中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (10): 1625-1633.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0726
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
聚乙二醇免疫伪装功能的应用
- 1广州医科大学附属第三医院,广东省广州市 510150;2西安市第一医院,陕西省眼科研究所,陕西省眼科学重点实验室,陕西省眼科临床研究中心,陕西省西安市 710002
-
收稿日期:2018-01-21出版日期:2018-04-08发布日期:2018-04-08 -
通讯作者:王双勇,博士,主治医师,美国伊利罗伊大学芝加哥分校访问学者,广州医科大学附属第三医院眼科,广东省广州市 510150;西安市第一医院,陕西省眼科研究所,陕西省眼科学重点实验室,陕西省眼科临床研究中心,陕西省西安市 710002 -
作者简介:田英,女,1977年生,陕西省渭南市人,汉族,硕士,主治检验医师,主要从事微生物免疫及输血免疫研究。 -
基金资助:陕西省自然科学基金-面上项目(2016JM8017)
Polyethylene glycol: an expert of cellular camouflage confusing the immune system
- 1The Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; 2Shaanxi Provincial Eye Clinical Research Center, Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Shaanxi Institute of Ophthalmology, The First Hospital of Xi’an, Xi’an 710002, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2018-01-21Online:2018-04-08Published:2018-04-08 -
Contact:Wang Shuang-yong, M.D., Attending physician, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China; Shaanxi Provincial Eye Clinical Research Center, Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Shaanxi Institute of Ophthalmology, The First Hospital of Xi’an, Xi’an 710002, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Tian Ying, Master, Attending inspector, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, No. 2016JM8017
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
中图分类号:
引用本文
田 英,吴 洁,王双勇. 聚乙二醇免疫伪装功能的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(10): 1625-1633.
Tian Ying, Wu Jie, Wang Shuang-yong. Polyethylene glycol: an expert of cellular camouflage confusing the immune system[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1625-1633.
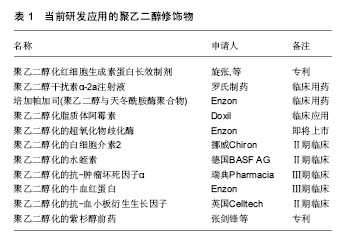
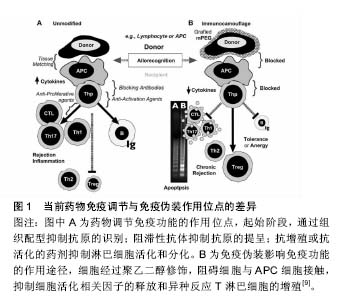
| [1]Roberts MJ,Bentley MD,Harris JM.Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(4):459-476.[2]Fruijtier-Polloth C.Safety assessment on polyethylene glycols (PEGs) and their derivatives as used in cosmetic products. Toxicology.2005;214(1-2):1-38.[3]Gundersen SI,Palmer AF.Conjugation of methoxypolyethylene glycol to the surface of bovine red blood cells.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2007;96(6):1199-1210.[4]Inui O,Teramura Y,Iwata H.Retention dynamics of amphiphilic polymers PEG-lipids and PVA-Alkyl on the cell surface.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2010;2(5):1514-1520.[5]Chen AM,Scott MD.Comparative analysis of polymer and linker chemistries on the efficacy of immunocamouflage of murine leukocytes.Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2006;34(3):305-322.[6]Teramura Y,Asif S,Ekdahl KN,et al.Cell Surface Engineering for Regulation of Immune Reactions in Cell Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol.2015;865:189-209.[7]Sutton TC,Scott MD.The effect of grafted methoxypoly (ethylene glycol) chain length on the inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus(RSV)infection and proliferation.Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):4223-4230.[8]Scott MD,Chen AM.Beyond the red cell: pegylation of other blood cells and tissues. Transfus Clin Biol.2004;11(1):40-46.[9]Wang D,Toyofuku WM,Chen AM,et al.Induction of immunotolerance via mPEG grafting to allogeneic leukocytes. Biomaterials.2011;32(35):9494-9503.[10]Jeong ST,Byun SM.Decreased agglutinability of methoxy-polyethylene glycol attached red blood cells: significance as a blood substitute.Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol.1996;24(5):503-511.[11]Le Y, Toyofuku WM, Scott MD. Immunogenicity of murine mPEG-red blood cells and the risk of anti-PEG antibodies in human blood donors. Exp Hematol 2017;47:36-47.[12]Li L,Noumsi GT,Kwok YY,et al.Inhibition of phagocytic recognition of anti-D opsonized Rh D+ RBC by polymer-mediated immunocamouflage.Am J Hematol. 2015;90(12):1165-1170.[13]Armstrong JK,Meiselman HJ,Fisher TC.Covalent binding of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) to the surface of red blood cells inhibits aggregation and reduces low shear blood viscosity. Am J Hematol. 1997;56(1):26-28.[14]Tan Y,Qiu Y,Xu H,et al.Decreased immunorejection in unmatched blood transfusions by attachment of methoxypolyethylene glycol on human red blood cells and the effect on D antigen.Transfusion. 2006;46(12): 2122-2127.[15]Murad KL,Gosselin EJ,Eaton JW,et al.Stealth cells: prevention of major histocompatibility complex class II-mediated T-cell activation by cell surface modification. Blood.1999;94(6):2135-2141.[16]Bradley AJ,Murad KL,Regan KL,et al.Biophysical consequences of linker chemistry and polymer size on stealth erythrocytes: size does matter.Biochim Biophys Acta.2002; 1561(2):147-158.[17]Doucet J,Gao ZH,MacLaren LA,et al.Modification of xenoantigens on porcine erythrocytes for xenotransfusion. Surgery.2004;135(2):178-186.[18]Scott MD,Bradley AJ,Murad KL.Camouflaged blood cells: low-technology bioengineering for transfusion medicine? Transfus Med Rev.2000;14(1):53-63.[19]Huang Y,Feng S,Tang R,et al.Efficacy of pretreatment of allografts with methoxypolyethylene glycol-succinimidyl-propionic acid ester in combination with an anti-OX40L monoclonal antibody in relieving graft-versus-host disease in mice.Int J Hematol.2010;92(4):609-616.[20]Chen AM,Scott MD.Immunocamouflage: prevention of transfusion-induced graft-versus-host disease via polymer grafting of donor cells.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;67(2): 626-636.[21]Kyluik-Price DL,Scott MD.Effects of methoxypoly (Ethylene glycol) mediated immunocamouflage on leukocyte surface marker detection, cell conjugation, activation and alloproliferation. Biomaterials. 2016;74:167-177.[22]Giraldo JA,Molano RD,Rengifo HR,et al.The impact of cell surface PEGylation and short-course immunotherapy on islet graft survival in an allogeneic murine model.Acta Biomater. 2017;49:272-283.[23]Manzoli V,Villa C,Bayer AL,et al.Immunoisolation of murine islet allografts in vascularized sites through conformal coating with polyethylene glycol.Am J Transplant.2017.doi: 10.1111/ajt.14547. [Epub ahead of print][24]Aghajani-Lazarjani H,Vasheghani-Farahani E,Shojaosadati SA,et al.The effect of two different polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives on the immunological response of PEG grafted pancreatic islets. J Artif Organs.2010;13(4):218-224.[25]Haque MR,Kim J,Park H,et al.Xenotransplantation of layer-by-layer encapsulated non-human primate islets with a specified immunosuppressive drug protocol.J Control Release.2017;258:10-21.[26]Jeong JH,Yook S,Hwang JW,et al.Synergistic effect of surface modification with poly(ethylene glycol) and immunosuppressants on repetitive pancreatic islet transplantation into antecedently sensitized rat.Transplant Proc.2013;45(2):585-590.[27]Haque MR,Jeong JH,Byun Y.Combination strategy of multi-layered surface camouflage using hyperbranched polyethylene glycol and immunosuppressive drugs for the prevention of immune reactions against transplanted porcine islets.Biomaterials.2016;84:144-156.[28]Lee DY,Lee S,Nam JH,et al.Minimization of immunosuppressive therapy after islet transplantation: combined action of heme oxygenase-1 and PEGylation to islet.Am J Transplant.2006;6(8):1820-1828.[29]Hashemi J,Hashemi-Najafabadi S,Vasheghani-Farahani E.Synergistic effect of PEGylation and pentoxifylline addition on immunoprotection of pancreatic islets.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017;28(1):33-49.[30]Collins GM,Wicomb WN,Levin BS,et al.Heart preservation solution containing polyethyleneglycol: an immunosuppressive effect? Lancet.1991;338(8771): 890-891.[31]Ben AH,El RZ,Steghens JP,et al.Effective pig liver preservation with an extracellular-like UW solution containing the oncotic agent polyethylene glycol: a preliminary study. Transplant Proc. 2002;34(3):762-763.[32]Faure JP,Petit I,Zhang K,et al.Protective roles of polyethylene glycol and trimetazidine against cold ischemia and reperfusion injuries of pig kidney graft.Am J Transplant.2004;4(4):495-504.[33]Jayle C,Corbi P,Eugene M,et al.Beneficial effect of polyethylene glycol in lung preservation: early evaluation by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Ann Thorac Surg.2003;76(3):896-902.[34]Itasaka H,Burns W,Wicomb WN,et al.Modification of rejection by polyethylene glycol in small bowel transplantation. Transplantation.1994;57(5):645-648.[35]Weber LM,Cheung CY,Anseth KS.Multifunctional pancreatic islet encapsulation barriers achieved via multilayer PEG hydrogels.Cell Transplant.2008;16(10):1049-1057.[36]Giraud S,Bon D,Neuzillet Y,et al.Concentration and chain length of polyethylene glycol in islet isolation solution: evaluation in a pancreatic islet transplantation model.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(9):2079-2088.[37]Yandza T,Tauc M,Canioni D,et al.Effect of polyethylene glycol in pig intestinal allotransplantation without immunosuppression. J Surg Res.2012;176(2):621-628.[38]Hauet T,Eugene M.A new approach in organ preservation: potential role of new polymers.Kidney Int. 2008;74(8):998-1003.[39]Dutheil D,Rioja-Pastor I,Tallineau C,et al.Protective effect of PEG 35,000 Da on renal cells: paradoxical activation of JNK signaling pathway during cold storage.Am J Transplant. 2006; 6(7):1529-1540.[40]冯翠,王祺,张纯,等.PEG定点修饰重组人睫状神经营养因子及其生物活性评价[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2015,35(5):15-21.[41]Basu A,Yang K,Wang M,et al.Structure-function engineering of interferon-beta-1b for improving stability, solubility, potency, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetic properties by site-selective mono-PEGylation.Bioconjug Chem. 2006; 17(3):618-630.[42]Da-Silva-Freitas D,Boldrini-Franca J,Arantes EC.PEGylation: a successful approach to improve the biopharmaceutical potential of snake venom thrombin-like serine protease. Protein Pept Lett. 2015;22(12):1133-1139.[43]Abuchowski A,van Es T,Palczuk NC,et al.Alteration of immunological properties of bovine serum albumin by covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol.J Biol Chem. 1977;252(11):3578-3581.[44]Ajisaka K,Iwashita Y.Modification of human hemoglobin with polyethylene glycol : a new candidate for blood substitute.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980;97(3): 1076-1081.[45]Sawhney P,Kumar S,Maheshwari N,et al.Site-Specific Thiol-mediated PEGylation of Streptokinase Leads to Improved Properties with Clinical Potential.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(38):5868-5878.[46]Ashihara Y,Kono T,Yamazaki S,et al.Modification of E. coli L-asparaginase with polyethylene glycol: disappearance of binding ability to anti-asparaginase serum.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978;83(2):385-391.[47]周笑艳,刘景晶.聚乙二醇对大肠杆菌L-天冬酰胺酶的化学修饰[J].中国药科大学学报,2000,31(3):230.[48]Kodera Y,Sekine T,Yasukohchi T,et al.Stabilization of L-asparaginase modified with comb-shaped poly(ethylene glycol) derivatives, in vivo and in vitro.Bioconjug Chem.1994; 5(4):283-286.[49]Ettinger LJ,Kurtzberg J,Voǔte PA,et al.An open-label,multicenter study of polyethylene glycol-L-asparaginase for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 2015; 75(5):1176-1181.[50]Ettinger LJ,Kurtzberg J,Voǔte PA,et al.An open-label, multicenter study of polyethylene glycol-L-asparaginase for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 2015;75(5):1176-1181.[51]Wen Z,Ren H,Ke X,et al.PEG-asparaginase in BFM-90 regimen improves outcomes in adults with newly diagnosed lymphoblastic lymphoma.Chin J Cancer Res.2017;29(1):66-74.[52]Hershfield MS. PEG-ADA: an alternative to haploidentical bone marrow transplantation and an adjunct to gene therapy for adenosine deaminase deficiency.Hum Mutat.1995;5(2):107-112.[53]吴影新,翟艳琴,雷建都,等.干扰素α-2b的聚乙二醇修饰[J].生物工程学报,2008,24(9):1658-1663.[54]Foster GR,Serfaty LD.Triple combination treatment for chronic hepatitis C with protease inhibitors, pegylated interferon and ribavirin: 'lead-in or no lead-in'?Liver Int. 2012;32 Suppl 1:61-63.[55]Heathcote EJ,Shiffman ML,Cooksley WG,et al.Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C and cirrhosis.N Engl J Med.2000;343(23):1673-1680.[56]Khan UT,Tanasescu R,Constantinescu CS.PEGylated IFNβ-1a in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther.2015;15(7):1077.[57]Eto Y,Gao JQ,Sekiguchi F,et al.Neutralizing antibody evasion ability of adenovirus vector induced by the bioconjugation of methoxypolyethylene glycol succinimidyl propionate (MPEG-SPA).Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27(6):936-938.[58]Croyle MA,Chirmule N,Zhang Y,et al.PEGylation of E1-deleted adenovirus vectors allows significant gene expression on readministration to liver.Hum Gene Ther.2002; 13(15):1887-1900.[59]Choi JW,Dayananda K,Jung SJ,et al.Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy and safety profile of tumor microenvironment-responsive oncolytic adenovirus nanocomplex by systemic administration. Acta Biomater.2015;28:86-98.[60]Lanciotti J,Song A,Doukas J,et al.Targeting adenoviral vectors using heterofunctional polyethylene glycol FGF2 conjugates.Mol Ther.2003;8(1):99-107.[61]Singarapu K,Pal I,Ramsey JD.Polyethylene glycol-grafted polyethylenimine used to enhance adenovirus gene delivery.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(7):1857-1864.[62]Gao JQ,Eto Y,Yoshioka Y,et al.Effective tumor targeted gene transfer using PEGylated adenovirus vector via systemic administration.J Control Release.2007;122(1):102-110.[63]Badkas A,Frank E,Zhou Z,et al.Modulation of in vitro phagocytic uptake and immunogenicity potential of modified Herceptin((R))-conjugated PLGA-PEG nanoparticles for drug delivery.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017;162:271-278.[64]Farace C,Sanchez-Moreno P,Orecchioni M,et al.Immune cell impact of three differently coated lipid nanocapsules: pluronic, chitosan and polyethylene glycol.Sci Rep.2016;6:18423.[65]Neuzillet Y,Giraud S,Lagorce L,et al.Effects of the molecular weight of peg molecules (8, 20 and 35 KDA) on cell function and allograft survival prolongation in pancreatic islets transplantation. Transplant Proc.2006;38(7):2354-2355[66]Bradley AJ, Scott MD. Immune complex binding by immunocamouflaged [poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted] erythrocytes. Am J Hematol 2007;82(11):970-975.[67]Lazarjani HA,Vasheghani-Farahani E,Barani L,et al.Effect of polymer concentration on camouflaging of pancreatic islets with mPEG-succinimidyl carbonate.Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2010;38(5):250-258.[68]Le Y,Li L,Wang D,et al.Immunocamouflage of latex surfaces by grafted methoxypoly(ethylene glycol) (mPEG): proteomic analysis of plasma protein adsorption.Sci China Life Sci.2012; 55(3):191-201.[69]Miron T, Wilchek M. A simplified method for the preparation of succinimidyl carbonate polyethylene glycol for coupling to proteins.Bioconjug Chem.1993;4(6):568-569.[70]Richter AW,Akerblom E.Polyethylene glycol reactive antibodies in man: titer distribution in allergic patients treated with monomethoxy polyethylene glycol modified allergens or placebo, and in healthy blood donors.Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol.1984;74(1):36-39.[71]Landersdorfer CB,Caliph SM,Shackleford DM,et al. PEGylated interferon displays differences in plasma clearance and bioavailability between male and female mice and between female immunocompetent C57Bl/6J and athymic nude mice.J Pharm Sci.2015;104(5):1848-1855.[72]Zhang P,Sun F,Liu S,et al.Anti-PEG antibodies in the clinic: Current issues and beyond PEGylation. J Control Release. 2016;244(Pt B):184-193.[73]Yang Q,Lai SK.Anti-PEG immunity: emergence, characteristics, and unaddressed questions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol.2015;7(5):655-677.[74]Ando H,Abu LA,Kawanishi M,et al.Reactivity of IgM antibodies elicited by PEGylated liposomes or PEGylated lipoplexes against auto and foreign antigens.J Control Release.2017;270:114-119.[75]Henry CE,Wang YY,Yang Q,et al.Anti-PEG antibodies alter the mobility and biodistribution of densely PEGylated nanoparticles in mucus.Acta Biomater.2016;43:61-70.[76]Ganson NJ,Kelly SJ,Scarlett E,et al.Control of hyperuricemia in subjects with refractory gout, and induction of antibody against poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), in a phase I trial of subcutaneous PEGylated urate oxidase.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(1):R12.[77]Armstrong JK,Hempel G,Koling S,et al.Antibody against poly(ethylene glycol) adversely affects PEG-asparaginase therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients.Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 2007;110(1):103-111.[78]Poppenborg SM,Wittmann J,Walther W,et al.Impact of anti-PEG IgM antibodies on the pharmacokinetics of pegylated asparaginase preparations in mice.Eur J Pharm Sci.2016;91:122-130.[79]Elsabahy M,Li A,Zhang F,et al.Differential immunotoxicities of poly(ethylene glycol)- vs. poly(carboxybetaine)-coated nanoparticles.J Control Release.2013;172(3):641-652.[80]Verhoef JJ,Carpenter JF,Anchordoquy TJ,et al.Potential induction of anti-PEG antibodies and complement activation toward PEGylated therapeutics.Drug Discov Today. 2014; 19(12):1945-1952.[81]Ishida T,Kiwada H.Accelerated blood clearance (ABC) phenomenon upon repeated injection of PEGylated liposomes. Int J Pharm.2008;354(1-2):56-62.[82]Carter MC,Meyerhoff ME.Instability of succinyl ester linkages in O2'-monosuccinyl cyclic AMP-protein conjugates at neutral pH.J Immunol Methods.1985;81(2):245-257. |
| [1] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [2] | 刘立华, 孙 伟, 王云亭, 高福强, 程立明, 李子荣, 王江宁. 头颈部开窗减压治疗L1型激素性股骨头坏死:单中心前瞻性临床研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [3] | 蒋 欣, 乔良伟, 孙 东, 李 明, 房 军, 曲青山. 肾移植患者血清中长链非编码RNA PGM5-AS1表达及调控人肾小球内皮细胞的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [4] | 杨 鑫, 金 喆, 冯 旭, 卢 兵. 沈阳市居民对器官、眼组织及遗体捐献的认知及意愿调查[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [5] | 李 黎, 马 力. 磁性壳聚糖微球固定化乳糖酶及其酶学性质[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [6] | 邢 浩, 张永红, 王 栋. 长骨大段骨缺损修复方法的优势与不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [7] | 曾祥洪, 梁博伟. 股骨头坏死保髋治疗的新策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [8] | 阮光萍, 姚 翔, 刘高米洋, 蔡学敏, 李自安, 庞荣清, 王金祥, 潘兴华. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗树鼩创伤性全身炎症反应综合征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [9] | 刘 鋆, 杨 龙, 王伟宇, 周玉虎, 吴 颖, 卢 涛, 舒莉萍, 马敏先, 叶 川. 聚3-羟基丁酸酯4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [10] | 周安琪, 唐渝菲, 吴秉峰, 向 琳. 骨膜组织工程设计:共性与个性的结合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [11] | 郎丽敏, 何 生, 姜增誉, 胡奕奕, 张智星, 梁敏茜. 导电复合材料在心肌梗死组织工程治疗领域的应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [12] | 陈 晓, 郭 智, 陈丽娜, 刘玄勇, 张弋慧智, 李旭绵, 王月乔, 韦丽娅, 谢 晶, 蔺 莉. 自体外周血造血干细胞动员采集的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [13] | 张剑慧, 马贺然, 谭 毅, 王芝辉. 人脂肪间充质干细胞无支架三维凝胶修复猪膝关节损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 2969-2975. |
| [14] | 张红庆, 谢旭芳, 吴晓牧. 干细胞治疗多发性硬化及视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病的有效性和临床应用限制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3049-3056. |
| [15] | 孙维兴, 赵永超, 赵然尊 . 间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死:问题、症结及新突破[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(19): 3103-3109. |
.jpg)
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||