| [1] 韦蕾,余一兵,俞雪春,等.专科学校篮球班男生身体成分与体质健康相关性的研究[J].广州体育学院学报,2009,29(5):108-111.[2] Smith TP,Mcnaughton LR,Marshall KJ.Effect of 4-wk training using Vmax\Tmax on VO2max and performance in athletes. Med Sci Sports Exe.1999;31(6):892-896.[3] Smith TP,Coombes JS,Geraghty DP.Optimising high-intensity treadmill training using the running speed at maximal O2 uptake and the time for which this Can Be maintained.Eur J Appsiol.2003;(89):337-343.[4] 许晓东,柏友萍,张晶,等.篮球、手球、足球运动员体成分及肌肉力量的比较分析[J].辽宁体育科技,2012,34(4):37-41.[5] 杨建雄,王健.6-21岁学生体成分的性别特点与年龄规律[J].体育科学,2005,25(8):67-70.[6] 叶心明,肖巧俐,易红赤.中国学龄儿童饮食习惯、营养摄入及与BMI相关研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2016,42(2):116-121.[7] Hung LS,Tidwell DK,Hall ME,et al.A meta-analysis of school-based obesity prevention programs demonstrates limited efficacy of decreasing childhood obesity.Nutr Res. 2015;35(3):229-240.[8] Ross R,Blair SN,Arena R,et al.Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice:A case for fitness as a clinical vital sign:a scientific statement from the american heart association.Circulation.2016;134(24):e653.[9] Blair SN,Kohl HW,Paffenbarger RS,et al.Physical fitness and all-cause mortality.A prospective study of healthy men and women.JAMA.1989;262(17):2395-2401.[10] 李新,李晓彤,王正珍,等.不同运动量对少年心肺耐力和身体成分影响的干预研究[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(5):110-116.[11] 汪媛,金永堂.肌力和体力活动与骨密度关系研究进展[J].卫生研究,2003,32(2):169-171.[12] 沈友青,姜霞.运动与儿童少年骨密度的改变[J].武汉体育学院学报,2004,38(5):56-57. [13] 徐锋鹏,胡敏,黄俊豪,等.不同类型运动对骨密度影响的研究进展[J].上海体育学院学报,2017,41(1):55-60.[14] Frost HM.Skeletal structure adapations to mechanical usage( SATMU):1.Redefining Wolff law:the bone modeline problem.Anat Rec.1990;226(4):403-413.[15] 丁焕香.不同专项学生身体成分调查分析[J].临沂师范学院学报,2009,31(6):97-101.[16] 詹晓梅,潘珊珊,陈文鹤.运动干预对肥胖青少年体成分、血脂、胰岛素抵抗及超敏C反应蛋白的影响[J].上海体育学院学报, 2012.6(6):62-66.[17] 廖鲁頔.不同技能主导类项目运动员身体成分的比较研究-以山西技能主导类优势项目运动员为例[J]. 2015,30(5): 124-128.[18] 袁凌燕.青少年儿童肥胖干预理论与实践[M].杭州:杭州出版社, 2013,7.[19] 黄优强,周武.对中国男篮后备人才培养模式的审视[J].北京体育大学学报,2014,37(4):133-139. [20] 黄长剑,徐瑞芳.我国青少年篮球培养现状与对策—以福建省为例[J].长沙大学学报,2011,25(5):153-156. [21] 高治.我国青少年校园篮球运动发展的动力机制研究[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2016.[22] 丁广鹏.我国7-12 岁儿童篮球启蒙训练的实证研究[J].湖北体育科技,2017,36(7):598-602.[23] 李治.明星效应对高校篮球公共课教学的影响研究[J].当代体育科技,2016,6(26):36-37. [24] 汪光胜,王东亮.中美篮球后备人才培养的比较研究[J].吉林体育学院学报,2015,31(6):36-40.[25] 吴新炎,陈月亮,李芙蓉.我国篮球儿童少年后备人才骨密度研究[J].湖北理工学院学报:人文社会科学版,2016,33(3):83-88. [26] 刘莉,姚兴家,白英龙,等.不同体成分儿童皮褶厚度性激素水平的探讨[J].中国公共卫生,2003,19(10):1186-1187.[27] 蔡富华,章晓霜,熊静宇.音、体、美、舞蹈专业教育对青春期女大学生体成分与骨密度的影响[J].广州体育学院学报, 2016, 36(1):106-108.[28] Hoy CL,Macdonald HM,Mckay HA.How does bone quality differ between healthy weight and overweight adolescents and young adults.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012;22(2):312-326.[29] 沈华.不同形式的健身运动和体成分对中老年女性骨密度的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,2008,34(12):71-74.[30] 张永桂.巧用篮球发展中学生上肢力量[J].中国学校体育(基础教育),2017(1):83.[31] 宋新民,袁平,刘琳.不同性别年龄钙骨密度测定分析[J].微量元素与健康研究,2000,17(4):22-23.[32] 陈金标,秦林林,马海波,等.桡骨超远端体积骨密度的测量及性别间的比较[J].中日友好医院学报,2000,14(3):125-128.[33] 李天乐.太极拳练习对男性中老年体成分和睾酮及骨密度影响的研究[D].宁波:宁波大学,2015. [34] 王峰.关于降钙素降低骨质疏松性骨折发病率的临床分析[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(2):163-164.[35] 杨路昕,郭郡浩,蔡辉.运动干预原发性骨质疏松症:不同运动方式、强度及频率对骨密度的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(38):6200-6204.[36] 刘云发,陶萍,石丽杰.不同生活方式对60-69岁老年人骨密度的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2013,32(5):99.[37] Cizza G.Major depressive disorder is a risk factor for low bone mass,central obesity,and other medical condition.Dialogues Clin Neurosci.2011;13(1):73-87.[38] Watts NB,GLOW investigators. Insights from the Global Longitudinal Study of Osteoporosis in Women( GLOW).Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(7):412-22.[39] Turner AG,Anderson PH,Morris HA.Vitamin D and bone health.J Clin Lab Invest Suppl.2012;243(4):65-72.[40] 王亮,马远征,张妍,等.北京地区9103例体检人群骨密度流行病学调查研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(8):952-955.[41] 易波,文重远,孙永林,等.脂肪分布对不同年龄正常人群骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(7):610-613,617. [42] 程淑敏,于大芳,郭文娟.3-10岁儿童年龄、身高及体重指数对全身及各部位骨密度的影响[J].现代预防医学, 2007,34(24): 4690-4691.[43] 邢晨芳,黄皓月,周颖,等.深圳市成年男性超声骨密度检测结果分析[J].现代医用影像学,2015,24(6):944-945,957. [44] 张莹,吴景欢,洪平,等.北京地区18-30岁成人骨密度影响因素分析[J].营养学报,2016,38(3):229-233.[45] 王纯,杨泽宏.成都市中老年健身女性体成分指标与骨密度和骨代谢指标的相关性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2007,13(11): 779-782.[46] 周莉,秦建平,邹丽华,等.253例青少年腰椎骨密度分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(4):662-665.[47] 莫娟,欧阳俊.年龄和体重指数对中青年男性骨密度的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(3):310-313.[48] 阿斯木古丽•克力木,热依拉•阿不拉,阿孜亚•赛辽汗.1092例0-6 岁儿童骨密度与体格发育调查[J].中国妇幼保健, 2014, 29(6):917-919. [49] 李雪莹.健美操锻炼对肥胖女大学生身体成分及身体形态影响的研究[J].辽宁体育科技,2017,39(2):54-56.[50] 王磊,王新雷.中北大学男跆拳道运动员身体成分与无氧代谢的研究[J].湖北体育科技,2016,35(10):869-872.[51] 蔡壮,王世超.不同田径专项专修男性大学生身体成分与体质特征比较-以山西省五所体育院校为例[J].南京体育学院学报(自然科学版),2016,15(3):73-75.[52] 肖丽娜.上海市青少年游泳运动员身体成分特征的研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2016.[53] 崔建梅,郭旭玥,李中华,等.太极拳锻炼对大学体育保健班学生心功能指数及身体成分的影响[J].中国学校卫生, 2016,37(3): 432-434.[54] 李荣娟,张瑞,陆碧琼,等.气排球运动对中老年女性身体成分及骨密度和肌肉力量的影响[J].内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版),2016,45(2):285-288.[55] 石峰.长期空竹锻炼老年人身体成分与体质特征[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(14):3955-3956. [56] 徐金庆.体育院系篮球专修大学生运动员体成分特征分析[J].宜春学院学报,2017,39(3):93-96.[57] 陈孝道.武术专选与篮球专选学生体成分的对比分析[J].体育研究与教育,2011,(s1):207-209.[58] 刘龙祥.抗阻训练对青少年骨密度的影响研究[J].当代体育科技, 2017,7(23):213-214.[59] 费加明.不同运动方式对绝经后妇女身体形态、肺活量及骨密度的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2017,33(4):339-341.[60] 钱芊.大学生田径运动员和普通大学生不同部位骨密度的均值比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(32) :5097-5102. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
少年篮球运动员:此群体主要分布于有篮球传统的中学,也分散分布在一些中学的篮球队里面。由于经常需要代表学校参加省(市、区)级比赛,因此训练水平和竞技能力都较高。根据国家体育总局篮球运动员技术等级标准的规定,此群体的运动水平相当于篮球三级运动员水平。
身体成分:身体成分简称体成分,它是人体脂肪组织和非脂肪组织的含量在体质量中所占的百分数。在通常状况下,人的身体主要由水、蛋白质、脂肪、无机物4种成分构成。在一定的时间内,这4种成分也是相对恒定的,并且不同人群有一定的正常比例。因此对身体成分的监测可以为人体健康状况评估提供参考。
文题释义:
少年篮球运动员:此群体主要分布于有篮球传统的中学,也分散分布在一些中学的篮球队里面。由于经常需要代表学校参加省(市、区)级比赛,因此训练水平和竞技能力都较高。根据国家体育总局篮球运动员技术等级标准的规定,此群体的运动水平相当于篮球三级运动员水平。
身体成分:身体成分简称体成分,它是人体脂肪组织和非脂肪组织的含量在体质量中所占的百分数。在通常状况下,人的身体主要由水、蛋白质、脂肪、无机物4种成分构成。在一定的时间内,这4种成分也是相对恒定的,并且不同人群有一定的正常比例。因此对身体成分的监测可以为人体健康状况评估提供参考。.jpg) 文题释义:
少年篮球运动员:此群体主要分布于有篮球传统的中学,也分散分布在一些中学的篮球队里面。由于经常需要代表学校参加省(市、区)级比赛,因此训练水平和竞技能力都较高。根据国家体育总局篮球运动员技术等级标准的规定,此群体的运动水平相当于篮球三级运动员水平。
身体成分:身体成分简称体成分,它是人体脂肪组织和非脂肪组织的含量在体质量中所占的百分数。在通常状况下,人的身体主要由水、蛋白质、脂肪、无机物4种成分构成。在一定的时间内,这4种成分也是相对恒定的,并且不同人群有一定的正常比例。因此对身体成分的监测可以为人体健康状况评估提供参考。
文题释义:
少年篮球运动员:此群体主要分布于有篮球传统的中学,也分散分布在一些中学的篮球队里面。由于经常需要代表学校参加省(市、区)级比赛,因此训练水平和竞技能力都较高。根据国家体育总局篮球运动员技术等级标准的规定,此群体的运动水平相当于篮球三级运动员水平。
身体成分:身体成分简称体成分,它是人体脂肪组织和非脂肪组织的含量在体质量中所占的百分数。在通常状况下,人的身体主要由水、蛋白质、脂肪、无机物4种成分构成。在一定的时间内,这4种成分也是相对恒定的,并且不同人群有一定的正常比例。因此对身体成分的监测可以为人体健康状况评估提供参考。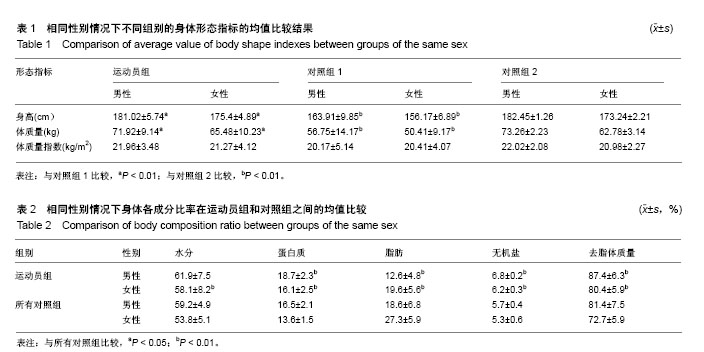
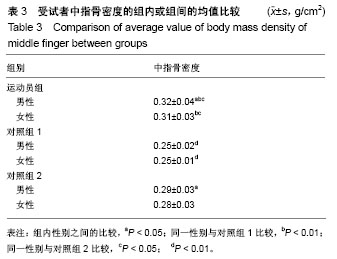
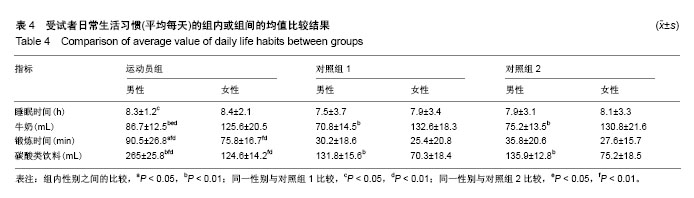
.jpg) 文题释义:
少年篮球运动员:此群体主要分布于有篮球传统的中学,也分散分布在一些中学的篮球队里面。由于经常需要代表学校参加省(市、区)级比赛,因此训练水平和竞技能力都较高。根据国家体育总局篮球运动员技术等级标准的规定,此群体的运动水平相当于篮球三级运动员水平。
身体成分:身体成分简称体成分,它是人体脂肪组织和非脂肪组织的含量在体质量中所占的百分数。在通常状况下,人的身体主要由水、蛋白质、脂肪、无机物4种成分构成。在一定的时间内,这4种成分也是相对恒定的,并且不同人群有一定的正常比例。因此对身体成分的监测可以为人体健康状况评估提供参考。
文题释义:
少年篮球运动员:此群体主要分布于有篮球传统的中学,也分散分布在一些中学的篮球队里面。由于经常需要代表学校参加省(市、区)级比赛,因此训练水平和竞技能力都较高。根据国家体育总局篮球运动员技术等级标准的规定,此群体的运动水平相当于篮球三级运动员水平。
身体成分:身体成分简称体成分,它是人体脂肪组织和非脂肪组织的含量在体质量中所占的百分数。在通常状况下,人的身体主要由水、蛋白质、脂肪、无机物4种成分构成。在一定的时间内,这4种成分也是相对恒定的,并且不同人群有一定的正常比例。因此对身体成分的监测可以为人体健康状况评估提供参考。