中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4369-4374.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1387
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
有氧运动对梗阻性黄疸模型小鼠肝纤维化治疗的机制
彭 瑞1,陈 伟2,毛海峰1,张 宇1
- (1宜春学院体育学院,江西省宜春市 336000;2湖南师范大学体适能与运动康复湖南省重点实验室,湖南省长沙市 410012)
Mechanism of aerobic exercise treating liver fibrosis in mouse models of obstructive jaundice
Peng Rui1, Chen Wei2, Mao Haifeng1, Zhang Yu1
- (1Sports College of Yichun University, Yichun 336000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness and Exercise Rehabilitation, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:长链非编码 RNA是一类不具有蛋白质编码能力的RNA分子,主要调控机制包括对转录前的调控机制、对染色质重塑的调控机制及对转录后的调控机制。
γ分泌酶:是由4个亚单位组成的膜内蛋白水解酶,主要参与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)和Notch等重要跨膜蛋白的切割和水解过程。早老素为该酶的催化亚单位。任何一个亚单位的表达水平降低都会导致酶复合体形成障碍。
文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:长链非编码 RNA是一类不具有蛋白质编码能力的RNA分子,主要调控机制包括对转录前的调控机制、对染色质重塑的调控机制及对转录后的调控机制。
γ分泌酶:是由4个亚单位组成的膜内蛋白水解酶,主要参与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)和Notch等重要跨膜蛋白的切割和水解过程。早老素为该酶的催化亚单位。任何一个亚单位的表达水平降低都会导致酶复合体形成障碍。
.jpg) 文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:长链非编码 RNA是一类不具有蛋白质编码能力的RNA分子,主要调控机制包括对转录前的调控机制、对染色质重塑的调控机制及对转录后的调控机制。
γ分泌酶:是由4个亚单位组成的膜内蛋白水解酶,主要参与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)和Notch等重要跨膜蛋白的切割和水解过程。早老素为该酶的催化亚单位。任何一个亚单位的表达水平降低都会导致酶复合体形成障碍。
文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:长链非编码 RNA是一类不具有蛋白质编码能力的RNA分子,主要调控机制包括对转录前的调控机制、对染色质重塑的调控机制及对转录后的调控机制。
γ分泌酶:是由4个亚单位组成的膜内蛋白水解酶,主要参与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)和Notch等重要跨膜蛋白的切割和水解过程。早老素为该酶的催化亚单位。任何一个亚单位的表达水平降低都会导致酶复合体形成障碍。摘要
背景:梗阻性黄疸时胆汁淤积造成肝细胞凋亡或坏死致使慢性肝损伤,肝纤维化是机体对其损伤所产生的修复反应,可引发肝功能失调、肝组织硬化等病理改变。
目的:分析基因LincRNA-p21在梗阻性黄疸小鼠肝组织中的表达及生物学功能的关系,并探讨有氧运动干预下LincRNA-p21通过Notch通路对梗阻性黄疸小鼠肝纤维化的改善作用机制。
方法:雄性ICR小鼠35只购于湖南斯莱克景达实验动物有限公司,实验过程已获得湖南师范大学医学伦理委员会的同意(伦审科第2018-183号)。所有ICR小鼠采用胆总管悬挂于腹壁构建梗阻性黄疸模型,随机抽取5只建模小鼠剖腹检查验证造模是否成功。剩余30只小鼠随机分成有氧运动组、模型组和对照组。有氧运动组随后进行有氧运动跑台适应性训练,为期1周:第一两天跑台坡度为零,转速为6 m/min,20 min/d;第三四天跑台坡度为5°,转速为8 m/min,40 min/d;第五六天跑台坡度为8°,转速为10 m/min,60 min/d。适应性训练结束后保持坡度为8°,转速为10 m/min的运动强度,60 min/d,6 d/周,直至第7周麻醉后取材,检测各项指标。
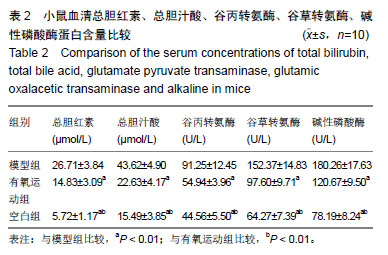
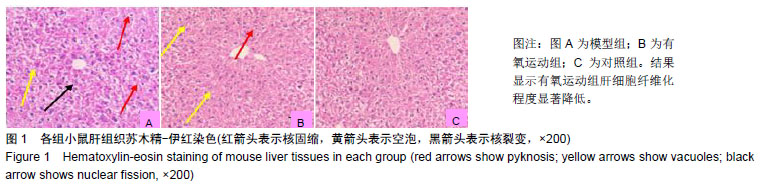
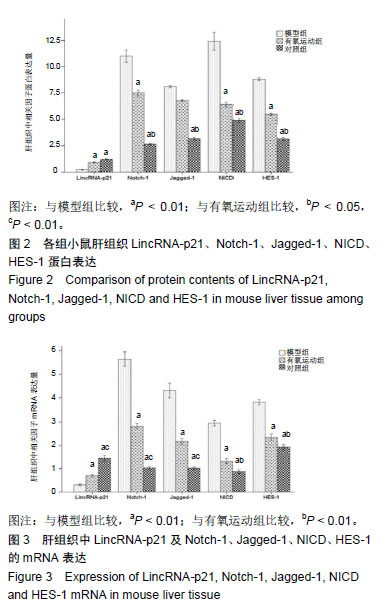
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,模型组血清总胆红素、总胆汁酸、谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶、碱性磷酸酶蛋白浓度显著增高(P < 0.01),有氧运动组相比模型组出现不同程度降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);②模型组苏木精-伊红染色肝细胞大面积纤维化且肝索排列紊乱,出现空泡、变性及坏死症状;与模型组比较,有氧运动组肝细胞纤维化程度显著降低;③与模型组比较,对照组、有氧运动组肝组织LincRNA-p21蛋白及mRNA表达有不同程度升高(P < 0.01);对照组高于有氧运动组;Notch-1、Jagged-1、NICD、HES-1蛋白及mRNA表达模型组最高(P < 0.01),有氧运动组次之;④结果说明,有氧运动干预能促进LincRNA-p21高表达,从而抑制Notch通路参与梗阻性黄疸后小鼠肝纤维化过程,并在一定程度上调节肝损伤后的修复。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:长链非编码 RNA是一类不具有蛋白质编码能力的RNA分子,主要调控机制包括对转录前的调控机制、对染色质重塑的调控机制及对转录后的调控机制。
γ分泌酶:是由4个亚单位组成的膜内蛋白水解酶,主要参与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)和Notch等重要跨膜蛋白的切割和水解过程。早老素为该酶的催化亚单位。任何一个亚单位的表达水平降低都会导致酶复合体形成障碍。
文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:长链非编码 RNA是一类不具有蛋白质编码能力的RNA分子,主要调控机制包括对转录前的调控机制、对染色质重塑的调控机制及对转录后的调控机制。
γ分泌酶:是由4个亚单位组成的膜内蛋白水解酶,主要参与β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)和Notch等重要跨膜蛋白的切割和水解过程。早老素为该酶的催化亚单位。任何一个亚单位的表达水平降低都会导致酶复合体形成障碍。