| [1]Singh A, Singh G, Chawla V. Characterization and mechanical behaviour of reinforced hydroxyapatite coatings deposited by vacuum plasma spray on SS-316L alloy. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;79:273.[2]Salih V, Georgiou G, Knowles JC, et al. Glass reinforced hydroxyapatite for hard tissue surgery--part II: in vitro evaluation of bone cell growth and function.Biomaterials. 2001;22(20):2817-2824.[3]Kim HW,Georgiou G,Knowles JC,et al.Calcium phosphates and glass composite coatings on zirconia for enhanced biocompatibility.Biomaterials.2004;25(18):4203.[4]Bhowmick A,Pramanik N,Manna PJ,et al.Development of porous and antimicrobial CTS-PEG-HAP-ZnO nano-composites for bone tissue engineering.Rsc Adv. 2015; 5(120):99385-99393.[5]Bhowmick A,Saha A,Pramanik N,et al.Novel magnetic antimicrobial nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering applications.Rsc Adva.2015;5(32):25437-25445. [6]Chou BY,Chang E.Influence of deposition temperature on mechanical properties of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on titanium alloy with ZrO2, intermediate layer.J Therm Spray Technol. 2003;12(2):199-207.[7]Chou BY, Chang E.Interface investigation of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on titanium alloy with ZrO2, intermediate layer as bond coat.Scripta Mater.2001;45(4): 487-493. [8]Müller U,Imwinkelried T, Horst M,et al.Do Human Osteoblasts Grow Into Open-Porous Titanium? Eur Cells and Mater. 2006; 11:8-15.[9]Chang CH,Lin FH,Kuo TF, et al.“Cartilage tissue engineering,” Biomedical Engineering: Applications.Basis Communicat. 2005;17:1-11.[10]Tamai N,Myoui A,Tomita T,et al.Novel hydroxyapatite ceramics with an interconnective porous structure exhibit superior osteoconduction in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 59:110-117.[11]An SH,Matsumoto T,Miyajima H,et al.Porous zirconia/ hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone reconstruction.Dent Mater. 2012;28(12):1221-1231.[12]Kim HW,Shin SY,Kim HE,et al.Bone formation on the apatite-coated zirconia porous scaffolds within a rabbit calvarial defect.J Biomater Appl.2008;22(6):485-504.[13]Quan RF,Tang YH,Huang ZM,et al.Difference of adherence, proliferation and osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on different HA/ZrO2 composites Chin J Traumatol. 2012;15(3):131-139.[14]Shao RX,Quan RF,Wang T,et al. Effects of a bone graft substitute consisting of porous gradient HA/ZrO2 and gelatin/chitosan slow-release hydrogel containing BMP-2 and BMSCs on lumbar vertebral defect repair in rhesus monkey. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2017;96(42):e8309.[15]Franco-Bernardes MF,Rocha OP,Pereira LC,et al.The herbicides trifluralin and tebuthiuron have no genotoxic or mutagenic potential as evidenced by genetic tests.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017;(1):1-9.[16]Li R,Ma Y,Zhang Y,et al.Potential of rhBMP-2 and dexamethasone-loaded Zein/PLLA scaffolds for enhanced in vitro osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;169:384.[17]Ressler A,Ródenas-Rochina A,Ivankovi? J,et al.Injectable chitosan-hydroxyapatite hydrogels promote the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;197:469-477. [18]Yu X,Liu S,Chen H,et al. CGRP gene-modified rBMSCs show better osteogenic differentiation capacity in vitro. J Mol Histol. 2018;49(4):357-367.[19]Ao HY,Xie YT,Yang SB,et al.Covalently immobilised type I collagen facilitates osteoconduction and osseointegration of titanium coated implants. J Orthop Translat.2016;5(5):16-25.[20]Greil P.Active‐Filler‐Controlled Pyrolysis of Preceramic Polymers.J Am Ceram Soc.2010;78(4):835-848.[21]Hench LL, Polak JM. Third-Generation Biomedical Materials. Science. 2002;295(5557):1014-1017.[22]Feng B,Weng J,Yang BC,et al.Characterization of surface oxide films on titanium and adhesion of osteoblast. Biomaterials.2003;24(25):4663.[23]Anselme K,Ponche A,Bigerelle M.Relative influence of surface topography and surface chemistry on cell response to bone implant materials. Part 2: biological aspects.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2010; 224(12):1487-507.[24]Zinger O,Anselme K,Denzer A,et al.Time-dependent morphology and adhesion of osteoblastic cells on titanium model surfaces featuring scale-resolved topography. Biomaterials. 2004;25(14):2695-2711.[25]Jiang L,Li Y,Wang X,et al.Preparation and properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose composite scaffold.Carbohydr Polym. 2008;74(3):680-684.[26]Jin QM,Takita H,Kohgo T,et al.Effects of geometry of hydroxyapatite as a cell substratum in BMP-induced ectopic bone formation. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(3):491-499.[27]王春燕,全仁夫,汪宏斌,等.HA粉末与烧结体的高温分解及再生特性[J].武汉理工大学学报, 2010,32(21):18-21.[28]全仁夫,杨迪生,苗旭东,等.二氧化锆梯度复合羟基磷灰石的生物相容性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2006,20(5):569-573.[29]Azqueta A,Lorenzo Y,Collins AR. In vitro comet assay for DNA repair: a warningconcerning application to cultured cells. Mutagenesis.2009;24:379-381.[30]Yamarik TA. Safety assessment of dichlorophene and chlorophene.Int J Toxicol.2004;23 Suppl 1:1-27.[31]Krucińska I,?ywicka B,Komisarczyk A,et al. Biological Properties of Low-Toxicity PLGA and PLGA/PHB Fibrous Nanocomposite Implants for Osseous Tissue Regeneration. Part I: Evaluation of Potential Biotoxicity.Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2092.[32]蒋媛,杨杨.二氧化锆的临床研究进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2017,33(2):125-127.[33]Szymonowicz M,Korczynski M,Dobrzynski M,et al. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of High-Temperature Annealed Nanohydroxyapatite in Contact with Fibroblast Cells. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(6):590.[34]孙开瑜,徐铭恩,周永勇.基于3D打印的Ⅰ型胶原涂覆β-TCP骨组织工程支架研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2018,37(3): 335-343.[35]董溪溪,张彤,曹均凯.关于诱导性多潜能干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013,11(4):239-243.[36]Strong M,Farrugia A,Rebulla P.Stem cell and cellular therapy developments. Biologicals. 2009;37(2):103-107.[37]Nasu A,Ikeya M,Yamamoto T,et al. Genetically matched human iPS cells reveal that propensity for cartilage and bone differentiation differs with clones, not cell type of origin.PloS One. 2013; 8(1):e53771-e53771.[38]Chijimatsu R,Ikeya M,Yasui Y,et al.Characterization of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Like Cells Derived From Human iPSCs via Neural Crest Development and Their Application for Osteochondral Repair. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017: 1960965. |
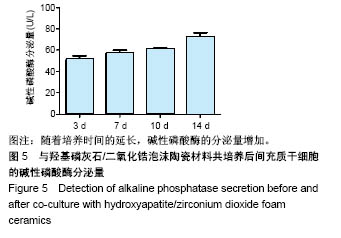
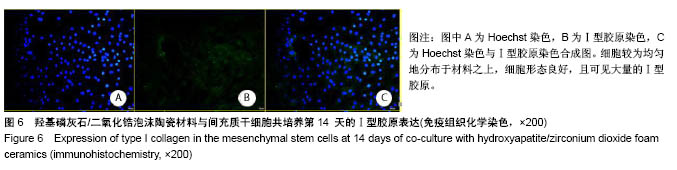
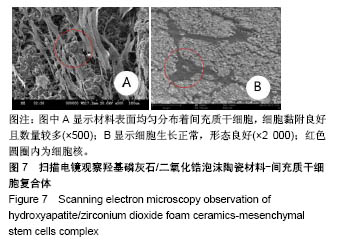
.jpg)

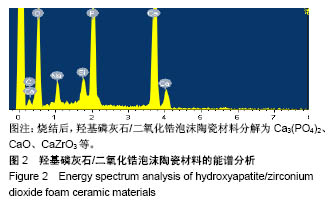
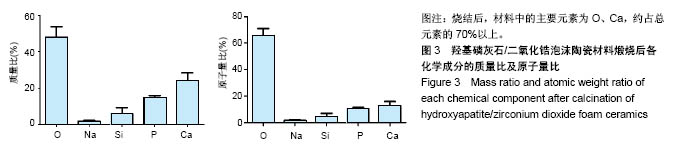
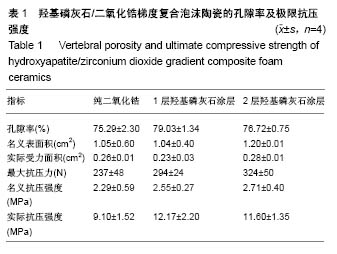
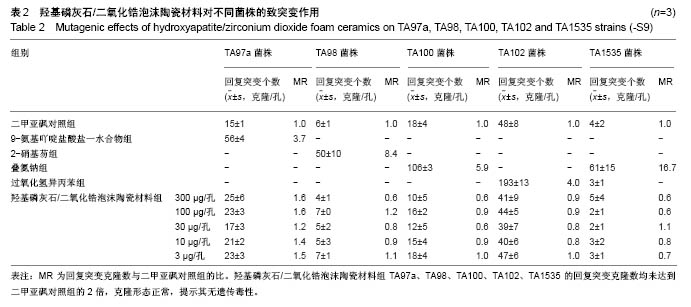
.jpg)