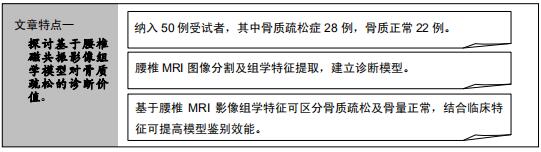
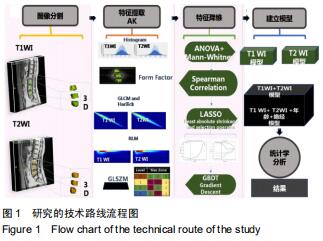
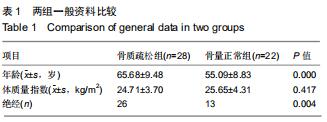
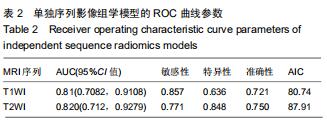
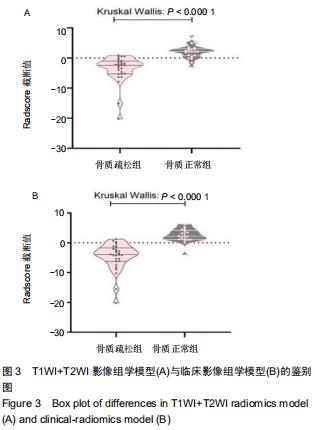
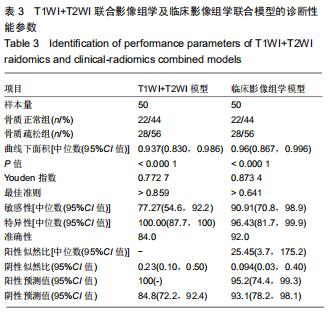
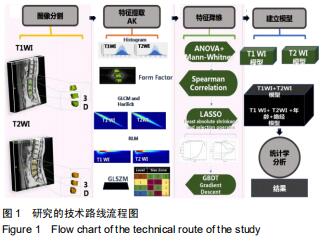
|
[1] 马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J].中华健康管理学杂志,2018,12(6):484-489.
[2] LINK TM. Osteoporosis imaging: state of the art and advanced imaging.Radiology. 2012;263(1):3-17.
[3] HOFBAUER LC, RACHNER TD. More DATA to guide sequential osteoporosis therapy.Lancet.2015;386:1116-1118.
[4] PISANI P, RENNA MD, CONVERSANO F, et al. Major osteoporotic fragility fractures: Risk factor updates and societal impact.World J Orthop.2016;7(3):171-181.
[5] 韩亚军,帖小佳,伊力哈木·托合提.中国中老年人骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(7): 1129-1134.
[6] MILLER PD. Underdiagnosis and Undertreatment of Osteoporosis: The Battle to Be Won. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(3):852-859.
[7] SAAD MM, AHMED TA, MOHAMED KE, et al. Role of lumbar spine signal intensity measurement by MRI in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women. Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2019;50(1):35-42.
[8] BANDIRALI M, DI LEO G, PAPINI GD, et al.A new diagnostic score to detect osteoporosis in patients undergoing lumbar spine MRI.Eur Radiol.2015;25(10):2951-2959.
[9] KUMAR V, GU Y, BASU S, et al. Radiomics: the process and the challenges.MagnReson Imaging.2012;30(9):1234-1248.
[10] E L, LU L, LI L, et al. Radiomics for Classification of Lung Cancer Histological Subtypes Based on Nonenhanced Computed Tomography.Acad Radiol.2019;26(9):1245-1252.
[11] HORVAT N, VEERARAGHAVAN H, KHAN M, et al. MR Imaging of Rectal Cancer: Radiomics Analysis to Assess Treatment Response after Neoadjuvant Therapy.Radiology. 2018;287(3):833-843.
[12] 吴亚平,刘博,顾建钦,等.基于影像组学的脑胶质瘤分级方法[J].中华放射学杂志,2017,51(12):902-905.
[13] 袁清玉,江玉明,吕闻冰,等.基于18F-FDG PET/CT图像的影像组学列线图对胃癌术后的预后评估[J].中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2019,39(1):2-5.
[14] 王超,刘侠,董迪,等.基于影像组学的非小细胞肺癌淋巴结转移预测[J].自动化学报,2019,45(6):1087-1093.
[15] MACKAY JW, MURRAY PJ, KASMAI B, et al. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: association between MRI texture analysis and histomorphometry.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(5):700-707.
[16] AREECKAL AS, JAYASHEELAN N, KAMATH J, et al. Early diagnosis of osteoporosis using radiogrammetry and texture analysis from hand and wrist radiographs in Indian population. Osteoporos Int.2018;29(3):665-673.
[17] TABARI A, TORRIANI M, MILLER KK, et al. Anorexia Nervosa: Analysis of Trabecular Texture with CT.Radiology. 2017;283(1):178-185.
[18] KANIS JA. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: synopsis of a WHO report. WHO Study Group.Osteoporos Int. 1994;4(6): 368-381.
[19] 王平,和建伟,黄刚,等.应用双能CT与定量CT对椎体骨密度测量的对照研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(2):159-162.
[20] DEYO RA, WEINSTEIN JN. Low back pain. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(5):363-370.
[21] MANENTI G, CAPUANI S, FUSCO A, et al.Osteoporosis detection by 3T diffusion tensor imaging and MRI spectroscopy in women older than 60 years.Aging Clin Exp Res.2013;25 Suppl 1:S31-S34.
[22] LI GW, XU Z, CHEN QW, et al. Quantitative evaluation of vertebral marrow adipose tissue in postmenopausal female using MRI chemical shift-based water-fat separation.Clin Radiol.2014;69(3):254-262.
[23] 何杰,方浩,李晓娜,等.腰椎MR扩散加权成像对骨质疏松的定量诊断价值[J].临床放射学杂志,2015(5):95-99.
[24] GRIFFITH JF, YEUNG DK, ANTONIO GE, et al. Vertebral bone mineral density, marrow perfusion, and fat content in healthy men and men with osteoporosis: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 2005;236(3):945-951.
[25] 常荣,张红,刘正华,等.MRI m-Dixon-Quant技术快速评估中老年骨质疏松症的可行性研究[J].实用放射学杂志,2018,34(12): 1908-1911.
[26] 郭志,许崇永.IDEAL-IQ技术在2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症诊断中的应用价值[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2019,17(5): 489-492.
[27] SCHWARTZ AV. Marrow fat and bone: review of clinical findings.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).2015;6:40.
[28] QIU X, FU Y, CHEN J, et al.The Correlation between Osteoporosis and Blood Circulation Function Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Med Syst.2019;43(4):91.
[29] BURIAN E, SUBBURAJ K, MOOKIAH MRK, et al.Texture analysis of vertebral bone marrow using chemical shift encoding-based water-fat MRI: a feasibility study. Osteoporos Int.2019;30(6):1265-1274.
[30] 翁子敬,黄学菁,俞健力,等.常规MRI信号评价腰椎骨质疏松的意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35):5667-5673.
[31] LECLER A, DURON L, BALVAY D, et al.Combining Multiple Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sequences Provides Independent Reproducible Radiomics Features.Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2068.
[32] 刘伯亮,潘万敏.骨质疏松发生与年龄、性别的关系:5200例分析[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(33):139-140.
[33] BLACK DM, ROSEN CJ. Clinical Practice. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis.N Engl J Med. 2016;374(3):254-262.
[34] FERIZI U, BESSER H, HYSI P, et al.Artificial Intelligence Applied to Osteoporosis: A Performance Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Fragility Fractures From MRI Data.J MagnReson Imaging. 2019;49(4): 1029-1038.
|