中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3649-3653.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1308
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
三种染色方法观察骨骺损伤后骨桥形成过程的组织形态学特征
潘源城,张信照,陈顺有
- (厦门大学附属福州第二医院小儿骨科,福建省福州市 350007)
Histomorphology of bone bridge formation after epiphyseal injury observed by three staining methods
Pan Yuancheng, Zhang Xinzhao, Chen Shunyou
- (Department of Pediatric Orthopedics, Fuzhou Second Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University, Fuzhou 350007, Fujian Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨桥:指的是相邻的两骨质之间原本属于软组织连接,由于多种原因如骨质增生、韧带钙化等导致两骨质之间变成骨性连接,而使两骨质部分融合,融合的部分称骨桥。常见于儿童的骨骺损伤,骨桥形成后常常影响肢体的骨骼发育。
纤维化(fibrosis):纤维化是医学上的一个概念,纤维化可发生于多种器官,主要病理改变为器官组织内纤维结缔组织增多,实质细胞减少,持续进展可致器官结构破坏和功能减退,乃至衰竭,严重威胁人类健康和生命。
文题释义:
骨桥:指的是相邻的两骨质之间原本属于软组织连接,由于多种原因如骨质增生、韧带钙化等导致两骨质之间变成骨性连接,而使两骨质部分融合,融合的部分称骨桥。常见于儿童的骨骺损伤,骨桥形成后常常影响肢体的骨骼发育。
纤维化(fibrosis):纤维化是医学上的一个概念,纤维化可发生于多种器官,主要病理改变为器官组织内纤维结缔组织增多,实质细胞减少,持续进展可致器官结构破坏和功能减退,乃至衰竭,严重威胁人类健康和生命。
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨桥:指的是相邻的两骨质之间原本属于软组织连接,由于多种原因如骨质增生、韧带钙化等导致两骨质之间变成骨性连接,而使两骨质部分融合,融合的部分称骨桥。常见于儿童的骨骺损伤,骨桥形成后常常影响肢体的骨骼发育。
纤维化(fibrosis):纤维化是医学上的一个概念,纤维化可发生于多种器官,主要病理改变为器官组织内纤维结缔组织增多,实质细胞减少,持续进展可致器官结构破坏和功能减退,乃至衰竭,严重威胁人类健康和生命。
文题释义:
骨桥:指的是相邻的两骨质之间原本属于软组织连接,由于多种原因如骨质增生、韧带钙化等导致两骨质之间变成骨性连接,而使两骨质部分融合,融合的部分称骨桥。常见于儿童的骨骺损伤,骨桥形成后常常影响肢体的骨骼发育。
纤维化(fibrosis):纤维化是医学上的一个概念,纤维化可发生于多种器官,主要病理改变为器官组织内纤维结缔组织增多,实质细胞减少,持续进展可致器官结构破坏和功能减退,乃至衰竭,严重威胁人类健康和生命。摘要
背景:国内外的研究表明,多种染色法联合应用有利于探究骨与软骨组织疾病的形态学表现。目前对于多种染色法探究骨骺损伤后骨桥形成过程的组织形态学表现研究较少。
目的:通过苏木精-伊红染色、番红O-固绿染色、Masson染色3种染色方法观察骨骺损伤后骨桥形成过程的组织形态表现。
方法:SD大鼠40只由福建中医药大学实验动物中心提供,实验方案经福建中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准。随机将40只SD大鼠分为2组:对照组不做处理;模型组建立胫骨近端骨骺损伤模型。分别于造模后1,7,28 d拍摄X射线片和7,28 d行MRI扫描;于造模后1,7,14,28 d麻醉大鼠后取胫骨损伤区组织,行苏木精-伊红染色、番红O-固绿染色、Masson染色,观察术后不同时间点生长板损伤区的组织形态表现。
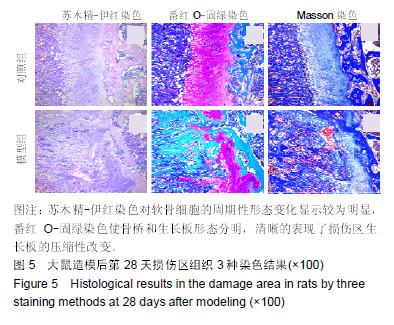
结果与结论:①X射线片显示:造模后1 d,胫骨干骺端骨骺损伤,软骨膜周围生长板间隙增宽;第7天,骨骺损伤处骨膜反应明显;第28天,骨膜反应消失,干骺端与生长板间隙关系基本恢复正常;MRI显示:造模后第28天MRI T2WI示骺板模糊,并可见一黑色线条形低信号影,提示骨桥形成;②造模后第1天,3种染色均可显示入侵的血管,Masson染色更为清晰;第7天:苏木精-伊红染色较番红固绿染色及Masson染色显示了损伤区软骨细胞的形态变化更加明显;第14天,番红O-固绿染色生长板与骨桥对比鲜明,Masson染色可观察到骨桥内尚未骨化的纤维血管组织;第28天,苏木精-伊红染色软骨细胞的周期性形态变化较明显,番红O-固绿染色骨桥和生长板形态分明,可清晰的表现损伤区生长板的压缩性改变;③结果说明,3种染色方法的联合应用能够全面、客观地探究骨骺损伤后骨桥形成过程的组织形态学表现。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨桥:指的是相邻的两骨质之间原本属于软组织连接,由于多种原因如骨质增生、韧带钙化等导致两骨质之间变成骨性连接,而使两骨质部分融合,融合的部分称骨桥。常见于儿童的骨骺损伤,骨桥形成后常常影响肢体的骨骼发育。
纤维化(fibrosis):纤维化是医学上的一个概念,纤维化可发生于多种器官,主要病理改变为器官组织内纤维结缔组织增多,实质细胞减少,持续进展可致器官结构破坏和功能减退,乃至衰竭,严重威胁人类健康和生命。
文题释义:
骨桥:指的是相邻的两骨质之间原本属于软组织连接,由于多种原因如骨质增生、韧带钙化等导致两骨质之间变成骨性连接,而使两骨质部分融合,融合的部分称骨桥。常见于儿童的骨骺损伤,骨桥形成后常常影响肢体的骨骼发育。
纤维化(fibrosis):纤维化是医学上的一个概念,纤维化可发生于多种器官,主要病理改变为器官组织内纤维结缔组织增多,实质细胞减少,持续进展可致器官结构破坏和功能减退,乃至衰竭,严重威胁人类健康和生命。