中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4841-4847.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1409
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
改性木葡聚糖温敏水凝胶的制备及生物相容性评价
闫志文1,李硕峰1,李 傲1,胡梓骐1,马丽桃1,张二帅2,李景武3,姚芳莲2,车鹏程1,孙 红1
- 1华北理工大学基础医学院,河北省慢性病重点实验室,河北省唐山市 063210;2天津大学化工学院高分子科学与工程系,天津市 300350;3唐山市人民医院胃肠外科,河北省唐山市 063001
Preparation and biocompatibility evaluation of modified thermosensitive xyloglucan hydrogels
Yan Zhiwen1, Li Shuofeng1, Li Ao1, Hu Ziqi1, Ma Litao1, Zhang Ershuai2, Li Jingwu3, Yao Fanglian2, Che Pengcheng1, Sun Hong1
- 1Key Laboratory for Chronic Diseases of Hebei Province, School of Basic Medical Sciences, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China; 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Tangshan People’s Hospital, Tangshan 063001, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
温敏水凝胶:是一类通过热刺激引发相转变而形成交联结构的物理凝胶;由于凝胶过程不需要额外的添加剂和化学反应参与,而温度是生物体本身所具备的一种体征,因而自温敏凝胶发现以来,其在生物医用领域的研究和使用一直是人们研究的热点。
生物相容性:是指生物材料植入宿主后不引起宿主明显的不适,无溶血、组织坏死、炎症反应、过敏、中毒等不良反应。
背景:可注射温敏水凝胶能随环境温度变化发生可逆性相转变并可结合微创疗法,在术后防粘连领域得到了广泛关注,但现有的可注射温敏水凝胶在预防术后粘连方面存在生物安全性差及防粘连效果不佳等问题。
目的:制备改性木葡聚糖可注射温敏水凝胶,评价其生物相容性。
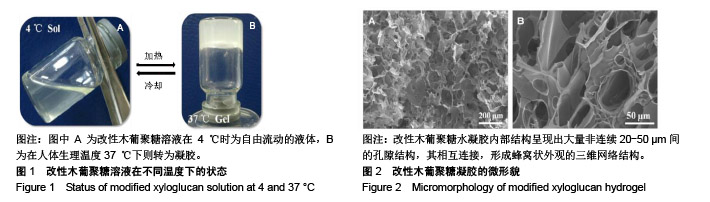
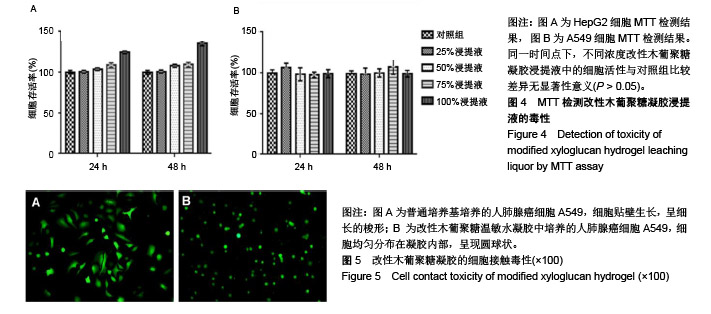
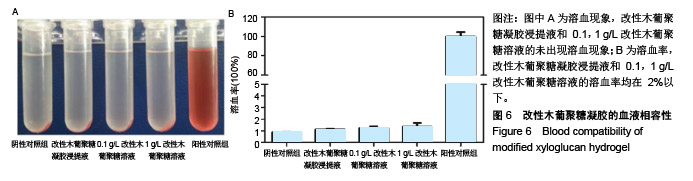
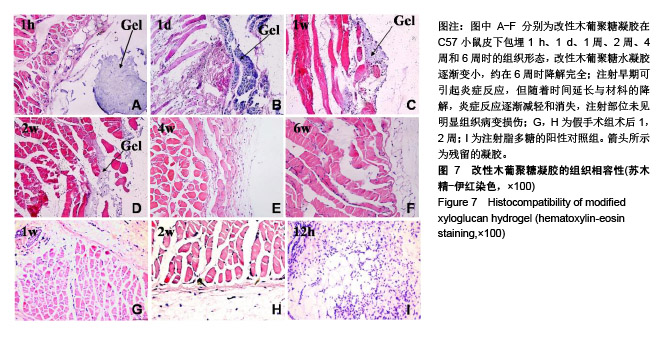
方法:通过温和的酶解反应脱除木葡聚糖侧链的部分半乳糖,得到具有可逆“溶胶-凝胶”转变的改性木葡聚糖可注射温敏水凝胶。通过活/死细胞染色定性检测与MTT法定量检测改性木葡聚糖水凝胶浸提液对人肝癌细胞HepG2和人肺腺癌细胞A549的毒性。将人肺腺癌细胞A549包埋于改性木葡聚糖水凝胶内,培养24 h后观察细胞形态。在抗凝兔血中分别加入改性木葡聚糖水凝胶浸提液与0.1,1 g/L改性木葡聚糖溶液,1 h后检测溶血率。将改性木葡聚糖溶液注射至C57小鼠(中国人民解放军军事医学科学院北京实验动物中心提供)背部皮下,跟踪材料的体内降解行为,评价植入部位及周围组织的炎性反应。动物实验获得华北理工大学实验动物伦理委员会批准,批准号:SYXK(冀)2015-0038。
结果与结论:①AO/PI染色与MTT检测显示,不同浓度改性木葡聚糖水凝胶浸提液中的HepG2细胞、A549细胞增殖活性均在100%左右;②包埋在改性木葡聚糖水凝胶内的A549细胞仍有很好的活性;③改性木葡聚糖水凝胶浸提液与0.1,1 g/L改性木葡聚糖溶液的溶血率均在2%以下;④随着注射时间的延长,动物体内的改性木葡聚糖水凝胶逐渐变小,约在6周时降解完全;注射早期可引起炎症反应,但随着时间延长与材料的降解,炎症反应逐渐减轻和消失,注射部位未见明显组织病变损伤;⑤结果表明,改性木葡聚糖水凝胶具有温敏特性,还有良好的细胞相容性、血液相容性与生物降解性。
中图分类号:


.jpg)