中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (35): 5642-5647.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1010
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
三维有限元法分析成人髋关节发育不良重建髋臼的生物力学特征
田丰德1,2,赵德伟1,2,李东怡2,郭 林2,安 宁2,张 耀1,2,程亮亮2,郝瑞胡2,杨 帆1
- 1大连理工大学电子信息与电气工程学部,辽宁省大连市 116024;2大连大学附属中山医院关节外科,辽宁省大连市 116001
Biomechanical properties of acetabular reconstruction in adult developmental dysplasia of the hip by a three-dimensional finite element analysis
Tian Fengde1, 2, Zhao Dewei1, 2, Li Dongyi2, Guo Lin2, An Ning2, Zhang Yao1, 2, Cheng Liangliang2, Hao Ruihu2, Yang Fan1
- 1Faculty of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
髋关节发育不良:是骨关节外科常见疾病,髋臼部位的骨性缺损是成人髋关节发育不良的典型特征之一。该骨性缺损使得髋臼对股骨头包容不足,二者接触面积减少、局部压强增大,久之使得髋关节磨损加快,导致关节炎的发生,因而髋臼缺损是导致和促进髋关节发育不良病情变化的主要因素。
髋臼重建:髋臼缺损是导致和促进髋关节发育不良病情变化的主要因素,将缺损的髋臼重建至正常是髋关节发育不良治疗最理想的方法。自从髋关节发育不良被发现,如何重建髋臼便一直是专家学者们研究的热点,目前重建髋臼方法较多,主要集中于各种关节周围截骨术,通过手术增加髋臼对股骨头的包容,部分患者取得了较满意的临床效果。但由于技术问题(缺损的精确测量、定位及截骨移位深度、旋转角度等),修复后的髋臼仍无法完全与股骨头匹配,使得该方法的临床疗效仍不完美,需要改进提高。
摘要
背景:成人髋关节发育不良目前主要的治疗方法有髋关节周围截骨术、髋臼旋转截骨术、髋臼加盖术等,方法多样,疗效不一。由于技术条件的限制,各种方法虽然不同程度的改善了头臼关系,但距离理想状态仍有一定差距,部分患者因而效果不佳,病情继续发展。
目的:应用三维有限元方法从力学角度分析成人髋关节发育不良髋臼重建的可行性及有效性,为以后的科研及临床研究提供理论依据。
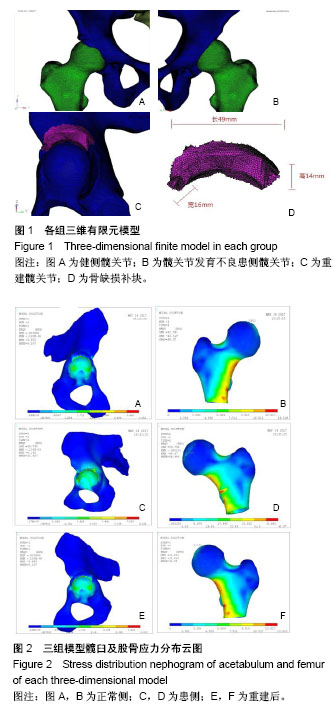
方法:选择单侧髋关节发育不良患者髋关节CT薄层扫描数据,利用Mimics 15.0、Hypermesh软件分别建立健髋及髋关节发育不良患髋模型,利用镜像消减计算患侧髋臼缺损的部位及范围,模拟重建髋臼,建立重建髋关节模型,应用Ansys 10.0加载关节负荷,分析单足着地情况下各髋关节软骨下骨Von Mises应力分布情况。
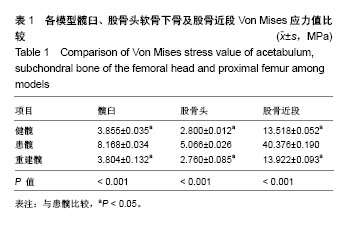
结果与结论:①各模型结果与实际情况相符合,最大Von Mises应力值出现在髋臼顶穹部及股骨颈后内侧;②患髋骨性缺损出现在髋臼前外侧,大小为43 mm×14 mm×7 mm;③应力加载后各组Von Mises应力峰值分别为:健髋股骨头(2.800±0.012)MPa,髋臼(3.855±0.035)MPa;髋关节发育不良患髋股骨头(5.066±0.026)MPa,髋臼(8.168±0.034)MPa;重建髋股骨头(2.769±0.085)MPa,髋臼(3.804±0.132)MPa,统计学分析结果显示髋关节发育不良患髋各部位Von Mises应力峰值明显高于另外二者(P < 0.001),差异有显著性意义;而重建髋与健髋各部位数值相近(P > 0.05),证明髋臼重建后髋关节应力分布恢复正常;④通过有限元模型受力分析证明,髋臼重建能够恢复髋关节力学结构,该方法治疗早期成人髋关节发育不良是可行性的。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8451-7004(田丰德)
中图分类号:
.jpg)