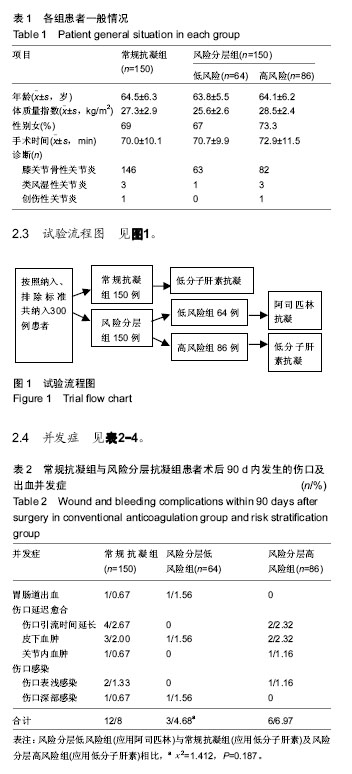
| [1] 杨庆铭,王鸿利.骨科大手术后静脉血栓栓塞症预防的临床趋势[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(11):1121-1128.[2] Dorr LD, Gendelman V, Maheshwari AV, et al. Multimodal thromboprophylaxis for total hip and knee arthroplasty based on risk assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(12):2648-2657.[3] 彭慧明,翁习生,翟吉良,等.初次全膝关节成形术后常规抗凝患者症状性静脉血栓症发生率的调查研究[J].中华骨与关节外科, 2014, 7(2):101-104. [4] Suen K, Westh RN, Churilov L, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin and the relative risk of surgical site bleeding complications: results of a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of venous thromboprophylaxis in patients after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9): 2911-2919.e6.[5] Patel VP, Walsh M, Sehgal B, et al. Factors associated with prolonged wound drainage after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):33-38. [6] Huang RC, Parvizi J, Hozack WJ, et al. Aspirin is as effective as and safer than warfarin for patients at higher risk of venous thromboembolism undergoing total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):83-86. [7] Drescher FS, Sirovich BE, Lee A, et al. Aspirin versus anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism major lower extremity orthopedic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(9):579-585.[8] Lieberman JR, Pensak MJ. Prevention of venous thromboembolic disease after total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(19):1801-1811.[9] Chu JN, Maselli J, Auerbach AD, et al. The risk of venous thromboembolism with aspirin compared to anticoagulants after hip and knee arthroplasty. Thromb Res. 2017;155:65-71.[10] Deirmengian GK, Heller S, Smith EB, et al. Aspirin can be used as prophylaxis for prevention of venous thromboembolism after revision hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10): 2237-2240.[11] Raphael IJ, Tischler EH, Huang R, et al. Aspirin: an alternative for pulmonary embolism prophylaxis after arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(2):482-488.[12] Jameson SS, Charman SC, Gregg PJ, et al. The effect of aspirin and low-molecular-weight heparin on venous thromboembolism after hip replacement: a non-randomised comparison from information in the National Joint Registry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(11):1465-1470.[13] Cafri G, Paxton EW, Chen Y, et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of drug prophylaxis for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(11):3524-3528.e1.[14] Bala A, Huddleston JI 3rd, Goodman SB, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after TKA: aspirin, warfarin, enoxaparin, or factor Xa inhibitors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017; 475(9):2205-2213.[15] Nielen JT, Dagnelie PC, Emans PJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of new oral anticoagulants and low-molecular-weight heparins compared with aspirin in patients undergoing total knee and hip replacements. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016;25(11): 1245-1252.[16] Odeh K, Doran J, Yu S, et al. Risk-stratified venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total joint arthroplasty: aspirin and sequential pneumatic compression devices vs aggressive chemoprophylaxis. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):78-82.[17] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨关节炎诊治指南(2007年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2007,1(4):280-283.[18] González Della Valle A, Serota A, Go G, et al. Venous thromboembolism is rare with a multimodal prophylaxis protocol after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;444: 146-153.[19] Dorr LD, Gendelman V, Maheshwari AV, et al. Multimodal thromboprophylaxis for total hip and knee arthroplasty based on risk assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(12):2648-2657.[20] Parvizi J, Smith EB, Pulido L, et al. The rise in the incidence of pulmonary embolus after joint arthroplasty: is modern imaging to blame. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;463:107-113.[21] Parvizi J, Huang R, Rezapoor M, et al. Individualized risk model for venous thromboembolism after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9 Suppl):180-186.[22] Ogonda L, Hill J, Doran E, et al. Aspirin for thromboprophylaxis after primary lower limb arthroplasty: early thromboembolic events and 90 day mortality in 11,459 patients. Bone Joint J.2016; 98-B (3):341-348.[23] 钱文伟,翁习生,常晓,等.人工髋关节置换后深静脉血栓形成影响因素的回顾分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4):622-625.[24] Sharrock NE, Gonzalez Della Valle A, Go G, et al. Potent anticoagulants are associated with a higher all-cause mortality rate after hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466(3):714-721.[25] Huang R, Buckley PS, Scott B, et al. Administration of aspirin as a prophylaxis agent against venous thromboembolism results in lower incidence of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9 Suppl):39-41. [26] Markel DC, York S, Liston MJ Jr, et al. Venous thromboembolism: management by American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(1):3-9.e1-2.[27] Devereaux PJ, Mrkobrada M, Sessler DI, et al. Aspirin in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(16): 1494-1503.[28] Ozbudak O, Ero?ullari I, O?ü? C, et al. Doppler ultrasonography versus venography in the detection of deep vein thrombosis in patients with pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2006;21(2):159-162.[29] Colwell CW Jr, Froimson MI, Mont MA, et al. Thrombosis prevention after total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized trial comparing a mobile compression device with low-molecular- weight heparin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(3):527-535.[30] Jiang Y, Du H, Liu J, et al. Aspirin combined with mechanical measures to prevent venous thromboembolism after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(12):2201-2205.[31] Parvizi J, Huang R, Restrepo C, et al. Low-dose aspirin is effective chemoprophylaxis against clinically important venous thromboembolism following total joint arthroplasty: a preliminary analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(2):91-98.[32] Khatod M, Inacio MC, Bini SA, et al. Pulmonary embolism prophylaxis in more than 30,000 total knee arthroplasty patients: is there a best choice. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(2):167-172. |
.jpg)
.jpg)