| [1] Usami Y, Gunawardena AT, Iwamoto M, et al.Wnt signaling in cartilage development and diseases: lessons from animal studies. Lab Invest.2016;96(2):186-196.[2] Lotz M.Osteoarthritis year 2011 in review: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2012;20(3):192-196.[3] Clouet J,Vinatier C,Merceron C,et al.From osteoarthritis treatments to future regenerative therapies for cartilage. Drug Discovery Today.2009;14(19-20):913-925.[4] Qi H, Jin M, Duan Y,et al.FGFR3 induces degradation of BMP type I receptor to regulate skeletal development. Biochim Biophys Acta.2014;1843(7):1237-1247.[5] Yuan H, Huang L, Hu X, et al.FGFR3 gene mutation plus GRB10 gene duplication in a patient with achondroplasia plus growth delay with prenatal onset. Orphanet J Rare Dis.2016; 11(1):89.[6] Müller C, Khabut A, Dudhia J, et al.Quantitative proteomics at different depths in human articular cartilage reveals unique patterns of protein distribution. Matrix Biol.2014;40:34-45.[7] Önnerfjord P, Khabut A, Reinholt FP, et al.Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Eight Cartilaginous Tissues Reveals Characteristic Differences as well as Similarities between Subgroups. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(23):18913-18924.[8] Brodsky B, Persikov AV.Molecular structure of the collagen triple helix. Adv Protein Chem.2005;70:301-339.[9] Bäcklund J, Treschow A, Bockermann R, et al.Glycosylation of type II collagen is of major importance for T cell tolerance and pathology in collagen-induced arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32(12):3776-3784.[10] Ota KG, Kuratani S.Expression pattern of two collagen type 2 alpha1 genes in the Japanese inshore hagfish (Eptatretus burgeri) with special reference to the evolution of cartilaginous tissue. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol.2010;314(2):157-165.[11] Yeung Tsang K, Wa Tsang S, Chan D, et al.The chondrocytic journey in endochondral bone growth and skeletal dysplasia. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014;102(1):52-73.[12] Nishimura R, Hata K, Ono K, et al.Regulation of endochondral ossification by transcription factors. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).2012;17: 2657-2666.[13] Ballock RT, O'Keefe RJ.Physiology and pathophysiology of the growth plate. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today.2003; 69(2):123-143.[14] Long F, Ornitz DM.Development of the Endochondral Skeleton. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.2013;5(1):a008334.[15] Hayakawa E, Menschaert G, De Bock PJ, et al.Improving the Identification Rate of Endogenous Peptides Using Electron Transfer Dissociation and Collision-Induced Dissociation. J Proteome Res.2013;12(12):5410-5421.[16] Geho DH, Liotta LA, Petricoin EF, et al.The amplified peptidome: the new treasure chest of candidate biomarkers. Curr Opin Chem Biol.2006;10(1):50-55.[17] Soloviev M, Finch P. Bridging the gap between proteome and metabolome. Proteomics.2006;6(3):744-747.[18] Adermann K, John H, Ständker L, et al.Exploiting natural peptide diversity: novel research tools and drug leads. Curr Opin Biotechnol.2004;15(6):599-606.[19] Shores KS, Knapp DR. Assessment Approach for Evaluating High Abundance Protein Depletion Methods for Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Proteomic Analysis. J Proteome Res. 2007;6(9): 3739-3751.[20] Srinivasan M, Patel MS. Metabolic programming in the immediate postnatal period. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2008; 19(4):146-152.[21] Wallin E, von Heijne G. Genome-wide analysis of integral membrane proteins from eubacterial, archaean, and eukaryotic organisms.Protein Sci. Protein Sci. 1998;7(4): 1029-1038.[22] Mao Y, Kuta A, Crespo-Enriquez I, et al. Dchs1-Fat4 regulation of polarized cell behaviours during skeletal morphogenesis. Nat Commun.2016;7:11469.[23] Kuta A, Mao Y, Martin T, et al. Fat4-Dchs1 signalling controls cell proliferation in developing vertebrae. Development. 2016;143(13):2367-2375.[24] Juarranz Y, Gutierrez-Canas I, Santiago B, et al.Differential expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide and its functional receptors in human osteoarthritic and rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum.2008;58(4):1086-1095.[25] Jiang W, Gao SG, Chen XG, et al. Expression of synovial fluid and articular cartilage VIP in human osteoarthritic knee: a new indicator of disease severity?. Clin Biochem.2012; 45(18): 1607-1612.[26] von Rechenberg B, Mcilwraith CW, Akens MK, et al. Spontaneous production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin (PGE2) and neutral metalloproteinases (NMPs) in media of explant cultures of equine synovial membrane and articular cartilage from normal and osteoarthritic joints. Equine Vet J.2000;32(2):140-150.[27] Hernanz A, Medina S, de Miguel E, et al. Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide, neuropeptide Y, substance P, and vasoactive intestinal peptide on interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by peripheral whole blood cells from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Regul Pept.2003;115(1):19-24.[28] Matsukawa N, Grzesik W J, Takahashi N, et al. The natriuretic peptide clearance receptor locally modulates the physiological effects of the natriuretic peptide system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1999;96(13):7403-7408.[29] Yasoda A, Komatsu Y, Chusho H, et al. Overexpression of CNP in chondrocytes rescues achondroplasia through a MAPK-dependent pathway. Nat Med.2004;10(1):80-86.[30] Krejci P, Masri B, Fontaine V, et al. Interaction of fibroblast growth factor and C-natriuretic peptide signaling in regulation of chondrocyte proliferation and extracellular matrix homeostasis. J Cell Sci.2005;118(Pt 21):5089-5100.[31] Amizuka N, Henderson JE, Hoshi K, et al. Programmed cell death of chondrocytes and aberrant chondrogenesis in mice homozygous for parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene deletion. Endocrinology.1996;137(11):5055-5067.[32] Fan Y, Jianying F, Chenyan L, et al. Influence on Indian hedgehog-parathyroid hormone-like related protein pathway induced by altered masticatory loading in the condylar cartilage of growing rabbits.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017;35(2):127-132.[33] Kong L, Zhao Y P, Tian Q Y, et al. Extracellular matrix protein 1, a direct targeting molecule of parathyroid hormone-related peptide, negatively regulates chondrogenesis and endochondral ossification via associating with progranulin growth factor. The FASEB Journal.2016;30(8):2741-2754.[34] Zhang H, Wang H, Zeng C, et al. mTORC1 activation downregulates FGFR3 and PTH/PTHrP receptor in articular chondrocytes to initiate osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(6):952-963.[35] Fischer J, Ortel M, Hagmann S, et al. Role of PTHrP(1-34) Pulse Frequency Versus Pulse Duration to Enhance Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Chondrogenesis.J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(12):2673-2681.[36] Moore ER, Jacobs CR. The primary cilium as a signaling nexus for growth plate function and subsequent skeletal development. J Orthop Res. 2017 Sep 13. doi: 10.1002/jor.23732. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
多肽:多肽类化合物广泛存在于自然界中,一般来自细胞的分泌或蛋白的分解。一般有3-50个氨基酸,相对分子质量小于10 000。这些内源多肽在生物体的各个系统内扮演了重要的角色。生命活动中的细胞分化、神经递质调节、肿瘤病变、免疫调节等均与活性多肽密切相关。
定量分析:定量分析是依据统计模型,建立数学模型,并用数学模型计算出分析对象的各项指标及其数值的一种方法。本实验通过液相色谱-串联质谱定量分析两组软骨多肽的数值,以此来判断差异多肽的高表达。
文题释义:
多肽:多肽类化合物广泛存在于自然界中,一般来自细胞的分泌或蛋白的分解。一般有3-50个氨基酸,相对分子质量小于10 000。这些内源多肽在生物体的各个系统内扮演了重要的角色。生命活动中的细胞分化、神经递质调节、肿瘤病变、免疫调节等均与活性多肽密切相关。
定量分析:定量分析是依据统计模型,建立数学模型,并用数学模型计算出分析对象的各项指标及其数值的一种方法。本实验通过液相色谱-串联质谱定量分析两组软骨多肽的数值,以此来判断差异多肽的高表达。.jpg) 文题释义:
多肽:多肽类化合物广泛存在于自然界中,一般来自细胞的分泌或蛋白的分解。一般有3-50个氨基酸,相对分子质量小于10 000。这些内源多肽在生物体的各个系统内扮演了重要的角色。生命活动中的细胞分化、神经递质调节、肿瘤病变、免疫调节等均与活性多肽密切相关。
定量分析:定量分析是依据统计模型,建立数学模型,并用数学模型计算出分析对象的各项指标及其数值的一种方法。本实验通过液相色谱-串联质谱定量分析两组软骨多肽的数值,以此来判断差异多肽的高表达。
文题释义:
多肽:多肽类化合物广泛存在于自然界中,一般来自细胞的分泌或蛋白的分解。一般有3-50个氨基酸,相对分子质量小于10 000。这些内源多肽在生物体的各个系统内扮演了重要的角色。生命活动中的细胞分化、神经递质调节、肿瘤病变、免疫调节等均与活性多肽密切相关。
定量分析:定量分析是依据统计模型,建立数学模型,并用数学模型计算出分析对象的各项指标及其数值的一种方法。本实验通过液相色谱-串联质谱定量分析两组软骨多肽的数值,以此来判断差异多肽的高表达。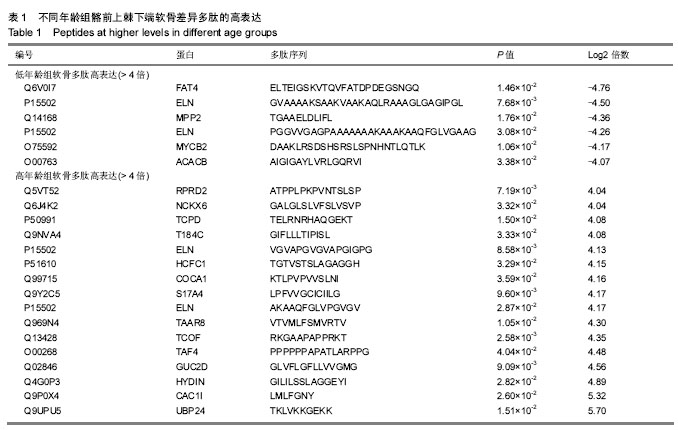
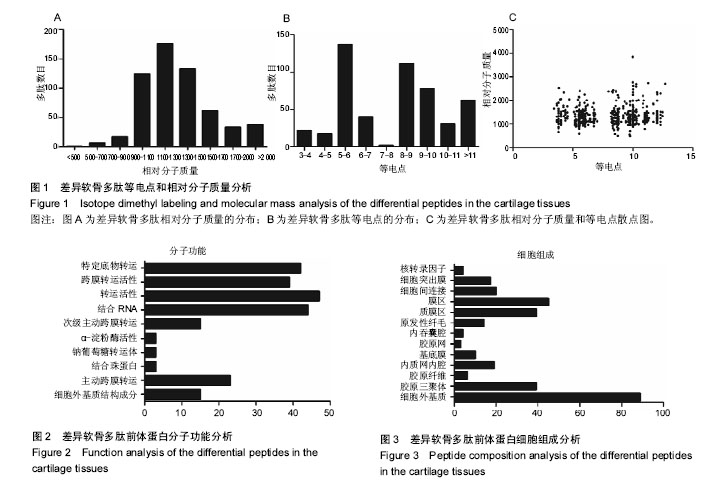
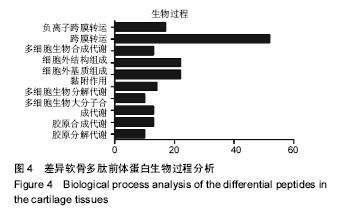
.jpg) 文题释义:
多肽:多肽类化合物广泛存在于自然界中,一般来自细胞的分泌或蛋白的分解。一般有3-50个氨基酸,相对分子质量小于10 000。这些内源多肽在生物体的各个系统内扮演了重要的角色。生命活动中的细胞分化、神经递质调节、肿瘤病变、免疫调节等均与活性多肽密切相关。
定量分析:定量分析是依据统计模型,建立数学模型,并用数学模型计算出分析对象的各项指标及其数值的一种方法。本实验通过液相色谱-串联质谱定量分析两组软骨多肽的数值,以此来判断差异多肽的高表达。
文题释义:
多肽:多肽类化合物广泛存在于自然界中,一般来自细胞的分泌或蛋白的分解。一般有3-50个氨基酸,相对分子质量小于10 000。这些内源多肽在生物体的各个系统内扮演了重要的角色。生命活动中的细胞分化、神经递质调节、肿瘤病变、免疫调节等均与活性多肽密切相关。
定量分析:定量分析是依据统计模型,建立数学模型,并用数学模型计算出分析对象的各项指标及其数值的一种方法。本实验通过液相色谱-串联质谱定量分析两组软骨多肽的数值,以此来判断差异多肽的高表达。