中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (32): 5197-5202.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0370
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
有氧运动与黑枸黄酮干预酒精性肝损伤模型小鼠炎性因子的变化
李 娣1,陈 锐1,陈嘉勤1,郑 核2,周柏存1,毛海峰1,3,陈伊琳1,屈红林1,3,陈 伟1,彭 琪1,罗赤苗2
- 1湖南师范大学体适能与运动康复湖南省重点实验室,湖南省长沙市 410012;2邵阳市中心医院,湖南省邵阳市 422000;3宜春学院,江西省宜春市 336000
Effect of the combination of aerobic exercise and flavonoids from Lycium ruthenicum Murr on the inflammatory cytokine levels in a mouse model of alcoholic liver injury
Li Di1, Chen Rui1, Chen Jia-qin1, Zheng He2, Zhou Bai-cun1, Mao Hai-feng1, 3, Chen Yi-lin1, Qu Hong-lin1, 3, Chen Wei1, Peng Qi1,Luo Chi-miao2
- 1Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness and Exercise Rehabilitation of Hunan Province, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410012, Hunan Province, China; 2Central Hospital of Shaoyang, Shaoyang 422000, Hunan Province, China; 3Yichun University, Yichun 336000, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
黑枸黄酮:是以黑果枸杞为原料制备的纯天然植物提取物,主要分布于中国青海、甘肃等地区的一种野生药用植物资源,安全可靠且无毒副作用。在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖等方面具有较广的应用价值。
酒精性肝损伤:是由长期大量饮酒造成的肝脏损伤,可诱发酒精性脂肪肝、酒精性肝纤维化及肝硬化等一系列损伤类疾病。在中国,酒精性肝病已经成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病类型。
文题释义:
黑枸黄酮:是以黑果枸杞为原料制备的纯天然植物提取物,主要分布于中国青海、甘肃等地区的一种野生药用植物资源,安全可靠且无毒副作用。在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖等方面具有较广的应用价值。
酒精性肝损伤:是由长期大量饮酒造成的肝脏损伤,可诱发酒精性脂肪肝、酒精性肝纤维化及肝硬化等一系列损伤类疾病。在中国,酒精性肝病已经成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病类型。
.jpg) 文题释义:
黑枸黄酮:是以黑果枸杞为原料制备的纯天然植物提取物,主要分布于中国青海、甘肃等地区的一种野生药用植物资源,安全可靠且无毒副作用。在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖等方面具有较广的应用价值。
酒精性肝损伤:是由长期大量饮酒造成的肝脏损伤,可诱发酒精性脂肪肝、酒精性肝纤维化及肝硬化等一系列损伤类疾病。在中国,酒精性肝病已经成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病类型。
文题释义:
黑枸黄酮:是以黑果枸杞为原料制备的纯天然植物提取物,主要分布于中国青海、甘肃等地区的一种野生药用植物资源,安全可靠且无毒副作用。在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖等方面具有较广的应用价值。
酒精性肝损伤:是由长期大量饮酒造成的肝脏损伤,可诱发酒精性脂肪肝、酒精性肝纤维化及肝硬化等一系列损伤类疾病。在中国,酒精性肝病已经成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病类型。摘要
背景:目前,针对酒精性肝损伤的治疗仍未得以较好的解决,研究发现黑果枸杞提取物在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖,抗氧化,心血管疾病的预防及治疗,肿瘤治疗等方面具有较广的应用价值。
目的:验证有氧运动联合黑果枸杞黄酮对酒精性肝损伤的干预效果并分享抗炎性的损伤机制。
方法:40只健康雄性昆明(KM)小鼠构建酒精性肝损伤模型,随机分为模型组、黑枸黄酮组、有氧运动组和有氧运动联合黑枸黄酮组。各干预组于建模成功后第1天开始进行有氧运动和黑枸黄酮灌胃干预。6周干预后,小鼠禁食过夜,随后分离出肝组织。苏木精-伊红染色、组织病理评分;生物化学分析法检测血清谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶和总胆红素含量;实时荧光定量(Realtime-PCR)技术检测肝组织和血液中肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子κB、白细胞介素6及白细胞介素10 mRNA表达水平。
结果与结论:①苏木精-伊红染色和组织病理变化:模型小鼠肝索结构排列紊乱、小叶结构损坏严重、胞质疏松内充满大小不一的脂肪空泡并伴有炎性细胞浸润;有氧运动组、黑枸黄酮组的小鼠肝组织破坏有不同程度的改善(P < 0.05);有氧运动联合黑枸黄酮组小鼠肝细胞坏死和脂肪蓄积得以改善,炎细胞浸润明显减少 (P < 0.01);②血液生化:有氧运动联合黑枸黄酮组谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶、总胆红素水平较模型组显著降低(P < 0.01),有氧运动组谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶、总胆红素水平也有所下降(P < 0.05);③Real-time PCR 检测结果:3个干预组炎性细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子κB及白细胞介素6在肝组织和血液中表达均明显低于模型组(P < 0.05),其中有氧运动联合黑枸黄酮组各炎性细胞因子的表达水平最低(P < 0.01);干预组白细胞介素10表达显著高于模型组;并且肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子κB、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素10 在肝组织和血液中的表达呈正相关;④结果说明,有氧运动、黑枸黄酮能有效降低炎性细胞因子的表达。作为一种微创性早期检测手段,推测以血浆中炎性因子的循环RNA检测可以作为酒精性肝损伤筛查诊断、观察及预后监测中一个重要标志物。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-0461-3862(李娣)
中图分类号:
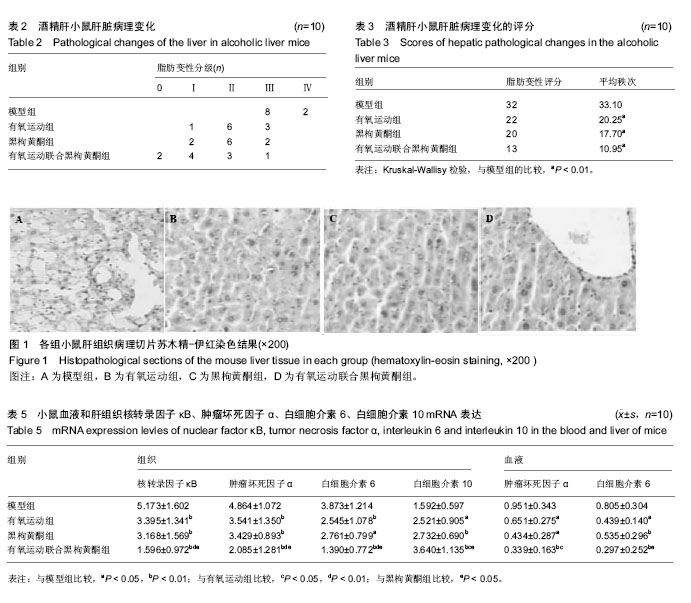
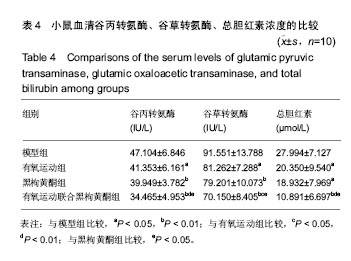
.jpg) 文题释义:
黑枸黄酮:是以黑果枸杞为原料制备的纯天然植物提取物,主要分布于中国青海、甘肃等地区的一种野生药用植物资源,安全可靠且无毒副作用。在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖等方面具有较广的应用价值。
酒精性肝损伤:是由长期大量饮酒造成的肝脏损伤,可诱发酒精性脂肪肝、酒精性肝纤维化及肝硬化等一系列损伤类疾病。在中国,酒精性肝病已经成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病类型。
文题释义:
黑枸黄酮:是以黑果枸杞为原料制备的纯天然植物提取物,主要分布于中国青海、甘肃等地区的一种野生药用植物资源,安全可靠且无毒副作用。在免疫调节,降血脂、血糖等方面具有较广的应用价值。
酒精性肝损伤:是由长期大量饮酒造成的肝脏损伤,可诱发酒精性脂肪肝、酒精性肝纤维化及肝硬化等一系列损伤类疾病。在中国,酒精性肝病已经成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病类型。