| [1] Taylor CA, Braza D, Rice JB, et al. The incidence of peripheral nerve injury in extremity trauma. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;87(5):381-385. [2] Linley PA, Joseph S. Positive change following trauma and adversity: a review. J Trauma Stress. 2004;17(1):11-21. [3] Jonsson S, Wiberg R, McGrath AM, et al. Effect of delayed peripheral nerve repair on nerve regeneration, Schwann cell function and target muscle recovery. PLoS One. 2013;8(2): e56484. [4] Saito H, Kanje M, Dahlin LB. Delayed nerve repair increases number of caspase 3 stained Schwann cells. Neurosci Lett. 2009;456(1):30-33. [5] Midha R, Munro CA, Chan S, et al. Regeneration into protected and chronically denervated peripheral nerve stumps. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(6):1289-1299;discussion 1289-1299. [6] Boyd JG, Gordon T. A dose-dependent facilitation and inhibition of peripheral nerve regeneration by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;15(4):613-626. [7] Sulaiman OA, Gordon T. Role of chronic Schwann cell denervation in poor functional recovery after nerve injuries and experimental strategies to combat it. Neurosurgery. 2009;65(4 Suppl):A105-114. [8] Jessen KR, Mirsky R. The repair Schwann cell and its function in regenerating nerves. J Physiol. 2016;594(13): 3521-3531. [9] Mohseni MA, Pour JS, Pour JG. Primary and delayed repair and nerve grafting for treatment of cut median and ulnar nerves. Pak J Biol Sci. 2010;13(6):287-292. [10] Ruven C, Li W, Li H, et al. Transplantation of Embryonic Spinal Cord Derived Cells Helps to Prevent Muscle Atrophy after Peripheral Nerve Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):E511. [11] Gu L. Construction of Chinese peripheral nerve society and progress in repair and reconstruction of peripheral nerve injury. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018; 32(7):786-791. [12] Al-Majed AA, Neumann CM, Brushart TM, et al. Brief electrical stimulation promotes the speed and accuracy of motor axonal regeneration. J Neurosci. 2000;20(7): 2602-2608. [13] Gordon T. Electrical Stimulation to Enhance Axon Regeneration After Peripheral Nerve Injuries in Animal Models and Humans. Neurotherapeutics. 2016;13(2): 295-310. [14] Aydin MA, Mackinnon SE, Gu XM, et al. Force deficits in skeletal muscle after delayed reinnervation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113(6):1712-1718. [15] Sulaiman OA, Gordon T. Effects of short- and long-term Schwann cell denervation on peripheral nerve regeneration, myelination, and size. Glia. 2000;32(3):234-246. [16] Zheng J, Sun J, Lu X, et al. BDNF promotes the axonal regrowth after sciatic nerve crush through intrinsic neuronal capability upregulation and distal portion protection. Neurosci Lett. 2016;621:1-8. [17] Pereira Lopes FR, Lisboa BC, Frattini F, et al. Enhancement of sciatic nerve regeneration after vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene therapy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37(6):600-612. [18] Habtemariam S.The brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuronal plasticity and neuroregeneration: new pharmacological concepts for old and new drugs.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(6):983-984.[19] Cheng XL, Wang P, Sun B, et al. The longitudinal epineural incision and complete nerve transection method for modeling sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(10): 1663-1668. [20] Gladman SJ, Huang W, Lim SN, et al. Improved outcome after peripheral nerve injury in mice with increased levels of endogenous ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Neurosci. 2012;32(2):563-571. [21] Daeschler SC, Harhaus L, Schoenle P, et al. Ultrasound and shock-wave stimulation to promote axonal regeneration following nerve surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3168. [22] Li Y, Xiao W, Wu P, et al. The expression of SIRT1 in articular cartilage of patients with knee osteoarthritis and its correlation with disease severity. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):144. [23] Gordon T, Amirjani N, Edwards DC, et al. Brief post-surgical electrical stimulation accelerates axon regeneration and muscle reinnervation without affecting the functional measures in carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Exp Neurol. 2010;223(1):192-202. [24] Güven M, Günay I, Ozgünen K, et al. Effect of pulsed magnetic field on regenerating rat sciatic nerve: an in-vitro electrophysiologic study. Int J Neurosci. 2005;115(6):881-892. [25] Seo N, Lee SH, Ju KW,et al.Low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic field pretreated bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote the regeneration of crush-injured rat mental nerve.Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(1):145-153.[26] Huang J, Hu X, Lu L, et al. Electrical stimulation accelerates motor functional recovery in autograft-repaired 10 mm femoral nerve gap in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(10): 1805-1813. [27] Paolucci T, Piccinini G, Nusca SM, et al. Efficacy of dietary supplement with nutraceutical composed combined with extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic fields in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Phys Ther Sci. 2018;30(6):777-784. [28] Baptista AF, Gomes JR, Oliveira JT, et al. A new approach to assess function after sciatic nerve lesion in the mouse - adaptation of the sciatic static index. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;161(2):259-264. [29] Shenaq JM, Shenaq SM, Spira M. Reliability of sciatic function index in assessing nerve regeneration across a 1 cm gap. Microsurgery. 1989;10(3):214-219. [30] Vögelin E, Baker JM, Gates J, et al. Effects of local continuous release of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) on peripheral nerve regeneration in a rat model. Exp Neurol. 2006;199(2):348-353. [31] Hobson MI, Green CJ, Terenghi G. VEGF enhances intraneural angiogenesis and improves nerve regeneration after axotomy. J Anat. 2000;197 Pt 4:591-605. [32] Wu P, Spinner RJ, Gu Y, et al. Delayed repair of the peripheral nerve: a novel model in the rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci Methods. 2013;214(1):37-44. [33] Navarro X, Vivó M, Valero-Cabré A. Neural plasticity after peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;82(4):163-201. [34] Gordon T, Tyreman N, Raji MA. The basis for diminished functional recovery after delayed peripheral nerve repair. J Neurosci. 2011;31(14):5325-5334. [35] Foecking EM, Fargo KN, Coughlin LM, et al. Single session of brief electrical stimulation immediately following crush injury enhances functional recovery of rat facial nerve. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2012;49(3):451-458. [36] Höke A. Mechanisms of Disease: what factors limit the success of peripheral nerve regeneration in humans? Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006;2(8):448-454. [37] Liu K, Lu Y, Lee JK, et al. PTEN deletion enhances the regenerative ability of adult corticospinal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(9):1075-1081. [38] Cheah M, Fawcett JW, Haenzi B. Differential regenerative ability of sensory and motor neurons. Neurosci Lett. 2017; 652:35-40. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是指频率1-100 Hz,强度低于10 mT的低频、低强度调制磁场,在保留静态磁场治疗作用的基础上,使磁疗辐射产生强度可调的交变脉冲动态磁场;动态磁场强度可从5到100 Hz范围内调节,充分发挥出各个频率磁场的磁疗作用;不同的电磁场强度和频率有不同的生物效应。低频脉冲电磁场作用于神经组织,不产生热效应,而产生类似于流体机械塑形的作用,并通过不对称的宽幅脉冲影响许多异常的生物过程,进而改善神经细胞的病理状态,抑制神经细胞凋亡,促进神经生长。
周围神经损伤的延迟修复:创伤造成的周围神经损伤大多数无法Ⅰ期修复,因需优先处理危及生命的损伤,等待生命体征平稳后再进行Ⅱ期手术修复周围神经的损伤。
文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是指频率1-100 Hz,强度低于10 mT的低频、低强度调制磁场,在保留静态磁场治疗作用的基础上,使磁疗辐射产生强度可调的交变脉冲动态磁场;动态磁场强度可从5到100 Hz范围内调节,充分发挥出各个频率磁场的磁疗作用;不同的电磁场强度和频率有不同的生物效应。低频脉冲电磁场作用于神经组织,不产生热效应,而产生类似于流体机械塑形的作用,并通过不对称的宽幅脉冲影响许多异常的生物过程,进而改善神经细胞的病理状态,抑制神经细胞凋亡,促进神经生长。
周围神经损伤的延迟修复:创伤造成的周围神经损伤大多数无法Ⅰ期修复,因需优先处理危及生命的损伤,等待生命体征平稳后再进行Ⅱ期手术修复周围神经的损伤。.jpg) 文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是指频率1-100 Hz,强度低于10 mT的低频、低强度调制磁场,在保留静态磁场治疗作用的基础上,使磁疗辐射产生强度可调的交变脉冲动态磁场;动态磁场强度可从5到100 Hz范围内调节,充分发挥出各个频率磁场的磁疗作用;不同的电磁场强度和频率有不同的生物效应。低频脉冲电磁场作用于神经组织,不产生热效应,而产生类似于流体机械塑形的作用,并通过不对称的宽幅脉冲影响许多异常的生物过程,进而改善神经细胞的病理状态,抑制神经细胞凋亡,促进神经生长。
周围神经损伤的延迟修复:创伤造成的周围神经损伤大多数无法Ⅰ期修复,因需优先处理危及生命的损伤,等待生命体征平稳后再进行Ⅱ期手术修复周围神经的损伤。
文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是指频率1-100 Hz,强度低于10 mT的低频、低强度调制磁场,在保留静态磁场治疗作用的基础上,使磁疗辐射产生强度可调的交变脉冲动态磁场;动态磁场强度可从5到100 Hz范围内调节,充分发挥出各个频率磁场的磁疗作用;不同的电磁场强度和频率有不同的生物效应。低频脉冲电磁场作用于神经组织,不产生热效应,而产生类似于流体机械塑形的作用,并通过不对称的宽幅脉冲影响许多异常的生物过程,进而改善神经细胞的病理状态,抑制神经细胞凋亡,促进神经生长。
周围神经损伤的延迟修复:创伤造成的周围神经损伤大多数无法Ⅰ期修复,因需优先处理危及生命的损伤,等待生命体征平稳后再进行Ⅱ期手术修复周围神经的损伤。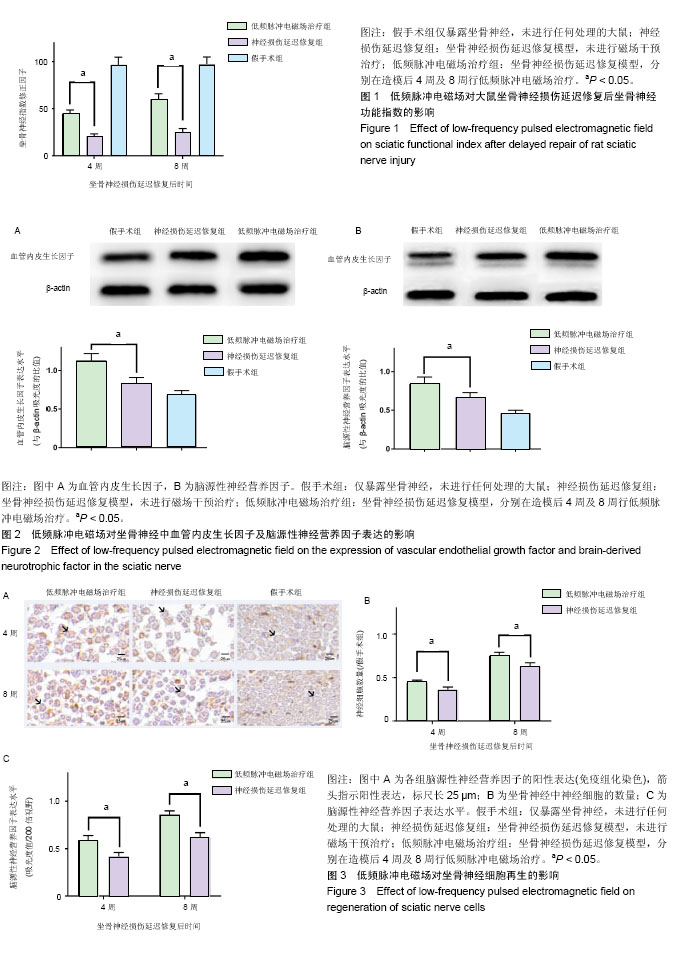
.jpg) 文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是指频率1-100 Hz,强度低于10 mT的低频、低强度调制磁场,在保留静态磁场治疗作用的基础上,使磁疗辐射产生强度可调的交变脉冲动态磁场;动态磁场强度可从5到100 Hz范围内调节,充分发挥出各个频率磁场的磁疗作用;不同的电磁场强度和频率有不同的生物效应。低频脉冲电磁场作用于神经组织,不产生热效应,而产生类似于流体机械塑形的作用,并通过不对称的宽幅脉冲影响许多异常的生物过程,进而改善神经细胞的病理状态,抑制神经细胞凋亡,促进神经生长。
周围神经损伤的延迟修复:创伤造成的周围神经损伤大多数无法Ⅰ期修复,因需优先处理危及生命的损伤,等待生命体征平稳后再进行Ⅱ期手术修复周围神经的损伤。
文题释义:
低频脉冲电磁场:是指频率1-100 Hz,强度低于10 mT的低频、低强度调制磁场,在保留静态磁场治疗作用的基础上,使磁疗辐射产生强度可调的交变脉冲动态磁场;动态磁场强度可从5到100 Hz范围内调节,充分发挥出各个频率磁场的磁疗作用;不同的电磁场强度和频率有不同的生物效应。低频脉冲电磁场作用于神经组织,不产生热效应,而产生类似于流体机械塑形的作用,并通过不对称的宽幅脉冲影响许多异常的生物过程,进而改善神经细胞的病理状态,抑制神经细胞凋亡,促进神经生长。
周围神经损伤的延迟修复:创伤造成的周围神经损伤大多数无法Ⅰ期修复,因需优先处理危及生命的损伤,等待生命体征平稳后再进行Ⅱ期手术修复周围神经的损伤。