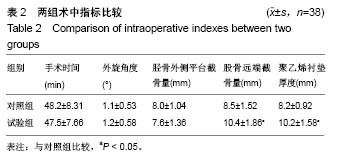
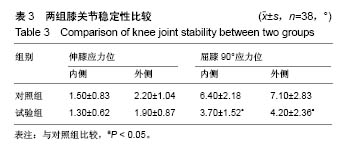
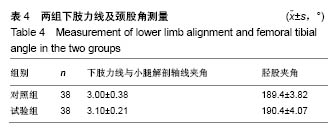
| [1]钟航,黄强,杨静,等.人工全膝关节置换中滑移截骨矫正重度外翻畸形的疗效观察[J].中国修复重外科杂志,2016,2(2):143-147.[2]谢军,刘巍,袁凤来.股骨假体旋转角对全膝关节置换后膝关节功能恢复影响的3年随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4283-4287.[3]Tsukeoka T, Tsuneizumi Y, Yoshino K. The rectangular flexion gap is associated with an increased knee flexion angle in a cruciate-sacrificing rotating platform mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(2):313-317. [4]吴搏,王岩,张国强,等.两种股骨截骨角度对膝关节置换中股骨假体冠状位对线的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(9):838-843.[5]Eid AS, Nassar WAM, Fayyad TAM. Total knee replacement with tibial tubercle osteotomy in rheumatoid patients with stiff knee. Int Orthop. 2016;40(11):1-5. [6]Nagai K, Muratsu H, Takeoka Y, et al. The influence of joint distraction force on the soft-tissue balance using modified gap-balancing technique in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(10):2995-2999. [7]杨帆,张庆猛,李恒,等.个性化截骨技术在全膝关节置换中临床应用和疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(17):1571-1575.[8]洪伟祥,冯建民,王毅,等.测量截骨与间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换中应用的中期随访比较[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(4):255-259.[9]Heesterbeek PJ, Haffner N, Wymenga AB, et al. Patient-related factors influence stiffness of the soft tissue complex during intraoperative gap balancing in cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9): 2760-2768. [10]林治平,汤炀炀,谭宏昌,等.单髁置换术与全膝关节置换治疗膝单间室骨性关节炎的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(4): 424-425.[11]Saragaglia D, Massfelder J, Refaie R, et al. Computer-assisted total knee replacement after medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy: medium-term results in a series of ninety cases. Int Orthop. 2016;40(1):35-40. [12]汪锡龙,尚希福,李国远,等.个体化股骨远端外翻角度截骨技术在初次人工全膝关节置换中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,1(1): 27-30.[13]刘璞,蔡谞,吴厦.全膝关节置换中切除后交叉韧带和松解内侧副韧带浅层对关节间隙的影响[J].解放军医学院学报,2015,36(5):454-457.[14]赵宇驰,王诗军,赵中原,等.全膝关节置换中截骨技术对下肢动态力线影响的数学分析[J].中华外科杂志,2016,54(4):241-246.[15]康波,丁韶龙.关节镜下清理结合腓骨上段部分截骨治疗膝关节骨性关节炎[J].临床骨科杂志,2017,20(4):486-486.[16]Tang H, Chen H, Yang D, et al. Distinctions of introarticular force distribution between genesis-II posterior stabilized and cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty: an intraoperative comparative study of 45 patients. Clin Biomech. 2017;42:1-8. [17]杨朝君,孙智文,田洪涛.腓骨近端截骨术与人工全膝关节置换治疗内翻型膝关节骨关节炎的短期疗效比较[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2016,2(1):38-43.[18]廖红兴,邹学农,黄健,等.个体化置换前模拟截骨在全膝关节置换胫骨平台假体选择中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(4):470-475.[19]李广伟,王红军,孙晓智,等.全膝关节置换修复膝内翻畸形:胫股角及膝关节活动度随访评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(9):1313-1320.[20]吴厦,蔡谞,缪力,等.膝关节置换中内侧副韧带浅层贴骨剥离松解的效用分析[J].解放军医学院学报,2015,36(7):710-712.[21]黄承,徐斌,王瑞,等.关节镜清理辅助腓骨近端截骨术治疗伴内翻畸形内侧胫股关节骨关节炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(9):850-852.[22]王伟刚,张勇.膝关节炎合并外翻畸形全膝关节置换的疗效评价[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):860-862.[23]黄一帆,张国栋,王国华,等.两种确定股骨外旋截骨的方式对膝关节置换置换后患者下蹲功能的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(11): 670-675.[24]蒋超,叶灿华,钱文伟,等.人工全膝关节置换中两种截骨技术的系统评价[J].骨科,2016,7(5):322-327.[25]Wdahl A, Robertsson O. Similar outcome for total knee arthroplasty after previous high tibial osteotomy and for total knee arthroplasty as the first measure. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(4): 395-400. [26]彭育沁,顾叶,薛峰,等.单髁膝关节置换与全膝关节置换治疗膝关节内侧单间室退变的疗效[J].山东医药,2016,56(37):84-86.齐志远,陈秀民,王在斌,等.全膝关节置换中测量截骨与间隙平衡截骨的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(2):144-1 |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)