| [1]王瑞元,周越.骨骼肌与运动[M].北京:人民体育出版社,2013.[2]Armstrong RB,Warren GL,Warren JA.Mechanisms of exercise-induced muscle fiber injury.Sports Med. 1991;12(3):184-207.[3]Armstrong RB.Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscle soreness: a brief review.Med Sci Sport Exerc.1984;16(6):529-538.[4]Barash IA, Peters D, Friden J, et al. Desmin cytoskeletal modification after a bout of eccentric exercise in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Inter Comp Physiol.2002;283(4):R958-R963.[5]马新东,高前进,李俊平.离心运动对细胞外基质蛋白含量及膜完整性的影响[J].北京体育大学学报, 2008, 31(5): 618-622.[6]Bao ZZ,Lakonishok M,Kaufman S,et al.Alpha7 beta1 integrin is a component of the myotendinous junction on skeletal muscle.J Cell Sci.1993;106(Pt2): 579-589.[7]Boppart MD, Burkin DJ, Kaufman SJ. Alpha7beta1-integrin regulates mechanotransduction and prevents skeletal muscle injury.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2006;290(6): C1660-1665.[8]Kaariainen M, Nissinen L, Kaufman S, et al. Expression of alpha7 beta1 integrin splicing variants during skeletal muscle regeneration. Am J Pathol.2002;161(3): 1023-1031.[9]蒋晓萍.低氧?低氧运动对大鼠骨骼肌黏着斑复合体的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2008.[10]Armstrong RB, Ogilvie RW, Schwane JA. Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983;54(1):80-93.[11]Pica A, Brooks GA. Effects of training and age on VO2max in laboratory rats.Med Sci Sports Exerc.1982; 14(3): 249-252.[12]Wong VW,Akaishi S,Longaker MT,et al.Pushing back: would mechanotransduction in repair and regeneration.J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131(11): 2186-2196.[13]Lamon S,Wallace MA,Stefanetti RJ,et al.Regulation of the STARS signaling pathway in response to endurance and resistance exercise and training.Pflugers Arch.2013;465(9): 1317-1325.[14]Emil R,Kristian V.Mechanosensitive molecular networks involved in transducing resistance exercise-signals into muscle protein accretion. Front Physiol.2016;7: 547.[15]Chen HC,Guan JL.Association of focal adhesion kinase with its substrate phosphatidylinositol kinase.Proc Nat Acad Sci USA.1994;91(21): 10148-10152.[16]Burkin DJ,Wallace GQ,Nicol KJ,et al.Enhanced expression of the alpha 7 beta 1 integrin reduces muscular dystrophy and restores viability in dystrophic mice.J Cell Biol.2001;152(6): 1207-1218.[17]Liu J,Milner DJ,Boppart MD,et al.β1D chain increases α7β1 integrin and laminin and protects against sarcolemmal damage in mdx mice.Hum Mol Genet.2012;21(7): 1592-1603.[18]Lueders TN,Zou K,Huntsman HD,et al.The α7β1-integrin accelerates fiber hypertrophy and myogenesis following a single bout of eccentric exercise. Am J Phsiol Cell Physiol.2011;301(4): C938-946.[19]Graham ZA,Touchberry CD,Gupte AA,et al.Changes in α7β1 integrin signaling after eccentric exercise in heat-shocked rat soleus.Muscle Nerve.2015;51(4): 562-568.[20]Rintanen N,Karjalainen M,Alanko J,et al. Calpains promote α2β1 integrin turnover in nonrecycling integrin pathway.Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23(3):448-463.[21]Zhang F, Guo F. Effect of transplantation of cardiac stem cells overexpressing integrin?linked kinase on cardiac function of rats with acute myocardial infarction. Exp Ther Med.2018;16(2): 746-750.[22]Mahmassani ZS, Son K, Pincu Y, et al. α7β1 Integrin regulation of gene transcription in skeletal muscle following an acute bout of eccentric exercise. Am J Phsiol Cell Physiol.2017;312(5): C638-C650.[23]Wang D,Gao CQ,Chen RQ,et al.Focal adhesion kinase and paxillin promote migration and adhesion to fibronectin by swine skeletal muscle satellite cells.Oncotarget.2016;7(21): 30845-30854.[24]Franchi MV,Ruoss S,Valdivieso P,et al.Regional regulation of focal adhesion kinase after concentric and eccentric loading is related to remodelling of human skeletal muscle.Acta Physiol(Oxf). 2018;223(3): e13056.[25]Bataille L,Delon I,Da Ponte JP,et al.Downstream of identity genes: muscle-type-specific regulation of the fusion process.Dev Cell.2010; 19(2): 317-328.[26]Hirth S,Buhler A,Buhrdel JB,et al.Paxillin and Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) Regulate Cardiac Contractility in the Zebrafish Heart. PloS One.2016;11(3): e0150323.[27]Jacob AE,Amack JD,Turner CE.Paxillin Genes and Actomyosin Contractility Regulate Myotome Morphogenesis in Zebrafish. Dev Biol.2017;425(1): 70-84.[28]Silva P,Mendoza P, Rivas S, et al. Hypoxia promotes Rab5 activation, leading to tumor cell migration, invasion and metastasis.Oncotarget. 2016;7(20):29548-29562.[29]Janik ME,Litynska A,Vereecken P.Cell migration-the role of integrin glycosylation.Biochim Biophys Acta.2010;1800(6):545-555.[30]Müller S,Djudjaj S,Lange J,et al.HIF stabilization inhibits renal epithelial cell migration and is associated with cytoskeletal alterations. Sci Rep.2018;8(1):9497. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
整合素:是一种重要的细胞表面受体家族,主要介导细胞与细胞外基质的黏附,使细胞之间得以附着而形成整体,故称整合素。整合素与细胞外基质的相互联系激活黏着斑激酶发生磷酸化,黏着斑激酶的活化在整合素介导的信号转导中占有重要地位,是依赖于整合素的信号转导通路的上游信号传递分子。
黏着斑激酶:是一种非受体酪氨酸激酶,高度表达于肥大骨骼肌中。通过整合素介导的细胞黏附于细胞外基质而激活,并刺激细胞内多种信号通路的活性,如桩蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)信号通路。黏着斑激酶与黏着斑位点的动态调控有关,是黏着斑相关蛋白激酶,这种动态调控是细胞迁移和黏附的关键过程。
文题释义:
整合素:是一种重要的细胞表面受体家族,主要介导细胞与细胞外基质的黏附,使细胞之间得以附着而形成整体,故称整合素。整合素与细胞外基质的相互联系激活黏着斑激酶发生磷酸化,黏着斑激酶的活化在整合素介导的信号转导中占有重要地位,是依赖于整合素的信号转导通路的上游信号传递分子。
黏着斑激酶:是一种非受体酪氨酸激酶,高度表达于肥大骨骼肌中。通过整合素介导的细胞黏附于细胞外基质而激活,并刺激细胞内多种信号通路的活性,如桩蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)信号通路。黏着斑激酶与黏着斑位点的动态调控有关,是黏着斑相关蛋白激酶,这种动态调控是细胞迁移和黏附的关键过程。.jpg) 文题释义:
整合素:是一种重要的细胞表面受体家族,主要介导细胞与细胞外基质的黏附,使细胞之间得以附着而形成整体,故称整合素。整合素与细胞外基质的相互联系激活黏着斑激酶发生磷酸化,黏着斑激酶的活化在整合素介导的信号转导中占有重要地位,是依赖于整合素的信号转导通路的上游信号传递分子。
黏着斑激酶:是一种非受体酪氨酸激酶,高度表达于肥大骨骼肌中。通过整合素介导的细胞黏附于细胞外基质而激活,并刺激细胞内多种信号通路的活性,如桩蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)信号通路。黏着斑激酶与黏着斑位点的动态调控有关,是黏着斑相关蛋白激酶,这种动态调控是细胞迁移和黏附的关键过程。
文题释义:
整合素:是一种重要的细胞表面受体家族,主要介导细胞与细胞外基质的黏附,使细胞之间得以附着而形成整体,故称整合素。整合素与细胞外基质的相互联系激活黏着斑激酶发生磷酸化,黏着斑激酶的活化在整合素介导的信号转导中占有重要地位,是依赖于整合素的信号转导通路的上游信号传递分子。
黏着斑激酶:是一种非受体酪氨酸激酶,高度表达于肥大骨骼肌中。通过整合素介导的细胞黏附于细胞外基质而激活,并刺激细胞内多种信号通路的活性,如桩蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)信号通路。黏着斑激酶与黏着斑位点的动态调控有关,是黏着斑相关蛋白激酶,这种动态调控是细胞迁移和黏附的关键过程。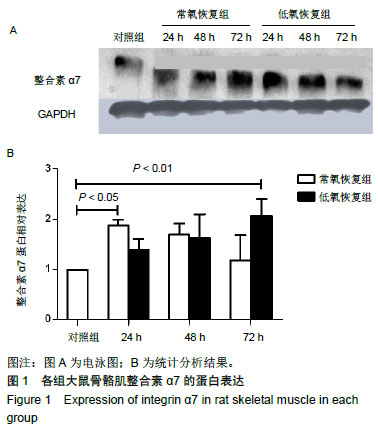
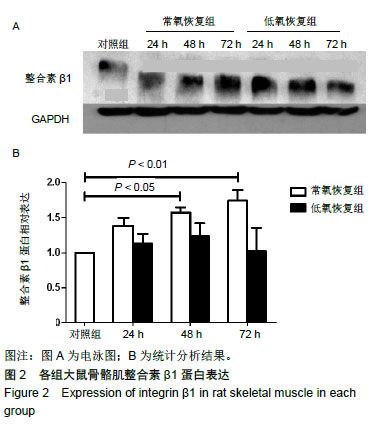
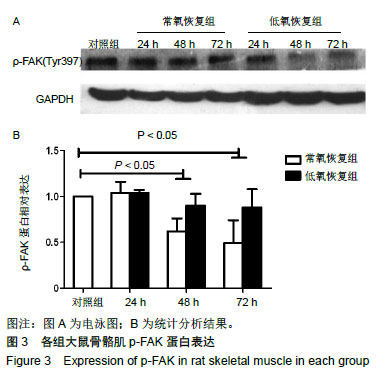
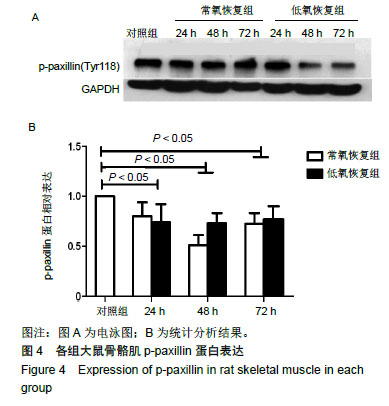
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
整合素:是一种重要的细胞表面受体家族,主要介导细胞与细胞外基质的黏附,使细胞之间得以附着而形成整体,故称整合素。整合素与细胞外基质的相互联系激活黏着斑激酶发生磷酸化,黏着斑激酶的活化在整合素介导的信号转导中占有重要地位,是依赖于整合素的信号转导通路的上游信号传递分子。
黏着斑激酶:是一种非受体酪氨酸激酶,高度表达于肥大骨骼肌中。通过整合素介导的细胞黏附于细胞外基质而激活,并刺激细胞内多种信号通路的活性,如桩蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)信号通路。黏着斑激酶与黏着斑位点的动态调控有关,是黏着斑相关蛋白激酶,这种动态调控是细胞迁移和黏附的关键过程。
文题释义:
整合素:是一种重要的细胞表面受体家族,主要介导细胞与细胞外基质的黏附,使细胞之间得以附着而形成整体,故称整合素。整合素与细胞外基质的相互联系激活黏着斑激酶发生磷酸化,黏着斑激酶的活化在整合素介导的信号转导中占有重要地位,是依赖于整合素的信号转导通路的上游信号传递分子。
黏着斑激酶:是一种非受体酪氨酸激酶,高度表达于肥大骨骼肌中。通过整合素介导的细胞黏附于细胞外基质而激活,并刺激细胞内多种信号通路的活性,如桩蛋白和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)信号通路。黏着斑激酶与黏着斑位点的动态调控有关,是黏着斑相关蛋白激酶,这种动态调控是细胞迁移和黏附的关键过程。