| [1]Dara M, Dadu A, Kremer K, et al. Epidemiology of tuberculosis in WHO European Region and public health response. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 4:549-555.[2]Charosky S, Guigui P, Blamoutier A, et al. Complications and risk factors of primary adult scoliosis surgery: a multicenter study of 306 patients. Spine. 2012;37(8):693-700. [3]O’Shaughnessy BA, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Does a long-fusion “T3-sacrum” portend a worse outcome than a shortfusion “T10-sacrum” in primary surgery for adult scoliosis? Spine. 2012;37(10):884-890.[4]Jin WD, Wang Q, Wang ZL. Complete debridement for treatment of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a clinical curative effect observation. Spine J. 2014;14(6):964-970.[5]武启军,王自立,戈朝晖,等.脊柱单节段前中柱切除后不同节段椎弓根螺钉内固定的稳定性测试[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010, 20(4):267-271.[6]Dreischarf M, Zander T, Shirazi-Adl A, et al. Comparison of eight published static finite element models of the intact lumbar spine: predictive power of models improves when combined together. J Biomech. 2014;47(8):1757-1766.[7]Salem W, Lenders C, Mathieu J. In vivo three-dimensional kinematics of thecervical spine during maximal axial rotation. Man Ther. 2013;18(4):339-344.[8]John JD, Saravana Kumar G, Yoganandan N. Cervical spine morphology and ligament property variations: a finite element study of their influence on sagittal bending characteristics. J Biomech. 2019;85:18-26.[9]Guan W, Sun Y, Qi X, et al. Spinal biomechanics modeling and finite element analysis of surgical instrument interaction. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2019. doi: 10.1080/24699322.2018.1560086.[10]Kamal Z, Rouhi G, Arjmand N, et al. A stability-based model of a growing spine with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a combination of musculoskeletal and finite element approaches. Med Eng Phys. 2019;64:46-55.[11]Xu G, Fu X, Du C. Biomechanical effects of vertebroplasty on thoracolumbar burst fracture with transpedicular fixation: a finite element model analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(4):379-383. [12]刘强,张军,孙树椿.有限元在脊柱生物力学中的应用[J].中国骨伤, 2017,30(2):190-194.[13]伍骥,郑超,黄蓉蓉.重新认识胸腰段脊柱骨折的诊断和治疗[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(6):401-404.[14]王健,李凯,陈博,等.胸腰椎体压缩性骨折三维有限元模型的建立和分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(16):1498-1503。[15]Kumar MN, Joseph B, Manur R. Isolated posterior instrumentation for selected cases of thoraco-lumbar spinal tuberculosis without anterior instrumentation and without anterior or posterior bone grafting. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):624-632.[16]Sterba M, Aubin CÉ, Wagnac E, et al. Effect of impact velocity and ligament mechanical properties on lumbar spine injuries in posterior-anterior impact loading conditions: a finite element study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019. doi: 10.1007/s11517-019-01964-5.[17]Wu Y, Chen CH, Tsuang FY, et al. The stability oflong- segment and short-segment fixation for treating severe burst fractures at the thoracolumbar junction in osteoporotic bone: a finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211676. [18]Yin H, Wang K, Gao Y, et al. Surgical approach and management outcomes for junction tuberculous spondylitis: aretrospective study of 77 patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13(1):312[19]Zhou Y, Li W, Liu J, et al. Comparison of single posterior debridement, bone grafting and instrumentation with single-stage anterior debridement, bone grafting and posterior instrumentation in the treatment ofthoracic and thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis.BMC Surg. 2018;18(1):71.[20]Norton RP, Milne EL, Kaimrajh DN, et al. Biomechanical analysis of four-versus six-screw constructs for short-segment pedicle screw and rod instrumentation of unstable thoracolumbar fractures. 2014;14(8):1734-1739.[21]Wadhwa RK, Thakur JD, Khan IS, et al. Adjustment of suboptimally placed lumbar pedicle screws decreases pullout strength and alters biomechanics of the construct: a pilotcadaveric study. World Neurosurg. 2014;2(14):1878-1880.[22]楚野,梁斌,曾佳兴.腰椎退变性疾病融合术后邻近节段退变的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(2):175-178.[23]Christiansen PA, La Bagnara M, Sure DR, et al. Complications of surgical intervention in adult lumbar scoliosis. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;3(9):281-289.[24]Smith JS, Klineberg E, Lalage V, et al. Prospective multicenter assessment perioperative and minimum-2-year postoperative complication rates associated with adult spinal deformity surgery. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(1):1-14.[25]张会军,鲁增辉,朱昌生.经病椎短钉内固定术治疗短节段脊柱结核的临床分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(2):178-181.[26]刘宁,杨波,贺西京.经皮与Wiltse入路短节段椎弓根钉内固定联合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段脊柱骨折的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(1):9-12.[27]Singh S, Kumaraswamy V, Sharma N, et al. Evaluation of role of anterior debridement and decompression of spinal cord and instrumentation in treatment of tubercular spondylitis. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(3):183-193.[28]Liu SH, Deng ZS, Chen J, et al. Surgical treatment for thoracic spinal tuberculosis with intraspinal abscesses by unilateral vertebral lamina limited decompression via posterior-only approach. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015;40(12):1345-1351.[29]Kim MW, Lee SB, Park JH. Cervical spondyloptosis successfully treated with only posterior short segment fusion using cervical pedicle screw fixation. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2019;59(1):33-38.[30]Kim HJ, Kang KT, Chang BS, et al. Biomechanical analysis of fusion segment rigidity upon stress at both the fusion and adjacent segments:a comparison between unilateral and bilateral pedicle screw fixation. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(5): 1386-1394. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义:
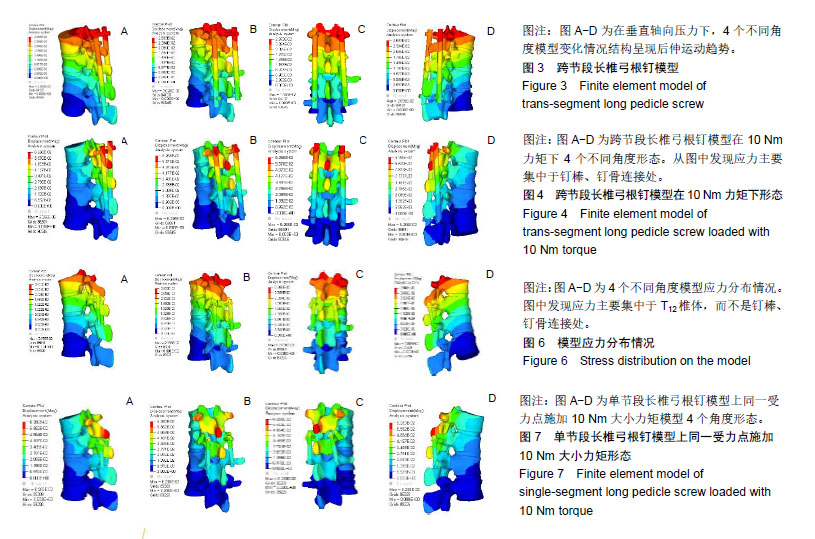

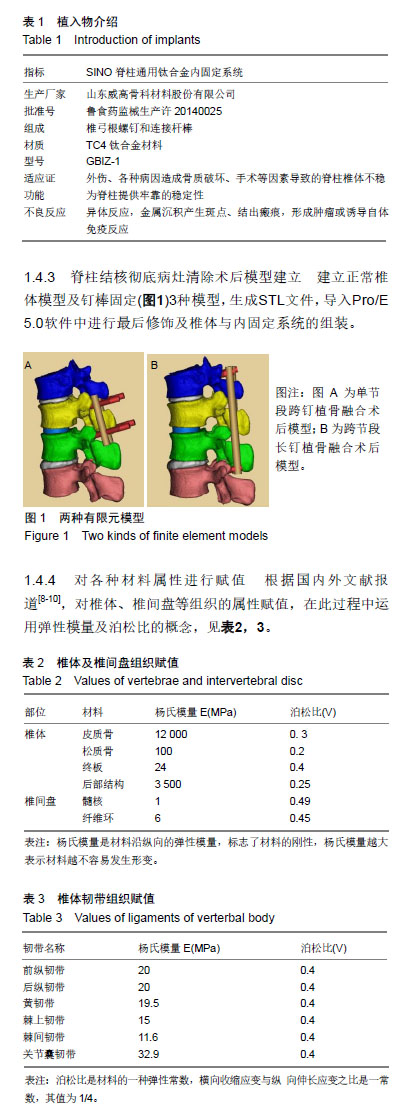
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: