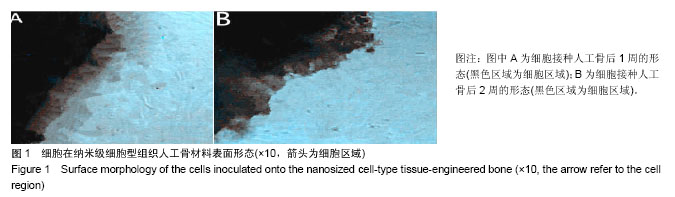
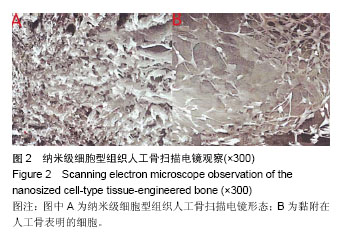
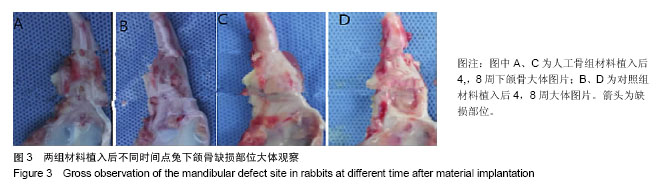
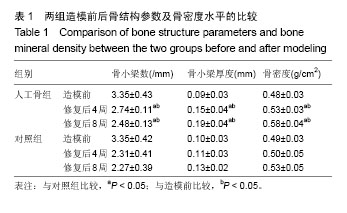
| [1] 张云绮,贾保军,敖建华,等.3D打印技术在下颌骨缺损修复中应用的初步临床研[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(5):517-520.[2] 陈怡憓,刘学蔚,侯绪浩,等.醛化白及多糖/羟丙基壳聚糖/纳米珍珠层粉复合材料促下颌骨缺损修复的动物实验研究[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2016,54(6):7-11.[3] Tompkins M, Hamann JC, Diduch DR, et al. Preliminary results of a novel single-stage cartilage restoration technique: particulated juvenile articular cartilage allograft for chondral defects of the patella. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(10):1661-1670. [4] Bachelet JT, Bourlet J, Château J, et al. Costal grafting in mandibular reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3(11):e565.[5] Colletti G, Autelitano L, Rabbiosi D, et al. Technical refinements in mandibular reconstruction with free fibula flaps: outcome-oriented retrospective review of 99 cases. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2014;34(5):342–348.[6] Huang RL, Kobayashi E, Liu K, et al. Bone Graft Prefabrication Following the In Vivo Bioreactor Principle. EBioMedicine. 2016;12:43-54.[7] Lei PF, Sun RX, Wang L, et al. A new method for xenogeneic bone graft deproteinization: comparative study of radius defects in a rabbit model. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0146005.[8] Gadjanski I, Vunjak-Novakovic G. Challenges in engineering osteochondral tissue grafts with hierarchical structures. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(11):1583-1599.[9] 景彩霞,刘昌奎,谭新颖,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与同种异体骨复合修复犬下颌骨缺损:成骨能力检测[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(14):2138-2143.[10] Maisani M, Pezzoli D, Chassande O, et al.Cellularizing hydrogel-based scaffolds to repair bone tissue: How to create a physiologically relevant micro-environment? J Tissue Eng. 2017;8:2041731417712073.[11] Jang DW, Franco RA, Sarkar SK, et al. Fabrication of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds as artificial bone preform and its biocompatibility evaluation. ASAIO J. 2014;60(2): 216-223.[12] Prakasam M, Locs J, Salma-Ancane K,et al. Fabrication, properties and applications of dense hydroxyapatite: a review.J Funct Biomater. 2015;6(4):1099-1140.[13] Yang K, Wei J, Wang CY, et al. A study on in vitro and in vivo bioactivity of nano hydroxyapatite/polymer biocomposite. Chinese Sci Bull. 2007;52(2):267-271.[14] Ignjatovic N, Ajdukovic Z, Savic V, et al. Nanoparticles of cobalt-substituted hydroxyapatite in regeneration of mandibular osteoporotic bones. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(2):343-354.[15] Ko JY, Kim KI, Park S, et al. In vitro chondrogenesis and in vivo repair of osteochondral defect with human induced pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35(11):3571-3581.[16] Wong KL, Lee KB, Tai BC, et al. Injectable cultured bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in varus knees with cartilage defects undergoing high tibial osteotomy: a prospective,randomized controlled clinical trial with 2 years’ follow-up. Arthroscopy.2013;29(12):2020-2028.[17] 林文清,胡砚平,张文峰.两种血管化游离骨肌瓣移植修复下颌骨缺损临床分析[J].口腔医学研究.2015,31(1):81-84.[18] Krappinger D, Irenberger A, Zegg M, et al. Treatment of large post traumatic tibial bone defects using the Ilizarov method: a subjective outcome assessment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(6):789-795.[19] Vo N, Niedernhofer LJ, Nasto LA, et al. An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(6):831-837. [20] Capeci CM, Turchiano M, Strauss EJ, et al. Osteochondral allografts: applications in treating articular cartilage defects in the knee. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;1(1):60-67. [21] 陈洁,蒋灿华,闵安杰,等.旋髂深动脉穿支嵌合髂骨皮瓣修复下颌骨复合性缺损[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2015,33(3):276-280.[22] Girard PJ, Kuhn KM, Bailey JR, et al. Bone transport combined with locking bridge plate fixation for the treatment of tibial segmental defects: a report of 2 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(9):e220-e226.[23] Qu XZ, Zhang CP, Zhong LP, et al. Deep circumflex iliac artery flap combined with a costochondral graft for mandibular reconstruction. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;49(8): 597-601.[24] Velasco MA, Narváez-Tovar CA, Garzón-Alvarado DA. Design, materials, and mechanobiology of biodegradable scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:729076.[25] Gadjanski I, Vunjak-Novakovic A. Challenges in engineering osteochondral tissue grafts with hierarchical structures Ivana Gadjanski, Gordana Vunjak Novakovic. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015; 15(11): 1583-1599.[26] Best C, Onwuka E, Pepper V, et al. Cardiovascular tissue engineering: preclinical validation to bedside application. Physiology (Bethesda). 2016;31(1):7-15.[27] Rauh J, JacobiA, Stiehler M. Identification of stable reference genes for gene expression analysis of three-dimensional cultivated human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(2):192-206.[28] Tsai MJ, Wu CT. Study of mandible reconstruction using a fibula flap with application of additive manufacturing technology.Biomed Eng Online. 2014;13:57.[29] Parada C, Chai Y. Mandible and tongue development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;115: 31-58.[30] 李超,蔡永聪,王薇,等.计算机辅助设计和制造技术辅助个体化修复下颌骨复杂节段性缺损一例[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016,51(10):780-782. |
.jpg)
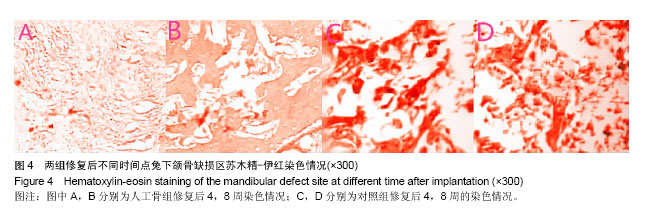
.jpg)