杨 明1
- 1广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510405
Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy of soft silicone dressing for treating radiation-induced skin reaction
Shi Xueping1, Lei Youjin2, Zeng Zhumei1, Luo Jianghe1, Huang Ruina1, Yang Ming1
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
软聚硅酮泡沫敷料:利用司肤泰克技术研制的,由防水透气的外层薄膜,由弹性的聚氨酯泡沫吸收层和软聚硅酮创面接触层组成,有封闭保湿、镇痛止痒、防治病原菌入侵的效果。
放射性皮肤损伤:放射治疗引起的皮肤细胞过度凋亡甚至坏死,皮肤萎缩、变薄、软组织纤维化、毛细血管扩张而导致急性放射性损伤,特别是在皮肤较薄、皱褶多、汗腺和皮脂腺分泌较活跃、易于摩擦的皮肤。
背景:研究证实,软聚硅酮泡沫敷料在防治放射性皮肤损伤方面具有良好效果,但由于现有研究样本量较少,因此有必要借助Meta分析方法对软聚硅酮泡沫敷料在放疗患者中的临床应用效果进行评价。
目的:探讨软聚硅酮泡沫敷料与常规护理措施防治放射性皮肤损伤的疗效差异。
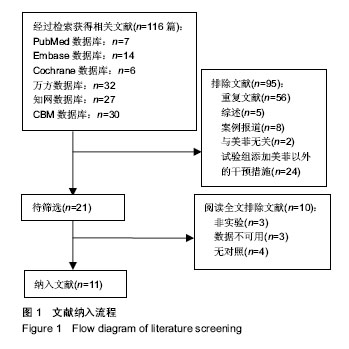
方法:检索中国知网、中国生物医学数据库、万方数据库、PubMed、COCHRANE LIBRARY 等数据库,查找关于软聚硅酮泡沫敷料和常规护理对放射性皮肤损伤患者临床疗效的临床随机对照试验或非随机对照试验,再用 Rev Man 5.3系统评价软件进行统计学分析。
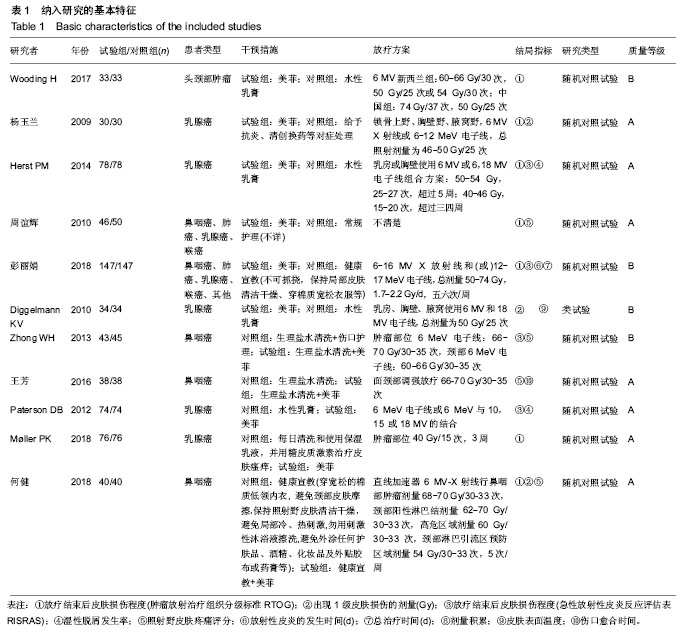
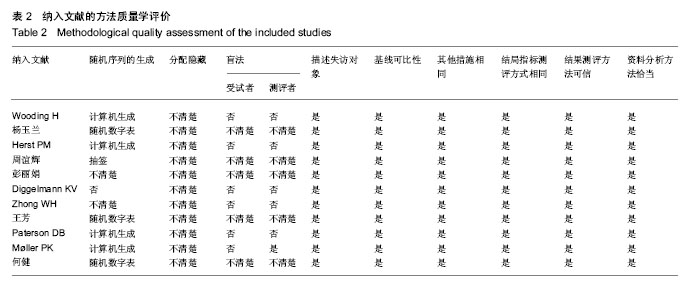
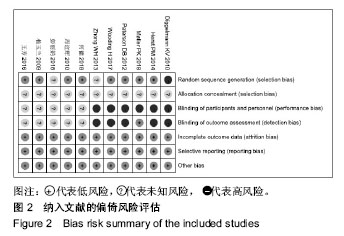
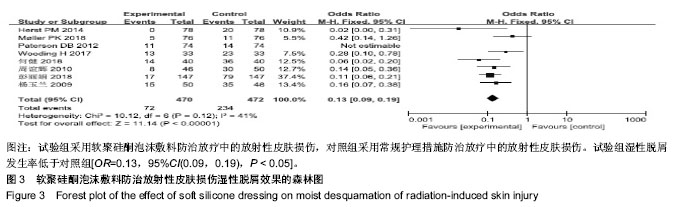
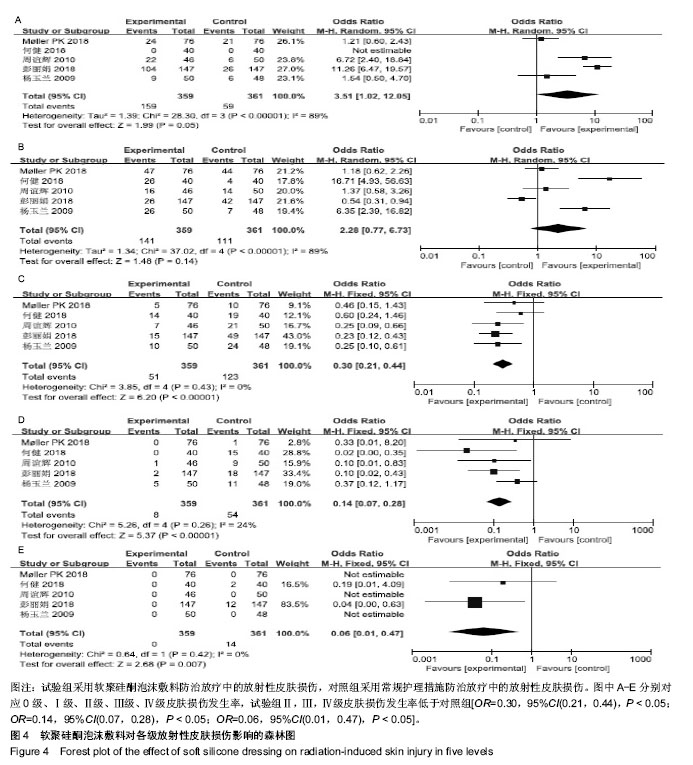
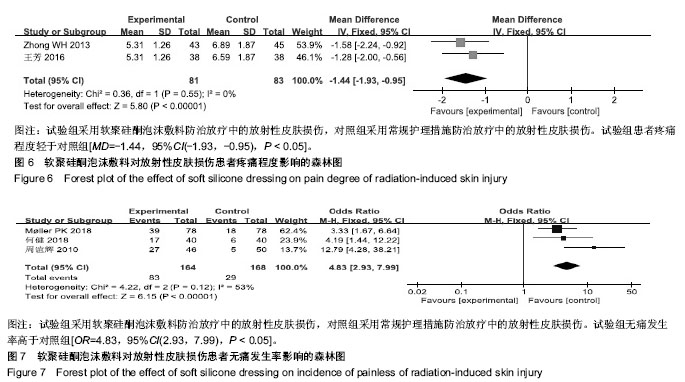
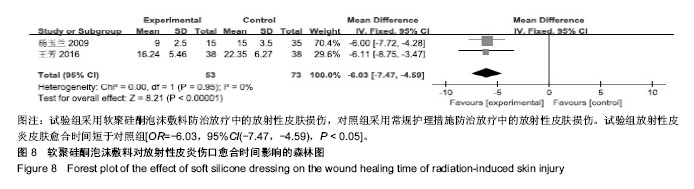
结果与结论:纳入分析文献11篇,包含1 284例癌症患者,其中试验组采用软聚硅酮泡沫敷料防治放疗中的放射性皮肤损伤,对照组采用常规护理措施防治放疗中的放射性皮肤损伤。Meta分析显示:与对照组比较,试验组湿性脱屑发生率降低[OR=0.13,95%CI(0.09,0.19),P < 0.05]、Ⅱ,Ⅲ,Ⅳ级皮肤损伤发生率降低[OR=0.30,95%CI(0.21,0.44),P < 0.05;OR=0.14,95%CI(0.07,0.28),P < 0.05;OR=0.06,95%CI(0.01,0.47),P < 0.05]、RISRAS联合评分减低[OR=-1.12,95%CI(-2.21,-0.04),P < 0.05]、患者疼痛程度减轻[MD=-1.44,95%CI(-1.93,-0.95),P < 0.05]、无痛发生率增加[OR=4.83,95%CI(2.93,7.99),P < 0.05]、伤口愈合时间缩短[OR=-6.03,95%CI(-7.47,-4.59),P < 0.05]。结果表明与常规干预措施比较,软聚硅酮泡沫敷料具有减轻放射性皮肤损伤严重程度、降低伤口疼痛程度及缩短伤口愈合时间的优势,是一种合理有效的防治放射性皮肤损伤方式。
中图分类号:

.jpg)