| [1] 王富友,杨柳,段小军,等. 人体正常膝关节钙化软骨层组成成分研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2008, 30(8): 687-690.[2] Wang F, Ying Z, Duan X, et al. Histomorphometric analysis of adult articular calcified cartilage zone. J Struct Biol. 2009; 168(3): 359-365.[3] Gupta HS et al. Two different correlations between nanoindentation modulus and mineral content in the bone-cartilage interface. J Struct Biol. 2005;149(2):138-148.[4] Flachsmann R, Broom ND, Hardy AE, et al. Why is the adolescent joint particularly susceptible to osteochondral shear fracture? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;1(381): 212-221.[5] Hargrave-Thomas E, van Sloun F, Dickinson M, et al. Multi-scalar mechanical testing of the calcified cartilage and subchondral bone comparing healthy vs early degenerative states. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(10): 1755-1762.[6] Burr DB. Anatomy and physiology of the mineralized tissues: role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthrosis . Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12 Suppl A: S20-30.[7] 宋伟,王富友,杨柳. 关节软骨钙化层研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011,25(11):1339-1342.[8] Norrdin RW, Kawcak CE, Capwell BA, et al. Calcified cartilage morphometry and its relation to subchondral bone remodeling in equine arthrosis. Bone. 1999;24(2):109-114.[9] Zizak I, Roschger P, Paris O, et al. Characteristics of mineral particles in the human bone/cartilage interface. J Struct Biol. 2003;141(3): 208-217.[10] Mente PL, Lewis JL. Elastic modulus of calcified cartilage is an order of magnitude less than that of subchondral bone . J Orthop Res. 1994; 12(5):637-647.[11] Allan KS, Pilliar RM, Wang J, et al. Formation of biphasic constructs containing cartilage with a calcified zone interface. Tissue Eng. 2007; 13(1):167-177.[12] St-Pierre JP, Gan L, Wang J, et al. The incorporation of a zone of calcified cartilage improves the interfacial shear strength between in vitro-formed cartilage and the underlying substrate. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(4):1603-1615.[13] Campbell SE, Ferguson VL, Hurley DC. Nanomechanical mapping of the osteochondral interface with contact resonance force microscopy and nanoindentation. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(12):4389-4396.[14] Stender ME, Carpenter RD, Regueiro RA, et al. An evolutionary model of osteoarthritis including articular cartilage damage, and bone remodeling in a computational study . J Biomech. 2016;49(14): 3502-3508.[15] Anderson DD, Brown TD, Radin EL. The influence of basal cartilage calcification on dynamic juxtaarticular stress transmission. Clin Orthop. 1993;286: 298-307.[16] Dar FH, Aspden RM. A finite element model of an idealized diarthrodial joint to investigate the effects of variation in the mechanical properties of the tissues. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2003;217(5): 341-348.[17] Taylor AM. Metabolic and endocrine diseases, cartilage calcification and arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013; 25(2):198-203.[18] Goldring SR, Goldring MB. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk . Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(11): 632-644.[19] Cheng HW, Luk KD, Cheung KM, et al. In vitro generation of an osteochondral interface from mesenchymal stem cell-collagen microspheres . Biomaterials. 2011;32(6): 1526-1535.[20] Lee WD, Hurtig MB, Pilliar RM, et al. Engineering of hyaline cartilage with a calcified zone using bone marrow stromal cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(8): 1307-1315.[21] 王富友,杨柳,段小军,等. 正常膝关节软骨钙化层形态结构研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(5): 524-527.[22] Simha NK, Jin H, Hall ML, et al. Effect of indenter size on elastic modulus of cartilage measured by indentation. J Biomech Eng. 2007; 129(5): 767-775.[23] Knecht S, Vanwanseele B, Stussi E. A review on the mechanical quality of articular cartilage-implications for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis . Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006;21(10): 999-1012.[24] Byers PD, Brown RA. Cell columns in articular cartilage physes questioned: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1): 3-12.[25] Frisbie DD, CrossM W, McIlwraith C W. A comparative study of articular cartilage thickness in the stifle of animal species used in human preclinical studies compared to articular cartilage thickness in the human knee. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2006;19(3): 142-146.[26] Daubs BM, Markel MD, Manley PA. Histomorphometric analysis of articular cartilage, zone of calcifed cartilage, and subchondral bone plate in femoral heads from clinically normal dogs and dogs with moderate or severe osteoarthritis. Am J Vet Res. 2006;67(10): 1719-1724.[27] Ferguson VL, Bushby AJ, Boyde A. Nanomechanical properties and mineral concentration in articular calcified cartilage and subchondral bone. J Anat. 2003;203(2): 191-202.[28] Malekipour F, Oetomo D, Lee PV. Equine subchondral bone failure threshold under impact compression applied through articular cartilage . J Biomech. 2016;49(10): 2053-2059.[29] Turley SM, Thambyah A, Riggs CM, et al. Microstructural changes in cartilage and bone related to repetitive overloading in an equine athlete model. J Anat. 2014; 224(6): 647-658.[30] 宋伟,杨柳,王富友. 膝关节原发性骨关节炎软骨和软骨下骨病理改变的定量研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011, 25(12): 1434-1439.[31] Burr DB, Radin EL. Microfractures and microcracks in subchondral bone: are they relevant to osteoarthrosis? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2003; 29(4): 675-685. |
.jpg)
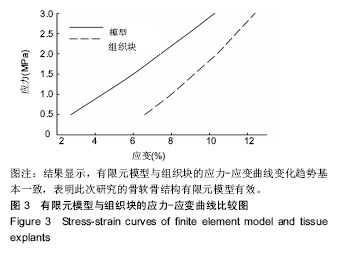

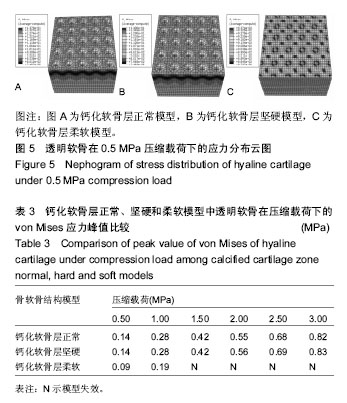
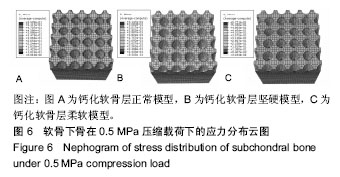
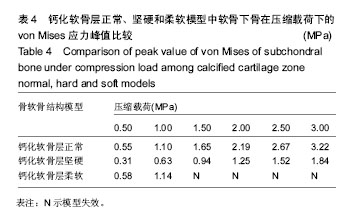
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)