| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎,等.使用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社, 2012:2073-2086.[2] Blanda J, Bethem D, Moats W, et al. Defects of pars interarticularis in athletes: a protocol for nonoperative treatment. J Spinal Disord. 1993; 6(5):406-411.[3] Sys J, Michielsen J, Bracke P, et al. Nonoperative treatment of active spondylolysis in elite athletes with normal X-ray findings: literature review and results of conservative treatment. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10(6):498-504.[4] Moller H, Hedlund R. Surgery versus conservative management in adult isthmic spondylisthesis a prospective randomized study: part I. Spine. 2000;25:1711-1715.[5] Fan J, Yu GR, Liu F, et al. Direct repair of spondylolysis by FSRH’s hook plus screw fixation and bone grafting: biomechanical study and clinical report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010; 130(2):209-215.[6] 张家立,王忠磊,钟远鸣,等. 腰椎双椎峡部裂并单椎滑脱症的手术治疗[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(6):416-420.[7] Wang M, Zhou Y, Wang J, et al. A 10-year follow-up study on long-term clinical outcomes of lumbar microendoscopi discectomy. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2012; 73(4):195-198.[8] Xing R, Dou Q, Li X, et al. Posterior dynamic stabilization with direct pars repair via wiltse approach for the treatment of lumbar spondylolysis: the application of a novel surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2016; 41(8):E494-502. [9] Dai LY, Jia LS, Yuan W, et al. Direct repair of defect in lumbar spondylolysis and mild isthmic spondylolisthesis by bone grafting, with or without facet joint fusion. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10(1):78-83.[10] de Bodman C, Bergerault F, de Courtivron B, et al. Lumbo -sacralmotion conserved after isthmic reconstruction: long-term results. J Child Orthop. 2014; 8(1):97-103.[11] Snyder LA, Shufflebarger H, O’Brien MF, et al. Spondylolysis out-comes in adolescents after direct screw repair of the pars interarticularis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 21:329-333.[12] Shin MH, Ryu KS, Rathi NK, et al. Direct pars repair surgery usingtwo different surgical methods: pedicle screw with universal hook system and direct pars screw fixation in symptomatic lumbar spondylosispatients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 51(1):14-19.[13] Peng B, Li D, Pang X, et al. Surgical management of 3-Level lumbar spondylolyses. Medicine(Baltimore). 2015;94(27): 1127.[14] Salib RM, Pettine KA. Modified repair of a defect in spondylolysis or minimal spondylolisthesis by pedicle screw, segmental wire fixation, andbone grafting. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1993;18(4):440-443.[15] Menga EN, Kebaish KM, Jain A, et al. Clinical results and functional outcomes after direct intralaminar screw repair of spondylolysis. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39( 1):104-110.[16] van der Werf GJ, Tonino AJ, Zeegers WS. Direct repair of lumbar spondylolysis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1985;56:378-379.[17] Pedersen AK, Hagen R. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: treatment by internal fixation and bone grafting of the defect. J Bone Joint Surg. 1988;70-A:15-24.[18] Albassir A, Samson I, Hendrickx L. Treatment of painful spondylolysis using Morscher’s hook. Acta Orthop Belg.1990; 56:489-495.[19] Jeanneret B. Direct repair of spondylolysis. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1993;251:111-115.[20] Altaf F, Osei NA, Garrido E, et al. Repair of spondylolysis using compression with a modular link and screws. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(1):73-77.[21] Ivanic GM, Pink TP, Achatz W, et al. Direct stabilization of lumbarspondylolysis with a hook screw: mean 11-year follow-up period for 113 patients. Spine(Pila pa 1976). 2003;28(3):255-259.[22] Jeanneret B. Direct repair of spondylolysis. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl.1993;251:111-115.[23] Suh PB, Esses SI, Kostuik JP. Repair of pars interarticularis defect: the prognostic value of pars infiltration. Spine.1991; 16(Suppl):445-448.[24] Pavlovcic V. Surgical treatment of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis with a hook screw. Int Orthop. 1994;18:6-9.[25] Kimura M. Mymethod of filling the lesion with spongy bone in spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Orthop Surg(Jpn). 1968; 19:285-295.[26] Kim YT, Lee H, Lee CS, et al. Direct repair of the pars interarticularis defect in dpondylolysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][27] Deguchi M, Rapof JA, Zdeblick AT. Biomechanieal comparison of spondylolysis fixation techniques. Spine. 1999; 24(4):328-333.[28] Amoretti N, Huwart L, Hauger O, et al. Computed tomography- and fluoroscopy-guided percutaneous screw fixation of low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults: a new technique. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22(12):2841-2847.[29] 张超远,付玉娟,付鹏军,等.椎弓根钉椎板钩系统治疗青少年腰椎峡部裂的临床疗效[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2012,33(3):196-198 [30] 李端明,杨洪,庞晓东,等.植骨加钉-钩固定治疗青年腰椎峡部裂[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012, 10(5): 280-283.[31] Gillet P, Petit M. Direct repair of spondylolysis without spondylolisthesis, using a rod-screw construct and bone grafting of the pars defect. Spine. 1999;24:1252-1256.[32] 杨双石,尹俊,曹海泉,等.单节段张力加压复位内固定系统治疗单纯性腰椎峡部裂[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2012, 4(3):189-192.[33] 李康,赵隆队,赖子云,等.U型棒加双侧椎弓根钉联合峡部植骨治疗腰椎峡部裂的观察[J].江西医药, 2015,50(4):320-322.[34] 张建党,邹德威,马华松,等.椎弓根钉-椎板钩系统和经椎板拉力螺钉治疗青少年腰椎峡部裂的临床比较[J].中国现代医药杂志,2010, 12(11):69-71.[35] Scott JH. The Edinburgh repair of isthmic (Group II) spondylolysis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 1987;69-B:491.[36] Bradford DS, Iza J. Repair of the defect in spondylolysis or minimal degrees of spondylolisthesis by segmental wire fixation and bone grafting. Spine. 1985;10:673-679.[37] 孙海涛,关家文.椎弓根钉-椎板钩系统治疗腰椎峡部裂[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(20):3726-3728. |
.jpg)
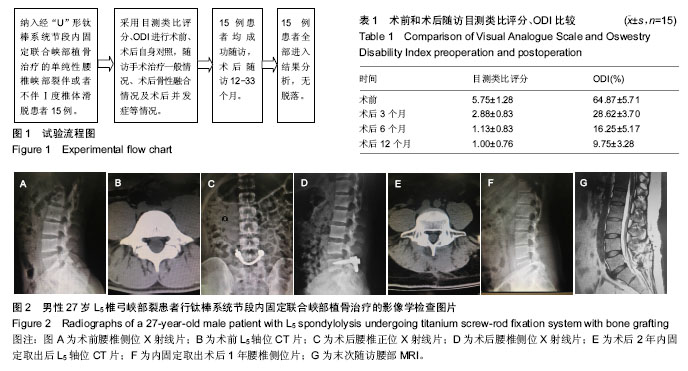
.jpg)