| [1]Sano H,Namekata K,Kimura A,et al.Differential effects of N-acetylcysteine on retinal degeneration in two mouse models of normal tension glaucoma.Cell Death Dis.2019;10(2):75.[2]Spana C, Taylor AW,Yee DG,et al. Probing the Role of Melanocortin Type 1 Receptor Agonists in Diverse Immunological Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2019;9:1535.[3]Storm T,Burgoyne T,Dunaief JL,et al.Selective Ablation of Megalin in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Results in Megaophthalmos, Macromelanosome Formation and Severe Retina Degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2019;60(1):322-330.[4]Xu Z,Fouda AY,Lemtalsi T,et al.Retinal Neuroprotection From Optic Nerve Trauma by Deletion of Arginase 2.Front Neurosc.2018;12:970. [5]FitzGerald P,Sun N,Shibata B,et al.Expression of the type VI intermediate filament proteins CP49 and filensin in the mouse lensepithelium.Mol Vis.2016;22:970-989.[6]Jones W,Rodriguez J,Bassnett S.Targeted deletion of fibrillin-1 in the mouse eye results in ectopia lentis and other ocular phenotypes associated with Marfan syndrome.Dis Model Mech.2019; 12(1). pii:dmm037283.doi: 10.1242/dmm.037283.[7]Jiang J,Shihan MH,Wang Y,et al.Lens Epithelial Cells Initiate an Inflammatory Response Following Cataract Surgery.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2018;59(12):4986-4997. [8]Zhao Y,Wilmarth PA,Cheng C,et al.Proteome-transcriptome analysis and proteome remodeling in mouse lens epithelium and fibers.Exp Eye Res. 2018;179:32-46. [9]张胜男,夏丽坤,胡媛.小鼠角膜组织石蜡切片制作方法的探讨[J].眼科新进展,2011,31(3):208-210.[10]高洪彬,林英,宋向荣,等.六种固定液对小鼠角膜固定效果的比较[J].中国比较医学杂志,2017,27(6):49-52.[11]高延娥,杜秀娟,董卫红,等.心脏灌注固定在大鼠视网膜石蜡切片中的应用[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2016,34(10):1109-1111.[12]张富军,朱昭亮,莫明树.不同方法制作小鼠视网膜组织石蜡切片的比较[J].眼科新进展,2011,31(7):623-628.[13]高洪彬,林英,宋向荣,等.四种固定液对小鼠视网膜固定效果的比较[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2016,32(3):352-353.[14]张亚楠,王子鸣,任广伟,等.不同固定方法制作大鼠眼球组织石蜡切片的比较[J].河北医科大学学报,2014,35(2):233-235.[15]李晶晶,朱鸿,施彩虹.三种方法对大鼠视网膜固定效果的比较研究[J].上海交通大学学报,2011,31(8):1105-1107.[16]于紫燕,王春霞,孙琦,等.3种小鼠晶状体组织石蜡切片固定液的比较[J].中国医科大学学报,2016,45(12):1063-1065.[17]王伟力,许成英,朱国良,等.5种固定液对冷冻切片苏木精-伊红染色法染色质量影响研究[J].海峡药学,2013,25(8):92-94.[18]Saadane A,Mast N,Charvet CD,et al.Retinal and nonocular abnormalities in Cyp27a1-/-Cyp46a1-/- mice with dysfunctional metabolism of cholesterol. Am J Pathol.2014;184(9):2403-2419.[19]Qi Y,Dai X,Zhang H, et al Trans-Corneal Subretinal Injection in Mice and Its Effect on the Function and Morphology of the Retina. PLoS One. 2015; 10(8):e0136523.[20]赵玉琼,陈华.不同固定液对大鼠肝脏组织石蜡切片质量的影响[J].实验动物与比较医学,2014,34(6):486-488.[21]Terada N,Ohno N,Saitoh S,et al.Immunoreactivity of glutamate in mouse retina inner segment of photoreceptors with in vivo cryotechnique.J Histochem Cytochem.2009;57(9):883-888.[22]Farias DR, Simioni C, Poltronieri E, et al.Fine-tuning transmission electron microscopy methods to evaluate the cellular architecture of Ulvacean seaweeds (Chlorophyta).Micron.2017;96:48-56. [23]Chua J,Bozue JA,Klimko CP,et al.Formaldehyde and Glutaraldehyde Inactivation of Bacterial Tier I Select Agents in Tissues.Emerg Infect Dis.2019;25(5).doi: 10.3201/eid2505.180928.[Epub ahead of print][24]Zemmoura I,Blanchard E,Raynal PI,et al.How Klingler's dissection permits exploration of brain structural connectivity? An electron microscopy study of human white matter.Brain Struct Funct.2016; 221(5):2477-2486.[25]Miki M,Ohishi N,Nakamura E,etal.Improved fixation of the whole bodies of fish by a double-fixation method with formalin solution and Bouin's fluid or Davidson's fluid.J Toxicol Pathol.2018;31(3):201-206.[26]Tokuda K,Baron B,Kuramitsu Y,et al.Optimization of fixative solution for retinalmorphology: a comparison with Davidson's fixative and other fixation solutions.Jpn J Ophthalmol.2018;62(4):481-490.[27]Wang H,Yang LL,Ji YL,et al.Different fixative methods influence histological morphology and TUNEL staining in mouse testes.Reprod Toxicol.2016;60:53-61.[28]Atzpodien EA,Jacobsen B,Funk J,et al.Advanced Clinical Imaging and Tissue-based Biomarkers of the Eye for Toxicology Studies in Minipigs. Toxicol Pathol.2016;44(3):398-413.[29]Chidlow G,Dayrnon M,Wood JP,et al.Localization of awide-RANGING panel of antigens in the rat retina by immunohistochemistry: comparison of Davidson’s solution and formalin as fixatives.J Histochem Cytoehem. 201l;59(10):884-898.[30]Chowers G,Cohen M,Marks-Ohana D,et al.Course of SodiumIodate- Induced Retinal Degeneration in Albino and Pigmented Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2017;58(4):2239-2249. |
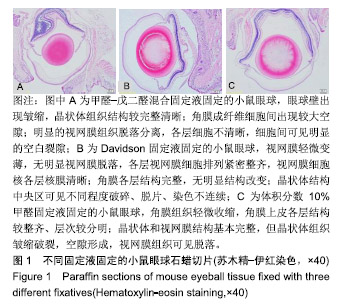
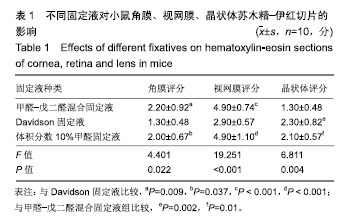
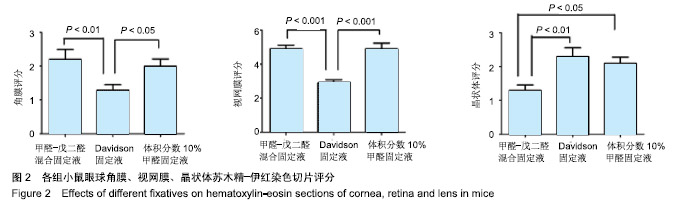
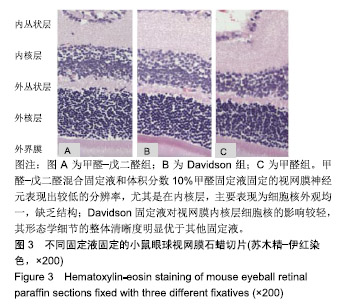
.jpg)
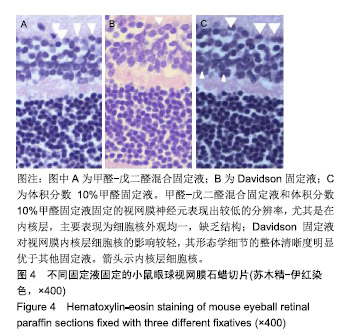
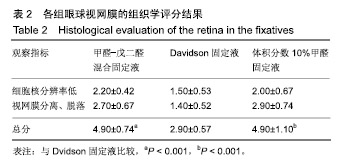
.jpg)