中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 348-353.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0601
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
低强度脉冲超声可缓解膝骨关节炎疼痛与修复关节软骨损伤
罗显文1,2, 李明星1
- (1西南医科大学附属医院超声科,四川省泸州市 646000;2自贡市第三人民医院超声科,四川省自贡市 643000)
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound can alleviate knee osteoarthritis pain and promote articular cartilage repair
Luo Xianwen1,2, Li Mingxing1
- (1Department of Ultrasound, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Ultrasound, Zigong Third People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
低强度脉冲超声波:是一种安全、无创的生物物理治疗,具有诱导成骨细胞分化、刺激细胞、细胞外基质增殖、加快钙盐沉积、促进细胞因子释放、改善局部微循环等多种生物学效应。
骨关节炎:往往由治疗不及时的关节软骨损伤发展而来,疼痛和运动障碍是主要临床表现。
超声波不良反应:皮肤毒性表现为照射区皮肤疼痛、红斑或灼伤;神经毒性表现为小腿内侧及足内侧缘皮肤的感觉障碍。
.jpg)
文题释义:
低强度脉冲超声波:是一种安全、无创的生物物理治疗,具有诱导成骨细胞分化、刺激细胞、细胞外基质增殖、加快钙盐沉积、促进细胞因子释放、改善局部微循环等多种生物学效应。
骨关节炎:往往由治疗不及时的关节软骨损伤发展而来,疼痛和运动障碍是主要临床表现。
超声波不良反应:皮肤毒性表现为照射区皮肤疼痛、红斑或灼伤;神经毒性表现为小腿内侧及足内侧缘皮肤的感觉障碍。
摘要
背景:大量研究证实低频脉冲超声治疗能有效缓解膝关节骨关节炎患者的关节肿胀与炎症。但同时探讨低强度脉冲超声波治疗对骨关节炎疼痛与关节软骨损伤修复作用的临床研究鲜有报道。
目的:探讨低强度脉冲超声波对膝骨关节炎疼痛与关节软骨损伤的治疗作用及疗效评价。
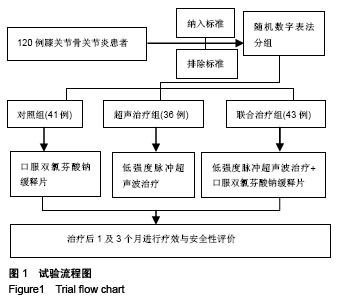
方法:将120例膝骨关节炎患者随机分为对照组、超声治疗组和联合治疗组,对照组患者接受双氯芬酸钠缓释片常规治疗,超声治疗组接受低强度脉冲超声波治疗,联合治疗组接受双氯芬酸钠缓释片联合低强度脉冲超声波治疗。治疗后1和3个月观察疼痛目测类比评分、Lequesne指数、Lysholm评分、Noyes关节软骨缺损评分、临床疗效和不良反应发生情况。
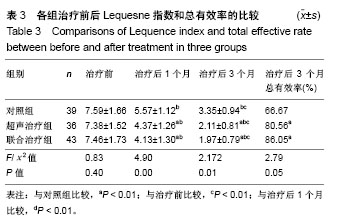
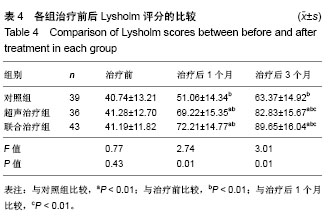
结果与结论:①治疗后1和3个月,超声治疗组和联合治疗组疼痛目测类比评分及Lequesne指数显著低于对照组,末次随访总有效率显著高于对照组(P < 0.01,P < 0.05);②治疗后1和3个月,超声治疗组和联合治疗组Lysholm评分显著高于对照组(P < 0.01);③治疗后1和3个月,超声治疗组和联合治疗组Noyes关节评分显著低于对照组(P < 0.01);④随访期间,仅对照组有2例发生药物相关性头痛和恶心,其他2组未发生超声波毒性反应和药物不良反应;⑤结果提示,低强度脉冲超声治疗膝关节骨关节炎疗效确切,能有效减轻疼痛并促进关节软骨损伤的修复,且低强度脉冲超声治疗并不影响药物的有效性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3047-4309(罗显文)
背景:大量研究证实低频脉冲超声治疗能有效缓解膝关节骨关节炎患者的关节肿胀与炎症。但同时探讨低强度脉冲超声波治疗对骨关节炎疼痛与关节软骨损伤修复作用的临床研究鲜有报道。
目的:探讨低强度脉冲超声波对膝骨关节炎疼痛与关节软骨损伤的治疗作用及疗效评价。
方法:将120例膝骨关节炎患者随机分为对照组、超声治疗组和联合治疗组,对照组患者接受双氯芬酸钠缓释片常规治疗,超声治疗组接受低强度脉冲超声波治疗,联合治疗组接受双氯芬酸钠缓释片联合低强度脉冲超声波治疗。治疗后1和3个月观察疼痛目测类比评分、Lequesne指数、Lysholm评分、Noyes关节软骨缺损评分、临床疗效和不良反应发生情况。
结果与结论:①治疗后1和3个月,超声治疗组和联合治疗组疼痛目测类比评分及Lequesne指数显著低于对照组,末次随访总有效率显著高于对照组(P < 0.01,P < 0.05);②治疗后1和3个月,超声治疗组和联合治疗组Lysholm评分显著高于对照组(P < 0.01);③治疗后1和3个月,超声治疗组和联合治疗组Noyes关节评分显著低于对照组(P < 0.01);④随访期间,仅对照组有2例发生药物相关性头痛和恶心,其他2组未发生超声波毒性反应和药物不良反应;⑤结果提示,低强度脉冲超声治疗膝关节骨关节炎疗效确切,能有效减轻疼痛并促进关节软骨损伤的修复,且低强度脉冲超声治疗并不影响药物的有效性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3047-4309(罗显文)
中图分类号:


.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
低强度脉冲超声波:是一种安全、无创的生物物理治疗,具有诱导成骨细胞分化、刺激细胞、细胞外基质增殖、加快钙盐沉积、促进细胞因子释放、改善局部微循环等多种生物学效应。#br#
骨关节炎:往往由治疗不及时的关节软骨损伤发展而来,疼痛和运动障碍是主要临床表现。#br#
超声波不良反应:皮肤毒性表现为照射区皮肤疼痛、红斑或灼伤;神经毒性表现为小腿内侧及足内侧缘皮肤的感觉障碍。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
低强度脉冲超声波:是一种安全、无创的生物物理治疗,具有诱导成骨细胞分化、刺激细胞、细胞外基质增殖、加快钙盐沉积、促进细胞因子释放、改善局部微循环等多种生物学效应。#br#
骨关节炎:往往由治疗不及时的关节软骨损伤发展而来,疼痛和运动障碍是主要临床表现。#br#
超声波不良反应:皮肤毒性表现为照射区皮肤疼痛、红斑或灼伤;神经毒性表现为小腿内侧及足内侧缘皮肤的感觉障碍。#br#
#br#