| [1] Cha HS,Kim JW,Hwang JH,et al.Frequency of bone graft in implant surgery.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;38(1):19. [2] Andreas S,Frank W,Marcus H,et al.Autonomic bone grafts in oralimplantology—is it still a “gold standard”?A consecutive review of 279 patients with 456 clinical procedures.Int J Implant Dent.2017;46(1):3-23.[3] 解邦杰,刘成龙,任在上,等.不同类型骨移植材料修复牙周牙槽骨缺损的临床研究[J].全科口腔医学杂志,2016,3(3):95-96.[4] Ashish S,Ibukunolima A,Osama E,et al.Role of bone grafts and bone graftsubstututes in isolated subtalar joint arthrodesis.Acta Ortopedica Brasileira.2017;25(5):183-187.[5] 黄洪超,马信龙,陈晓鹏,等.骨科移植物的分类及其研究进展[J].中国城乡企业卫生,2017,8(8):27-33. [6] Bhatt R.Bone Graft Substitutes.Hand Clinics. 2012;4(23): 457-468.[7] Cypher TJ,Grossman JP.Biological principles of bone graft healing.J Foot Ankle Surg.1996;35(5):413-417.[8] Van Houwelingen AP,McKee MD.Treatment of osteopenic humeral shaft nonunion with compression plating, humeral cortical allograft struts, and bone grafting.J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(1):36-42.[9] Park SM,Um IW.Clinical application of auto—tooth bone graft material.J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;38(1): 2-8.[10] 杨颖,仲维剑,刘国,等.自体骨髓浓缩物修复种植体周围的骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(10):1653-1658.[11] 靳夏莹,那日苏,郑辉,等.评价富血小板纤维蛋白单独用于上颌窦提升种植骨再生的效果[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(26): 4149-4154.[12] Passarelli MC,Filho JRT,Brizzi FAM,et al.Comparison of Puddu osteotomy with or withoutautologous bone grafting: a prospective clinical trial.Rev Bras Ortop.2017;52(5):555-560. [13] Meloni SM,Jovanovic SA,Urban I,et al.Horizontal Ridge Augmentation using GBR with a Native Collagen Membrane and 1:1 Ratio of Particulated Xenograft and Autologous Bone: A 1-Year Prospective Clinical Study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2017;19(1):38-45.[14] Fong EL,Wan X,Yang J,et al.A 3D in vitro model of patient-derived prostate cancer xenograft for controlled interrogation of in vivo tumor-stromal interactions. Biomaterials. 2016;77:164-172.[15] [Irinakis T,Dabuleanu V,Aldahlawi S.Complications During Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Associated with Interfering Septa: A New Classification of Septa.Open Dent J. 2017; 22(11):140-150.[16] Ratushny V,Capell BC,Rosenbach M.Presumed serum sickness following thymoglobulin treatment of acute cellular rejection of a cardiac allograft.Cutis.2017;100(3):186-188.[17] Andratschke M,Hagedorn H.First results of frontal sinus obliteration with a synthetic, resorbable and osteoconductive bone graft of ß-tricalcium phosphate.J Laryngol Otol. 2017; 131(6):534-540.[18] Acharya D,Rajapreyar I.Myocardial perfusion imaging for cardiac allograft vasculopathy assessment: Evidence grows, but questions remain.J Nucl Cardiol.2017.doi: 10.1007/s12350-017-1116-4. [Epub ahead of print][19] Ghate N,Cui H.Mineralized collagen artificial bone repair material products used for fusing the podarthral joints with internal fixation-a case report.Regen Biomater. 2017;4(5): 295-298.[20] Shi Y,Quan R,Xie S,et al.Evaluation of a Novel HA/ZrO2-Based Porous Bioceramic Artificial Vertebral Body Combined with a rhBMP-2/Chitosan Slow-Release Hydrogel. PLoS One.2016;11(7):e0157698.[21] Aldelaimi T,Khalil A.Maxillary Sinus Augmentation.J Craniofac Surg.2016;27(6):557-559.[22] 赖红昌,史俊宇.上颌窦提升术[J].口腔疾病防治, 2017,25(1): 8-12.[23] Boskey AL.Mineralization of bones and teeth. Elements. 2007;3(6):387-393.[24] Kabir MA,Murata M,Akazawa T,et al.Evaluationof perforated demineralized dentin scaffold on bone regeneration in critical-size sheep iliac defects.Clin OralImplants Res. 2017; 28(11):227-235.[25] Li J,Yang J,Zhong X,et al.Demineralized dentin matrix composite collagen materialfor bone tissue regeneration.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2013;24(13):1519-1528.[26] 郁卫东,秦书俭.骨形态发生蛋白-2在骨形成过程中的作用机制[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2000,18(1):82-83.[27] Minamide A,Kawakami M,Hashizume H,et al.Evaluation of carriers of bone morphogenetic proteinfor spinal fusion.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(8):933-939. [28] Ike M,Urist MR.Recycled dentin rootmatrix for a carrier of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein.J Oral Implantol.1998;24(3):124-132.[29] 申丁,仲维剑.牙本质作为骨移植材料的应用研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(6):656-658.[30] Moharamzadeh K,Freeman C,Blackwood K.Processed bovine dentine as a bone substitute.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(2):110-113.[31] Arora S,Kotwal U,Dogra M,et al.Growth Factor Variation in Two Types of Autologous Platelet Biomaterials: PRP Versus PRF.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus.2017;33(2):288-292.[32] Dohan DM,Choukroun J,Diss A,et al.PRF-a second Generation platelet concentrate.Prat two:platelet related biologic features.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):45-50.[33] Cortese A,Pantaleo G,Borri A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in implant dentistry in combination with new bone regenerative technique in elderly patients.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;28: 52-56.[34] Kim SJ,Song DH,Park JW,et al.Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate-Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon-Derived Stem Cells and Rotator Cuff Tendon Tear.Cell Transplant.2017;26(5):867-878.[35] Moatshe G,Morris E,Cinque ME,et al.Biological treatment of the knee with platelet-rich plasma or bone marrow aspirate concentrates.Acta Orthop.2017;88(6):670-674.[36] Dallari D,Fini M,Stagni C,et al.In vitro study on the healing of bone defects treated with bone marrow stromal cells, platelet-rich plasma, and freeze-dried bone allografts, alone and in combination.J Orthop Res.2006;24:877-888.[37] Hisatome T,Yasunaga Y,Yanada S,et al.Neovascularization and bone regeneration by implantation of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells.Biomaterials.2005;26:4550-4556. [38] Lee DH,Ryu KJ,Kim JW,et al.Bone marrow aspirate concentrate and platelet-rich plasma enhanced bone healing in distraction osteogenesis of the tibia.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(12):3789-3797. |
.jpg)
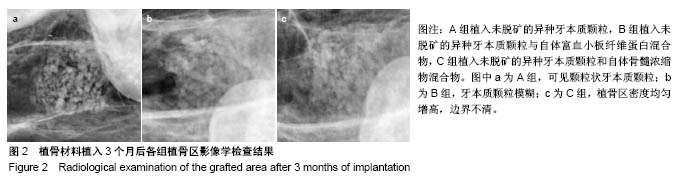
.jpg)
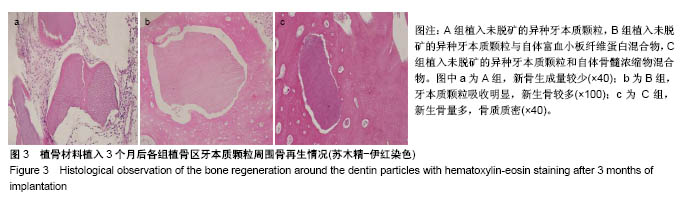
.jpg)