中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (35): 5626-5632.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1332
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
尿激酶原结合无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应干预模型大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤
刘志远1,张金盈2,刘江波1,赵晓宁1,刘 飞1,李 纲1
- (1南阳市中心医院心血管内科,河南省南阳市 473009;2郑州大学第一附属医院心血管内科,河南省郑州市 450052)
Prourokinase combined with non-invasive delayed limb ischemic preconditioning in rat models of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Liu Zhiyuan1, Zhang Jinying2, Liu Jiangbo1, Zhao Xiaoning1, Liu Fei1, Li Gang1
- (1Department of Vasculocardiology, Nanyang City Central Hospital, Nanyang 473009, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Vasculocardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
缺血预适应:通过经常对人体进行反复的、短暂的、无创伤、无危害的缺血预适应训练,能够激发人体免疫系统的应急机制,产生和释放内源性保护物质(如:腺苷、缓激肽、一氧化氮等,这些物质参与保护心肌和能量代谢)减轻和抵抗随后更长时间因为人体缺血缺氧造成的损伤。
溶栓:应用纤溶酶原激活剂一类的溶栓药物,通过一系列蛋白酶催化连锁反应,直接或间接的使血栓中的纤维蛋白溶解,从而使被阻塞的血管再通。
.jpg)
文题释义:
缺血预适应:通过经常对人体进行反复的、短暂的、无创伤、无危害的缺血预适应训练,能够激发人体免疫系统的应急机制,产生和释放内源性保护物质(如:腺苷、缓激肽、一氧化氮等,这些物质参与保护心肌和能量代谢)减轻和抵抗随后更长时间因为人体缺血缺氧造成的损伤。
溶栓:应用纤溶酶原激活剂一类的溶栓药物,通过一系列蛋白酶催化连锁反应,直接或间接的使血栓中的纤维蛋白溶解,从而使被阻塞的血管再通。
摘要
背景:研究发现,尿激酶原具有较好的溶解血凝块和血栓的作用,可以改善急性心肌梗死后的再灌注损伤。无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应是机体在反复短暂缺血预适应后重新出现保护作用。
目的:分析尿激酶原结合无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的影响。
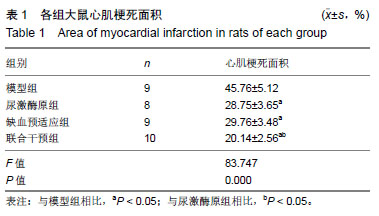
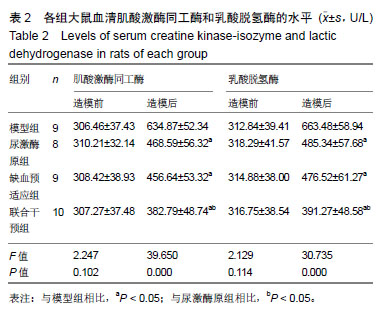
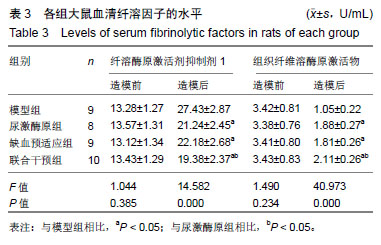
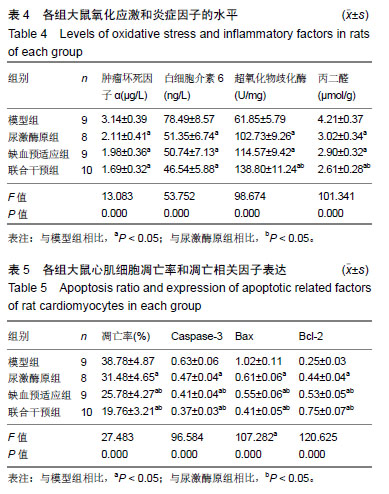
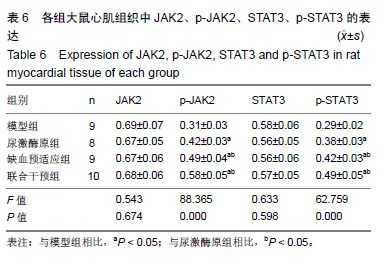
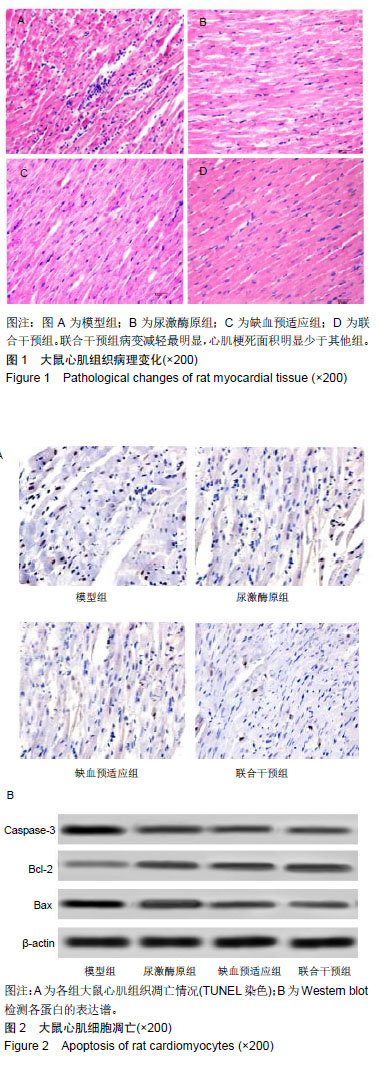
方法:实验方案经郑州大学实验动物伦理委员会批准(批准号为1811034)。将40只SD大鼠随机分为模型组、尿激酶原组、缺血预适应组和联合干预组各10只。造模前,缺血预适应组和联合干预组大鼠进行无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应3 d,尿激酶原组和联合干预组给予尾静脉注射尿激酶原。各组大鼠采用手术结扎法制备心肌缺血再灌注模型。于造模前后,检测血清中肌酸激酶同工酶、乳酸脱氢酶、纤溶酶原激活剂抑制剂1和组织纤维溶酶原激活物水平;造模后,苏木精-伊红染色检测大鼠心肌组织损伤,试剂盒检测肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、心肌组织超氧化物歧化酶和丙二醛水平;Western Blot检测酪氨酸激酶JAK2、p-JAK2、信号传导转录启动因子3(STAT3)、p-STAT3、Caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2的表达。
结果与结论:①与模型组相比,尿激酶原组、缺血预适应组和联合干预组大鼠心肌梗死面积明显减少(P < 0.05),联合干预组心肌梗死面积明显少于其他组(P < 0.05);②与模型组相比,其他3组肌酸激酶同工酶、乳酸脱氢酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、丙二醛水平、纤溶酶原激活剂抑制剂1活性明显降低(P < 0.05),联合干预组各指标明显低于其他组(P < 0.05);③与模型组相比,其他3组组织纤维溶酶原激活物、超氧化物歧化酶活性明显升高(P < 0.05),④与模型组相比,其他3组心肌组织细胞凋亡率明显下降(P < 0.05);心肌组织Caspase-3、Bax的表达量明显下调(P < 0.05),联合干预组2项指标明显低于其他组(P < 0.05);⑤与模型组相比,其他3组Bcl-2、p-JAK2、p-STAT3的表达量明显上调(P < 0.05),联合干预组3项指标明表达量明显高于其他组;⑥结果说明,尿激酶原联合无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应可以改善心肌缺血再灌注心肌损伤和功能障碍,其作用机制可能与JAK2/STAT3信号通路有关。
背景:研究发现,尿激酶原具有较好的溶解血凝块和血栓的作用,可以改善急性心肌梗死后的再灌注损伤。无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应是机体在反复短暂缺血预适应后重新出现保护作用。
目的:分析尿激酶原结合无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的影响。
方法:实验方案经郑州大学实验动物伦理委员会批准(批准号为1811034)。将40只SD大鼠随机分为模型组、尿激酶原组、缺血预适应组和联合干预组各10只。造模前,缺血预适应组和联合干预组大鼠进行无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应3 d,尿激酶原组和联合干预组给予尾静脉注射尿激酶原。各组大鼠采用手术结扎法制备心肌缺血再灌注模型。于造模前后,检测血清中肌酸激酶同工酶、乳酸脱氢酶、纤溶酶原激活剂抑制剂1和组织纤维溶酶原激活物水平;造模后,苏木精-伊红染色检测大鼠心肌组织损伤,试剂盒检测肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、心肌组织超氧化物歧化酶和丙二醛水平;Western Blot检测酪氨酸激酶JAK2、p-JAK2、信号传导转录启动因子3(STAT3)、p-STAT3、Caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2的表达。
结果与结论:①与模型组相比,尿激酶原组、缺血预适应组和联合干预组大鼠心肌梗死面积明显减少(P < 0.05),联合干预组心肌梗死面积明显少于其他组(P < 0.05);②与模型组相比,其他3组肌酸激酶同工酶、乳酸脱氢酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、丙二醛水平、纤溶酶原激活剂抑制剂1活性明显降低(P < 0.05),联合干预组各指标明显低于其他组(P < 0.05);③与模型组相比,其他3组组织纤维溶酶原激活物、超氧化物歧化酶活性明显升高(P < 0.05),④与模型组相比,其他3组心肌组织细胞凋亡率明显下降(P < 0.05);心肌组织Caspase-3、Bax的表达量明显下调(P < 0.05),联合干预组2项指标明显低于其他组(P < 0.05);⑤与模型组相比,其他3组Bcl-2、p-JAK2、p-STAT3的表达量明显上调(P < 0.05),联合干预组3项指标明表达量明显高于其他组;⑥结果说明,尿激酶原联合无创性延迟肢体缺血预适应可以改善心肌缺血再灌注心肌损伤和功能障碍,其作用机制可能与JAK2/STAT3信号通路有关。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
缺血预适应:通过经常对人体进行反复的、短暂的、无创伤、无危害的缺血预适应训练,能够激发人体免疫系统的应急机制,产生和释放内源性保护物质(如:腺苷、缓激肽、一氧化氮等,这些物质参与保护心肌和能量代谢)减轻和抵抗随后更长时间因为人体缺血缺氧造成的损伤。#br#
溶栓:应用纤溶酶原激活剂一类的溶栓药物,通过一系列蛋白酶催化连锁反应,直接或间接的使血栓中的纤维蛋白溶解,从而使被阻塞的血管再通。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
缺血预适应:通过经常对人体进行反复的、短暂的、无创伤、无危害的缺血预适应训练,能够激发人体免疫系统的应急机制,产生和释放内源性保护物质(如:腺苷、缓激肽、一氧化氮等,这些物质参与保护心肌和能量代谢)减轻和抵抗随后更长时间因为人体缺血缺氧造成的损伤。#br#
溶栓:应用纤溶酶原激活剂一类的溶栓药物,通过一系列蛋白酶催化连锁反应,直接或间接的使血栓中的纤维蛋白溶解,从而使被阻塞的血管再通。