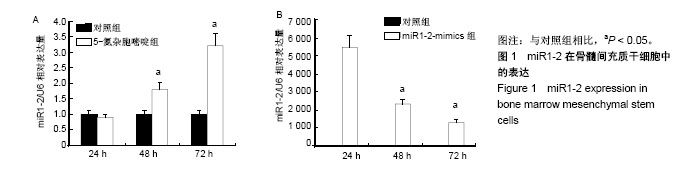
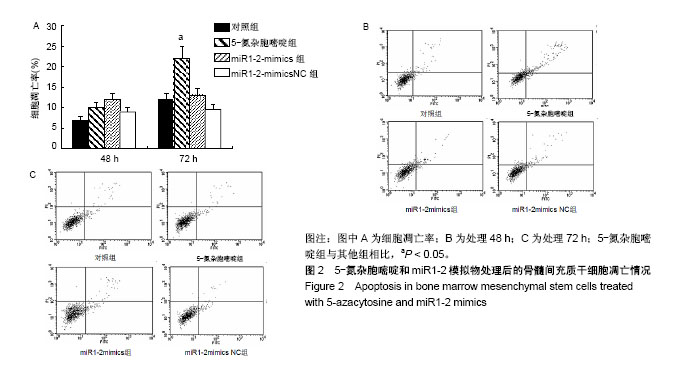
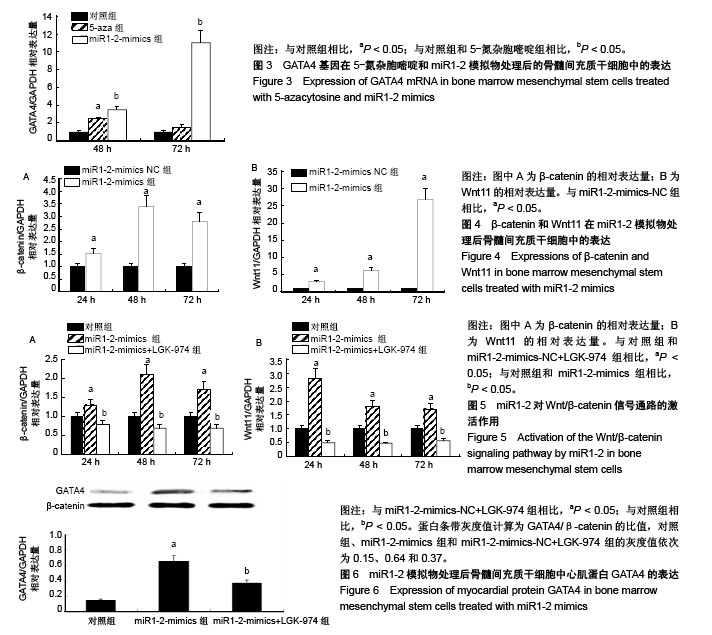
| [1] 牛丽丽,裴雪涛.骨髓间充质干细胞在心血管疾病治疗中的应用[J].中华内科杂志,2003,42(3):208-210.[2] 巫洪坤,梁贵友.间充质干细胞治疗心血管疾病的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2015,21(14):2538-2541.[3] 邹琪,张新超.诱导性多潜能干细胞在心血管疾病中的应用[J].中国心血管杂志,2015(4):313-316.[4] 王宏茂,邱彬,邓然,等.胚胎干细胞对孕鼠缺血受损心肌的修复作用[J].中国实验动物学报,2016,24(2):127-133.[5] 贺继刚,严丹,王平,等.GATA-4在心肌损伤修复中的作用机制研究进展[J].医学综述,2015,21(22):4033-4036.[6] Singh A, Singh A, Sen D. Mesenchymal stem cells in cardiac regeneration: a detailed progress report of the last 6 years (2010-2015). Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):82. [7] 贾晓静,韩艳,潘晋兵.骨髓间充质干细胞通过血管生成作用治疗慢性肾疾病的研究进展[J].国际泌尿系统杂志,2016,36(2).[8] 叶勖,王兴兵,汪健,等.MicroRNA-146a对人骨髓间充质干细胞分化能力的影响[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2016,24(2):596-601.[9] 邵帅,周晨红,徐丽丽.体外诱导骨髓与脐血间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化及其成骨活性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(23):3652-3657.[10] 郑蕊,廖承德,丁莹莹.体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2015(7):1027-1029.[11] Makino S, Fukuda K, Miyoshi S, et al. Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(5):697-705. [12] 孟春风,戴冬秋,郭科军.5-氮杂-2’-脱氧胞苷和曲古抑菌素A对卵巢癌顺铂耐药细胞中hMLH1表达及DNA甲基化的影响[J].癌症, 2008,27(12):1251-1255.[13] 顾忆,李小曼,郑禄枫,等.MicroRNA-10b调控乳腺癌细胞生长增殖与凋亡的研究[J].中国药科大学学报,2015,46(2):242-249.[14] 金向宇,洪卫.microRNA-34a在肺癌细胞凋亡中的作用[J].中华全科医学, 2016,14(6):940-943.[15] 陈宏,陈群,齐鑫,等.microRNA-184在小儿先天性心脏病中的表达及其与心肌细胞的关系[J].医学分子生物学杂志, 2017,14(1):18-21.[16] 王颖,王雷.微小RNA参与心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用机制及研究进展[J].心血管病学进展,2017,38(4):434-438.[17] Sluijter JPG, Mil AV, Vliet PV, et al. MicroRNA-1 and -499 regulate differentiation and proliferation in human-derived cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(4):859. [18] Takaya T, Ono K, Kawamura T, et al. MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133 in spontaneous myocardial differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Circ J. 2009;73(8):1492. [19] Kirby TJ, Chaillou T, Mccarthy JJ. The role of microRNAs in skeletal muscle health and disease. Front Biosci. 2015;20(1):37. [20] 邓海燕,曾俊义,魏云峰,等.microRNA-1诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌样细胞分化过程中Notch信号分子的表达变化[J].基础医学与临床, 2014,34(9):1204-1210.[21] 张怡,赵连三,唐红.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离与培养[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2004,21(5):746-748.[22] 朱淑霞,宋治远,罗向东,等.体外诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为心肌样细胞的研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2005,27(15):1555-1557.[23] Jiang X, Hao HX, Growney JD, et al. Inactivating mutations of RNF43 confer Wnt dependency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(31):12649. [24] Arminan A, Gandia CM. Cardiac differentiation is driven by NKX2. 5 and GATA4 nuclear translocation in tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(6):907-918. [25] 范丽君,肖倩蓉,林凯桑,等.大鼠脂肪干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞向内皮分化的能力比较[J].南方医科大学学报, 2016,36(9):1247-1254.[26] Glass C, Singla DK. MicroRNA-1 transfected embryonic stem cells enhance cardiac myocyte differentiation and inhibit apoptosis by modulating the PTEN/Akt pathway in the infarcted heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;301(5):2038-2049. [27] White RA, Dowler LL, Pasztor LM, et al. Assignment of the transcription factor gata4 gene to human chromosome 8 and mouse chromosome 14:Gata4, is a candidate gene for Ds, (Disorganization). Genomics. 1995;27(1):20-26. [28] Perrino C, Rockman HA. GATA4 and the two sides of gene expression reprogramming. Circ Res. 2006;98(6):715. [29] Zhou P, He A, Pu WT. Chapter five–Regulation of GATA4 Transcriptional Activity in Cardiovascular Development and Disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012;100:143-169. [30] Wang X, Luo E, Bi R, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is required for distraction osteogenesis in rats. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(1):45-54. [31] Geng R, Noda T, Mulvaney JF, et al. Comprehensive expression of wnt signaling pathway genes during development and maturation of the mouse cochlea. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148339. [32] Gwak J, Sun GH, Park HS, et al. Small molecule-based disruption of the Axin/lβ-catenin protein complex regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cell Res. 2012;22(1):237-247. [33] 张建康,卫俊俊,唐曌隆,等.Wnt和Notch通路在老龄个体骨髓间充质干细胞成骨中的调控[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2017,44(4):459-465.[34] 张成,章少中,张亚洲,等.诱导心脏肌成纤维细胞向心肌样细胞转分化的miRNA[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45):7924-7931.[35] Wang T, Xu Z. miR-27 promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;402(2):186-189. [36] Wang J, Guan X, Guo F, et al. miR-30e reciprocally regulates the differentiation of adipocytes and osteoblasts by directly targeting low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(10):e845. |
.jpg)
.jpg)